Boric Acid Ear Drops Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide in 2025
Boric acid ear drops are commonly used pharmaceutical products as anti-infective otic solutions. It’s used as a remedy for ear otitis and superficial infections of the external auditory canal. Boric acid ear drop manufacturing involves sourcing high-quality boric acid, to ensure a high standard of sterilization and maintain strict regulatory standards.
If you are a manufacturer you should have comprehensive knowledge about the process, challenges, and innovations. This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to the topic of boric acid ear drops manufacturing. Let’s explore it in detail.
1.What is boric acid ear drops manufacturing?

Boric Acid Ear Drops- Picture Courtesy: Schwitz Biotech
Boric acid ear drops manufacturing is the process of using boric acid as the active ingredient for the preparation of an otic solution. It primarily involves the dissolving of boric acid along with other excipients into solvents such as alcohol or distilled water to achieve a desired concentration.
The obtained otic solution is then further sterilized and packaged into dropper bottles for otic administration. These ear drops are effective against a wide range of pathogens that can cause itching or inflammation, owing to their antimicrobial and antifungal properties.
These solutions are often used with other medicines to enhance their effectiveness for more severe infections.
2.What is the mechanism of action of boric acid?

Boric Acid Role in Otic Formulation
Boric acid provides etiotropic treatment that targets and destroys pathogenic microbes. It creates an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi. It eliminates the bacteria through multiple processes of coagulation and denaturation.
Coagulation refers to the clumping of proteins while denaturation is the disruption of the protein’s tertiary structure.
The formulation mainly contains alcohol, which is a drying ingredient. The drying of the ear aids in the healing of infection. Since it removes the moisture that causes microbial growth.
3.What are boric acid's different strengths and formulations used in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?
Boric Acid Formulation
The concentration of boric acid used during the boric acid ear drops manufacturing depends on the specific formulation and its intended use. These are available in the market in different types of formulation, often in ranges of 1.5 % to 4 % in concentration.
2.75% Boric Acid with Isopropyl Alcohol Otic Solution

Otic Ear Drop Solution for Swimmer’s ear
This strength is available in the market in combination with isopropyl alcohol. These types of formulations are used for the prevention and cure of swimmer’s ear (for otitis externa).
As expected, boric acid is used as a mild antiseptic. While isopropyl alcohol aids in drying excess moisture in the ear canal, making an unfavorable environment for microbial growth.
2.75% Boric Acid with Xylitol 5%Otic Solution
This combination is used in otitis externa as well as other ear infections, and inflammation. Boric acid acts as an antiseptic. Xylitol acts as a moisturizer and anti-inflammatory, which provides a soothing effect and reduces irritation in the ear canal.

Medicated Ear Drops- Picture Courtesy: Marie Originals
3% Boric Acid with 96% Alcohol Solution

Ear Drops
This highest concentration is intended for the cure of acute and chronic otitis media. This combination is also used for the treatment of skin conditions such as eczema. It provides anti-septic effects against numerous pathogens.
4% boric acid Otic Solution
4% Boric acid Strength
These are used against a broad spectrum of pathogens. Since they have a high concentration of boric acid, provide enhanced anti-septic and anti-fungal effects. Higher concentrations are needed for severe conditions.
4.What are the key raw materials used in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?
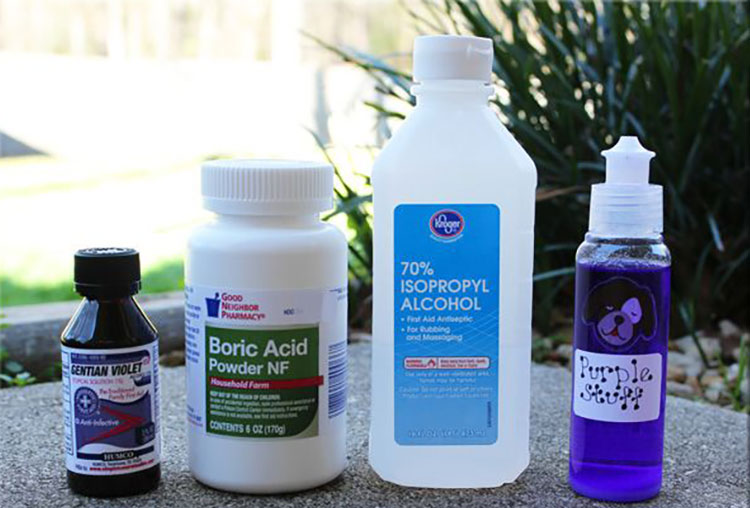

Boric Acid Ear Drops Ingredients
You need some key raw ingredients for boric acid ear drops manufacturing. Since each has its purpose for the product efficacy and safety. Let’s discuss the primary ingredients of formulation:
Active Ingredient
Boric acid acts as an active ingredient for its anti-microbial effects by creating a hostile environment for microbial growth in the ear canal.
Solvent
Isopropyl alcohol is commonly used to dissolve boric acid due to its favorable drying effects. Glycerin can also be added as humectants (for soothing effects and to prevent dryness).
Sterile Water
It is used as a medium to dissolve other components and to ensure that the solution is diluted appropriately.
Other Ingredients
Some additional agents can be used to enhance anti-bacterial and anti-fungal effects as well as anti-inflammatory properties. Such as acetic acid, hydrocortisone, etc.
5.What are the key stages in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?
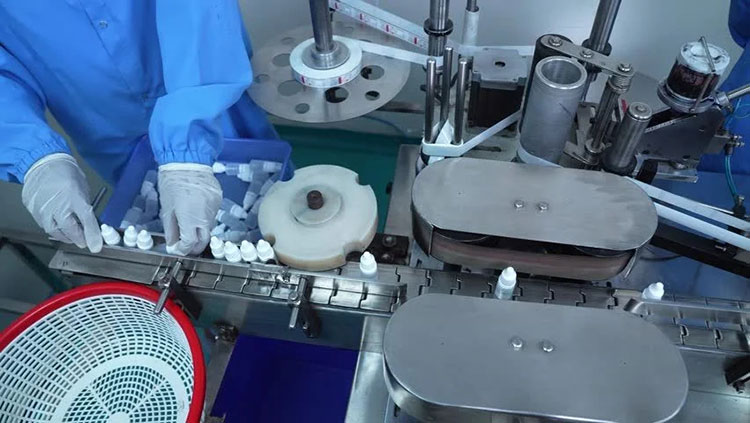

Manufacturing Process
The process contains several steps to make sure that the final product is safe, effective, and sterile. Let’s have an overview of these steps:
Step # 1- Weighing and Measuring

Measuring the Volume of Solvent
All the ingredients are sourced of pharmaceutical grade quality including boric acid. Precisely weigh and measured each ingredient following the formulation specifications. This will ensure that the formulation contains the correct concentration and volume.
Step # 2- Treatment of Water for Purification
Water is passed through purification treatment to meet the standards of sterile water and water for injection. It includes:
Pre-treatment: First you must filter the water to remove any sediments, impurities, and chlorine (by activated carbon filtration),
Purification: Purification can be achieved by utilizing advanced purification methods. You can choose any of them:
Reverse Osmosis (RO):A membrane filtration technique that utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to allow water to pass through while removing salts, ions, and impurities.
Deionization (DI):This technique uses ion exchange resins to remove impurities like calcium, magnesium, and sulfates resulting in deionized water.
Ultra-violet Sterilization:Water is exposed to UV light to kill microorganisms.
Ozonation:Ozone gas is an effective disinfectant used for water sterilization and the removal of biological contaminants.
Storage: The treated water is stored in sterile stainless steel tanks.with recirculation maintains its purity.
Step # 3- Liquid Processing
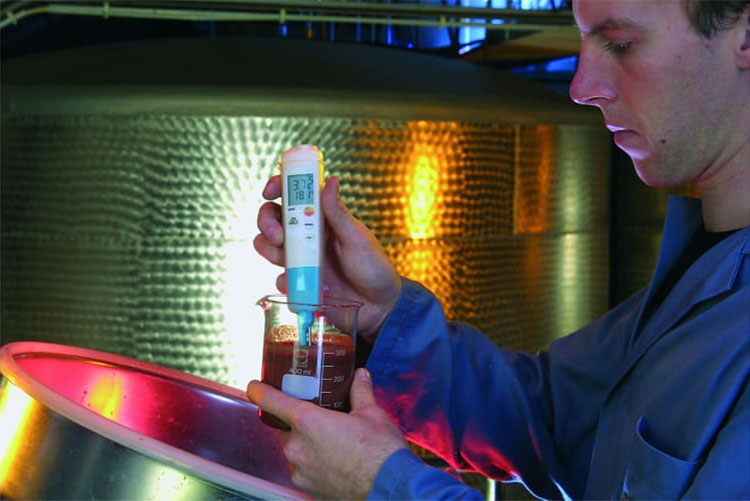

Monitors pH Level- Picture Courtesy: Testo
Dissolution:For formulation development, you must first dissolve boric acid in a sterile aqueous base under a controlled environment. You may have to heat it if it’s required for complete dissolution.
Mixing: After that, add other necessary ingredients such as preservatives, stabilizers, etc. These additional ingredients are added in an aseptic condition in a jacketed mixing tank.
Stir the solution for a complete dissolution. Agitation provides homogeneity
pH Adjustment: ThepH of the obtained solution is tested and then adjusted according to physiological pH conditions.
Step # 4- Filtration

The prepared solution is then passed through the filters. This is necessary to make sure that the product is pure and clean from any foreign material.
Step # 5- Sterilization

Sterilization in Pharma
Sterilization can be achieved through:
Autoclave system
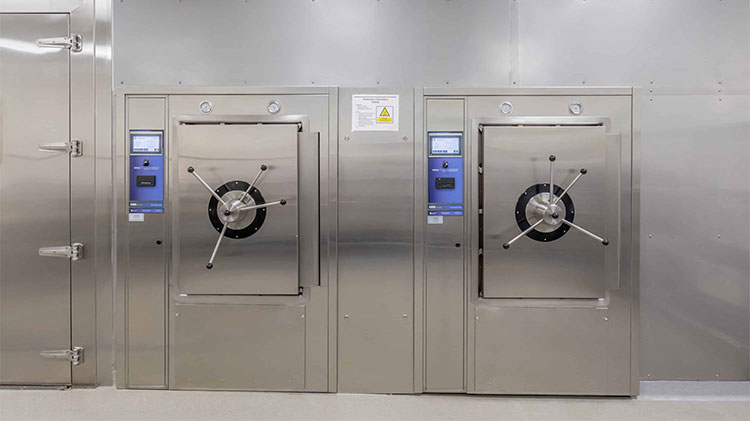

Autoclave System in Pharma- Picture Courtesy: CSS
The solution is heated under pressure to kill microorganisms in the autoclaving method.
Antiseptic processing

Clean Rooms in Pharma- Picture Courtesy: CLIN
In this process, clean rooms are required for preparation, and filtration of the formulation, ensuring sterility throughout the process.
Step # 6- Filling and Sealing
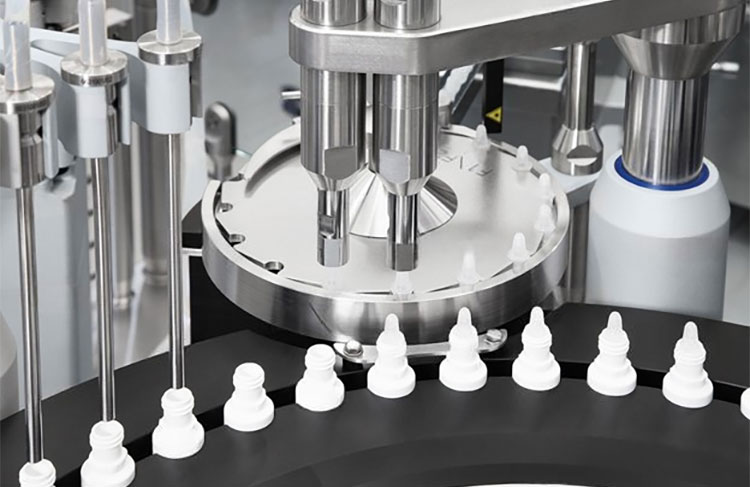

Filling and Sealing Simultaneously- Picture Courtesy: Dara Pharma
Preparation before Filling:‘Make sure that the filling area is maintained under a controlled environment, such as a Grade A or B cleanroom. It’s essential to avoid contamination throughout the entire filling process.
Containers, such as dropper bottles and caps, are sterilized by autoclaving or a dry heat method.
Filling Process: The sterilized solution is then transferred to dropper bottles (pre-sterilized) by automated filling machines. Nitrogen purging may be required to minimize oxidation.
Capping and Sealing: Then immediately seal the bottles preventing contamination. temper-evident caps or seals may be used.
Inspection: The filled bottles are inspected for leaks to ensure proper sealing, as well as for volume accuracy.
Step # 7- Labelling and Packaging

Labeling of Boric Acid Ear Drops- Picture Courtesy: Dailymed
The filled bottles are then passed through the labeling and packaging stage. The bottles are labeled with all the necessary details including strength, expiry date, dose, and direction of use. Ensuring the packaging material provides safe storage and transportation.
6.Why is sterility important in boric acid ear drops manufacturing and how is it maintained?
Otic Ear Drops administration- Picture Courtesy: Hearing Partners.
Maintaining sterility during boric acid ear drops manufacturing is mandatory for multiple reasons.:
If the product is contaminated, the ear canal becomes prone to infections as ear drops are directly applied to this sensitive area.
Contaminated ear drops can expose the ear canal to harmful; microorganisms. It will potentially worsen the existing infections and cause further inflammation.
Regulatory authorities such as the FDA or WHO require sterility of the otic ear drops to comply with GMP and to ensure public health.
Microorganisms can also affect the product efficacy by degrading the active ingredients.
If the product fails to meet sterility standards, the manufacturer may face a product recall, held legal liabilities, and damage to their reputation.
7.What are the packaging methods used in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?

Bottle Dropper for Otic Solution
The packaging methods adapted during boric acid ear drops manufacturing must be adhered to official pharmaceutical manufacturing guidelines. It’s the process that places the pharmaceutical products in such a way that they retain their therapeutic effectiveness after packaging till they are consumed. There are some key points to be considered for packaging:
The FDA emphasizes the use of inert materials that don’t interact with the product.
Boric acid ear drops are packaged with the temper-evident ring, sealing inset made of aluminum (preventing unauthorized access)., and child-resistant dropper bottles
During the packaging of ear drops, accurate dosing should be ensured.
Proper labeling including mentioning the expiry date should be ensured.
Now come to the types of materials used in packaging and how they are packaged. They commonly come in multi-dose containers.
The most commonly used packaged form is dropper bottles. It involves two types of containers, suitable plastic or glass materials. These containers have an integrated dropper or a screw cap with a dropper and plastic teat.
Plastic Dropper Bottles
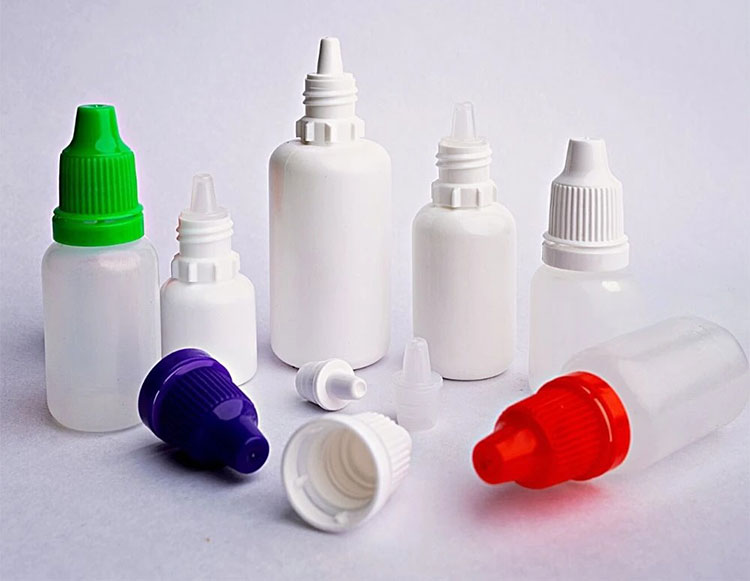

Plastic Bottle with Integrated Dropper- Picture Courtesy: Bharat Rubber Works
The plastic used in these types of bottles is made of HDPE (high-density polyethylene) or LDPE (Low-density polyethylene). These materials help maintain the stability and effectiveness of the boric acid. These materials have the following benefits that make them ideal for common use:
- Lightweight.
- Durable.
- Resistant to breakage.
- Prevent contamination from the external environment,
- Providing longer stability over a shelf life
Glass Dropper Bottles

Glass Bottle with Dropper and Plastic Teat
This type of container is used when there is a risk of degradation in the chemical composition of the otic solution. However, these are not resistant to breakage and are heavier than plastic ones. These materials are chosen for the following reasons:
- Higher chemical stability (preventing interaction between the product and the container).
- Impermeable to oxygen and other external factors.
- Prolong the shelf life of the product.
8.What are the basic types of equipment needed in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?
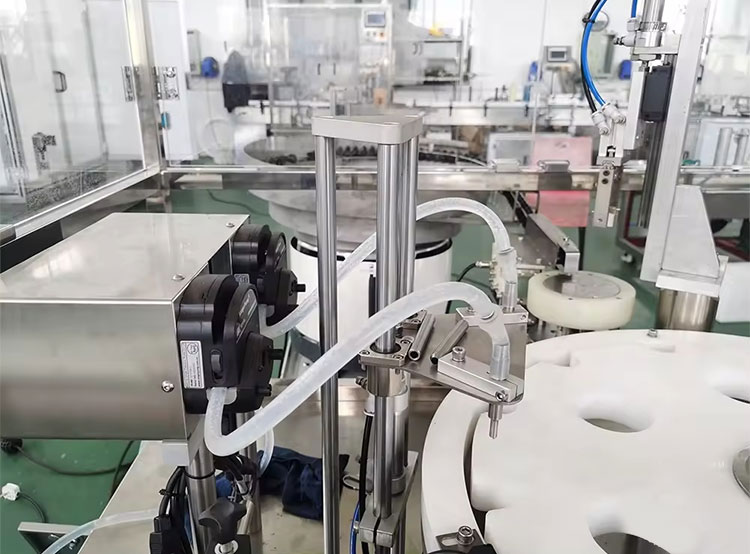

Ear Drops Manufacturing Equipment
When you are setting up a production line for boric ear drops manufacturing, you need some of the key equipment to ensure seamless production on a large scale. Let’s discuss them:
Mixer Equipment
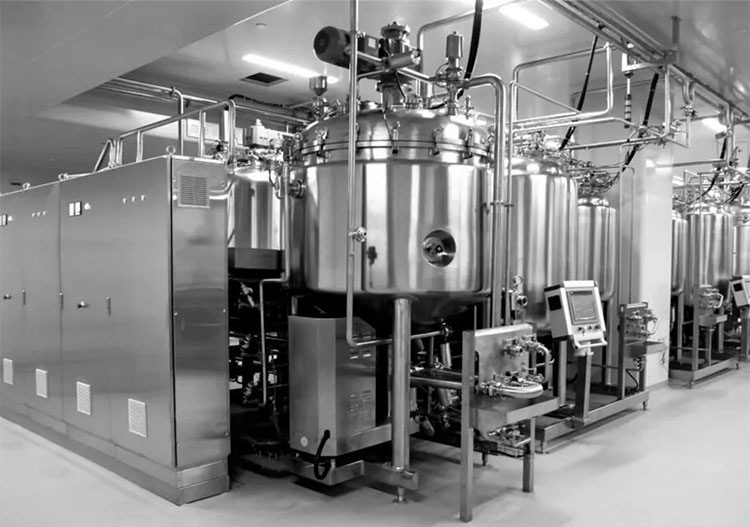

High-shear Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Cedarstone Industry
You should have a high-shear mixer for attaining a uniform mixture of boric acid and the solvent. You may need magnetic stirrers or agitators if the batches require continuous agitation during formulation.
Filtration System
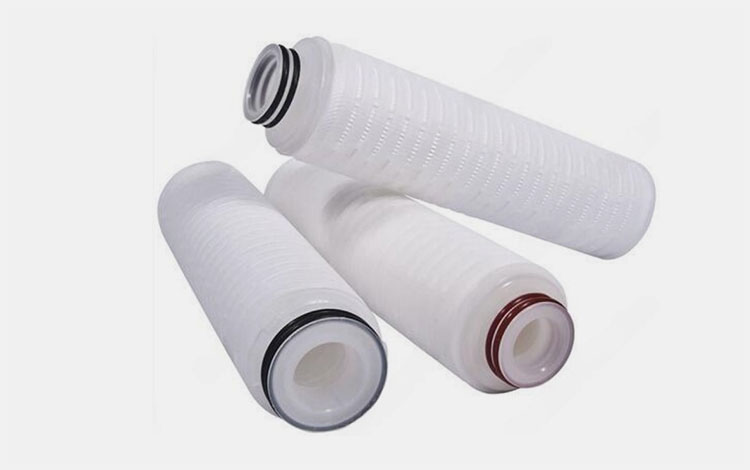

Pleated Filter Cartridge- Picture Courtesy: Bolefil
You need a filtration system for the removal of any foreign particles to ensure the final product should be free from any impurities. It requires the following filtration unit:
Pre-Filtration
It includes depth filters or cartridge filters (pore size 1–5 µm). Removes large particulate.
Final Sterilization
It includes membrane filters (pore size 0.2 µm). It ensures the solution is sterile as it removes microorganisms. It is done before filling the solution in an ear drops container.
Filtration Between Transfer
Inline filtration units are used as continuous filtration. It is installed in transfer pipelines. It prevents contamination during the transfer of the solution between mixing tanks and filling machines.
pH meter and adjustments system
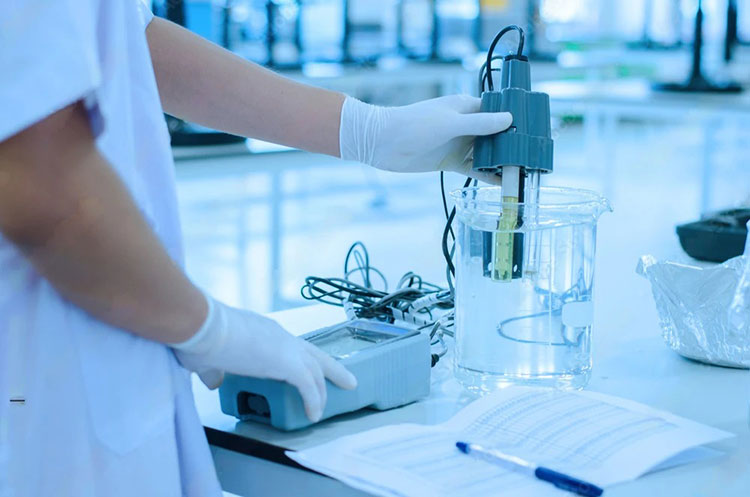

pH Adjustment
Digital pH meters are there to monitor and adjust the pH of the otic solution. An automated dosing system adds the neutralizing agent for pH adjustment during the mixing process.
Filling Machines
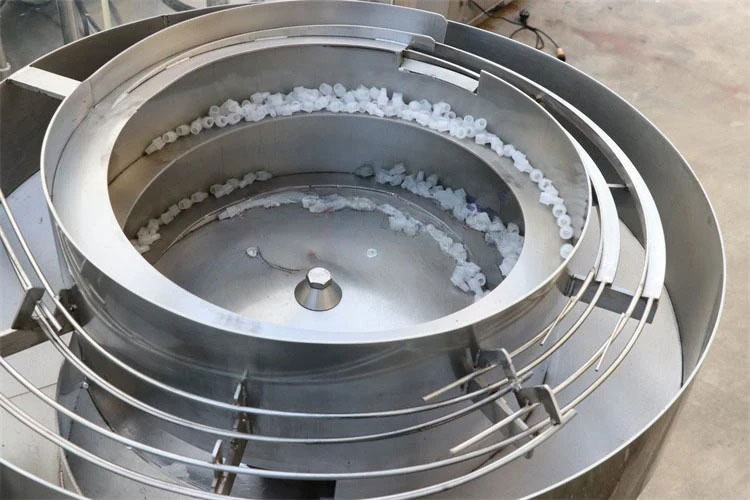

Filling Machine
The following equipment is utilized for the filling of boric acid ear drop solution. Let’s explore them:
Aseptic Filling Machine

Aseptic Filling Machine- Picture Courtesy: Adragos Pharma
The equipment fills the liquid into containers in an aseptic environment. It ensures that the product remains contaminant-free during the process. It operates in clean rooms or under a laminar airflow system with HEPA filters.
Automated Liquid-Filling Machines
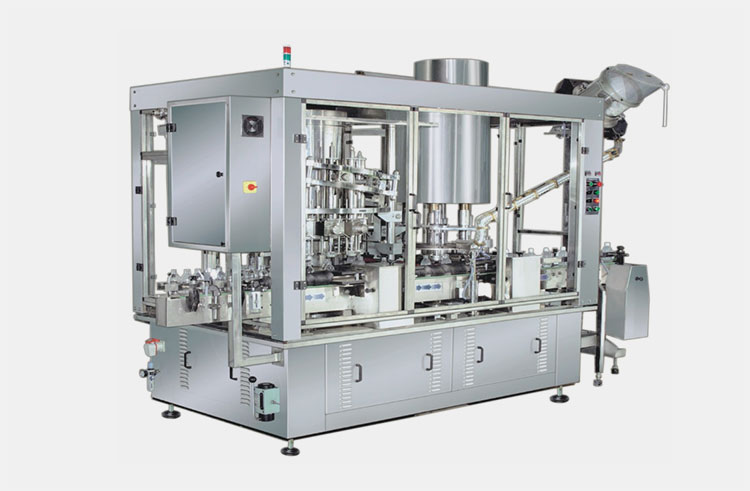

Monoblock Automatic Filling Machine
It smooths the production process by combining filling, capping, and sealing into a single operation. The induction sealers provide additional protection with foil seals. The equipment maintains the sterility of the product by reducing the contact of the product with machine parts.
It may use a flexible tubing system of pistons to pump the solution of boric acid ear drops, providing accurate volume dispensing. Such as monoblock and rotary filling equipment.
Sterilization Equipment
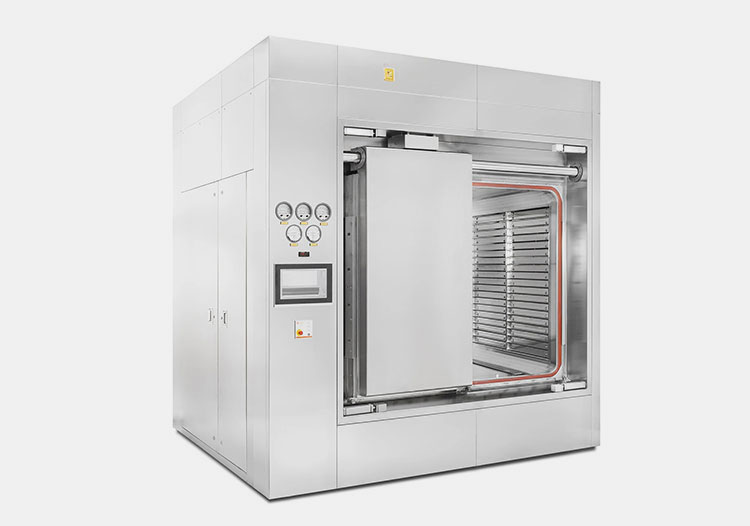

Dry Heat Sterilizer- Picture Courtesy: De Lama
Autoclave
It uses steam under pressure for the sterilization of the containers and the finished product.
Sterilizer using Dry Heat
It is used for heat-resistant components such as glass containers or metal tools used in production.
Quality Control Equipment
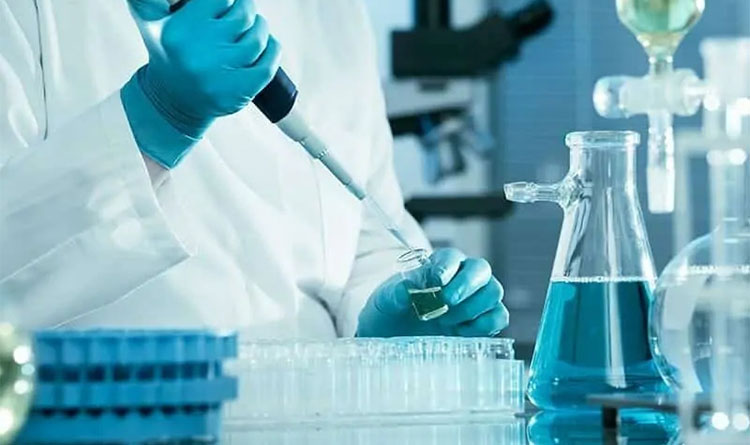

Quality Control Testing- Picture Courtesy: Pharma Specialists
Viscometer
Since the solution is for dropper dispensing, the monitoring of its viscosity is necessary for the solution.
Microbial Testing Equipment
Microbial testing equipment is used to ensure that the product is free from microbes. Such as an incubator.
Packaging Equipment

Carton Machine- Picture Courtesy: Universal Pack
Labelling Machine
These machines automatically apply the labels with product information such as expiry date, batch numbers, storage, and direction of use.
Carton Machine
The labeled bottles are then packed into cartons for distribution and sale.
9.What is the role of pH adjustment in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?

Ear Canal Swelling- Picture Courtesy: Houston ENT
The pH adjustment during manufacturing has logical reasons. These are:
Enhanced Anti-Microbial Effects
As we discussed boric acid works as an antibacterial and antifungal, so it should have an acidic pH. Because the neutral to alkaline environment is favorable for microbial growth. The acid pH of boric acid inhibits their growth.
Mimicking The Physiological pH
The physiological pH of the ear canal is 6.0 to 6.5. you have to adjust the pH of boric acid ear drops to mimic the physiological pH of the ear canal.
10.What is the shelf life of boric acid ear drops and how it’s determined in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?

Stability Chamber- Picture Courtesy: DJA Pharma
The shelf life of boric acid ear drops is determined through stability testing over a certain period. This testing ensures that the product is stable and safe for use until the designated expiry date. These studies include:
Physical Stability: Determine the changes in the appearance and consistency of the product.
Chemical Stability:Determine the changes in potency of active ingredients.
Microbial Stability:ensuring, the product is free from microorganisms over a certain period.
Shelf-Life Duration
The general shelf life of boric acid ear drops is several months to years. Once the container is opened, these antibacterial drops are stable and effective for up to 4 months, provided they are stored according to instructions.
Factors Affecting the Shelf Life
There are certain factors that influence the shelf life of boric acid ear drops:
- Shelf life vary formulation to formulation, i.e. ingredients and preservatives used in the product.
- Airtight and sterile packaging helps prolong the shelf life of the product.
- If stored according to instruction i.e. store in a cool, dry place, and away from sunlight.
11.How is quality control implemented in boric acid ear drops manufacturing?

Quality Control Implementation- Picture Courtesy: Compliance Quest
Some quality testing is essential to conducted to ensure efficacy, stability, and compliance with regulatory requirements. The quality control has several steps as follows:
Purity Testing
Ensures that boric acid and other ingredients have pharmaceutical-grade purity standards.
pH Testing
Adjusting and maintaining the pH of the solution within optimal range for effective anti-microbial activity.
Dose Accuracy
Ensuring the correct measurements and mixing of the ingredients to achieve the desired concentration of the product.
Sterility Assurance
Employing methods as discussed above, like autoclaving and filtration systems, to achieve a final product free from contamination.
Container Choice
Selecting a container that protects the product from light, air, and moisture (preserving stability).
Seal Testing
To protect the product from contamination during storage and use, verify that containers are sealed properly.
Stability Testing
Studies are conducted under various environmental conditions over time. These studies establish the expiration date and recommend optimal storage conditions.
Finished Product Testing
Assays are performed to verify the concentration of boric acid or other active ingredients, pH level, and sterility testing.
After all the tests are performed throughout the process, only those batches are released that meet all the predetermined quality specifications.
12.How to use boric acid ear drops?

Administration of Ear Drops- Picture Courtesy: VSM Pharmacy
By following these steps, you can use these drops without any discomfort:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before handling to avoid contamination.
- Make sure that the solution must be body temperature. If the solution is too cool, it will cause dizziness.
- Lie down or till your head, and place the towel around your ear to protect the eyes.
- Pull up and out to straighten the ear canal.
- Bring the dropper close to the ear. Avoid touching to prevent contamination
- Squeeze three drops of boric acid otic solution into the ear canal.
- Stay in the same position for a few minutes so that ear drops reach the affected area.
13.What are the potential side effects of boric acid ear drops?
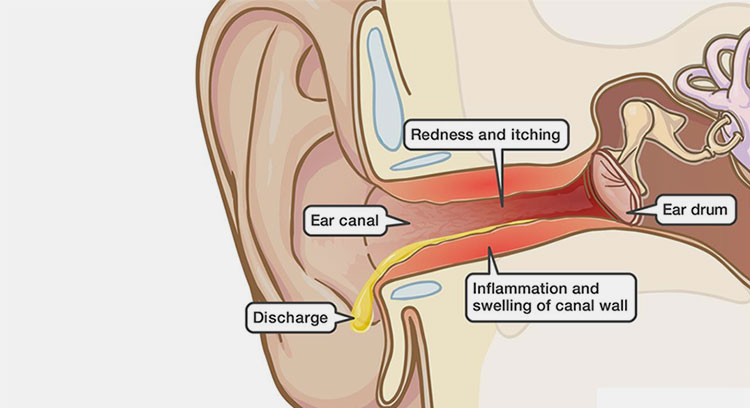
Ear Canal Infection
While these drops are effective for treating certain ear infections, they may cause some side effects in some individuals:
Common Side Effects
Pain or Burning
some patients may feel a temporary stinging or burning sensation in the ear canal upon administration. Some may also experience redness of the ear.
Rare Serious Side Effects
Allergic Reaction
Although rare, allergic reactions may occur in some individuals, who experience symptoms like itching, swelling, or rash. In that case, stop using it and consult your health care provider.
14.What are the precautions and recommendations while using the boric acid ear drops?
Perforated Eardrum- Picture Courtesy: Pacific Cross Vietnam
If you are a health care provider or if you are using boric acid ear drops, keep in consideration the following precautions and recommendations:
Precautions
Perforated Eardrum
Don’t use boric acid eardrops if you have a perforated eardrum. This may lead to further complications.
Prolonged Use
Don’t use boric acid eardrops for more than 7 days without medical supervision. Extended use may lead to skin sensitization or the emergence of resistant microbes.
Recommendations
Consultation of Health Care Provider
Always consult a physician or other health care professionals, before using these drops. Especially in children or if you have any underlying health concerns, ensure that they are appropriate for your condition.
Conclusion
Boric acid ear drops manufacturing relies on advanced equipment for its production process. AIPAK ENGINEERING offers highly advanced machinery for this process including high-shear mixers, filling machines, and labeling machines. By utilizing AIPAK ENGINEERING’s cutting-edge technology, you can streamline the production of boric acid ear drops while meeting global healthcare standards.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours