Vial Production Line: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Vials made of glass or plastic are routinely employed in the pharmaceutical industry to store parenteral formulations. Are you curious about how vials are filled? Well, the short answer is that these containers are gently handled and filled by an up-to-date system called a vial production line.
This production line is a well-accepted solution in pharmaceutical units due to its sterilizing processing of medical vials. The vial production line is committed to delivering top-notch quality vials to patients and health givers.
Are you pondering about the benefits, working, sterility aspects, and quality control processes of a vial production line? Then we recommend start reading this FAQ guide. It is written for the sole purpose of providing information about the vial production line to business owners, operators, and researchers. Here is a list of questions answered in this guide.
1.What is a vial production line?

AIPAK Engineering Vial Production Line
The vial production line is highly preferred in the pharmaceutical and medical care industries for dosing different vials with pharmaceutical compounds. It involves a set of sequential operations, such as ultrasonic washing, high-temperature drying, filling and stoppering, cap rolling, and labeling to pack the medical vials. The machines present in the vial production line operate together and also independently. They are fitted one after the other to precisely fill, stopper, and cap vials.
A vial production is pivotal in the medical sector to carry out vial packaging under strict sterile conditions to ensure patients' health and provide them with safe liquid and powder dosages.
2.What are the key purposes of a vial production line?
The vial production line is assembled with high-tech and sophisticated machines to safely, speedily, accurately, and hygienically process and fill refined end-products into sterile vials to ensure medications are suitable for administration. The vial production line is known for its stringent compliance with drug regulatory bodies.
Let’s delve into a few of the many key purposes of the vial production line:
Sterile Packaging
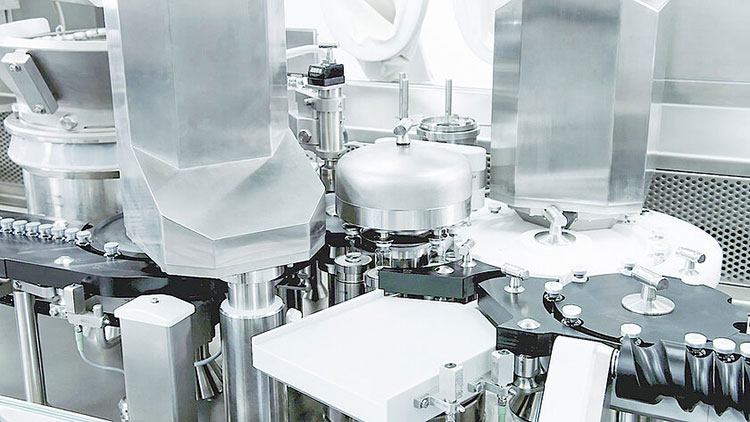

Sterile Packaging- Picture Courtesy: Groninger
One of the basic objectives for integrating a vial production line in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries is sterile filling and sealing of injectable medications, parenteral products, vaccines, antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and other biologicals under an aseptic environment. This is a key aspect in protecting the health of patients, as otherwise, it would result in product recall and fatal consequences for patients.
No Compromise on Product Integrity

No Compromise on Product Integrity- Picture Courtesy: Packaging Strategies
The vial production line is engineered for the specific purpose of maintaining product integrity during packaging stages, such as filling, stoppering, and labeling. It is integral because manual filling usually comprises the product composition by contamination from human errors or the environment. Moreover, proper sealing closures (stoppers and aluminum crimps) in the vial production line protect the therapeutic liquids and powders from oxidation and other chemical reactions.
Accelerated Vial Production

Accelerated Vial Production- Picture Courtesy: Sugar Medical
One of the lucrative advantages of the vial production line for businesses is its ability to process and pack bulk batches for vials. This leads to mass manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, biologics, and other medicinal component with increased efficiency. This benefit is especially important in case of disease outbreaks when a continuous supply of vaccines and other drugs is needed.
Regulatory Guidelines Compliance

Regulatory Guidelines Compliance
The vial production line is well-accepted in different healthcare sectors, as it meets the global regulatory requirements, for instance, GMP, FDA, EMA, and ISO. The regulatory agencies specify strict standards for sanitation, sterilization, accuracy, and traceability and this line undeniably fulfills these guidelines.
Cost-Efficiency

Cost-Efficiency- Picture Courtesy: Sigma-Aldrich
There is no need for manual labor with the vial production line because it completely automates every single step of production, leading to decreased error rate and high throughput. This in turn translates into minimized operation expense per unit, especially for industrial-scale manufacturing of products.
3.What are the steps involved in the operation of the vial production line?
A vial production line is a large arrangement with various automated and semi-automated machines that efficiently carry out jobs- assigned to them. The working steps involved in the operation of the vial production line are precisely consistent and coordinated. A detailed account of every operational step is written below for your information:
Vial Unscrambling
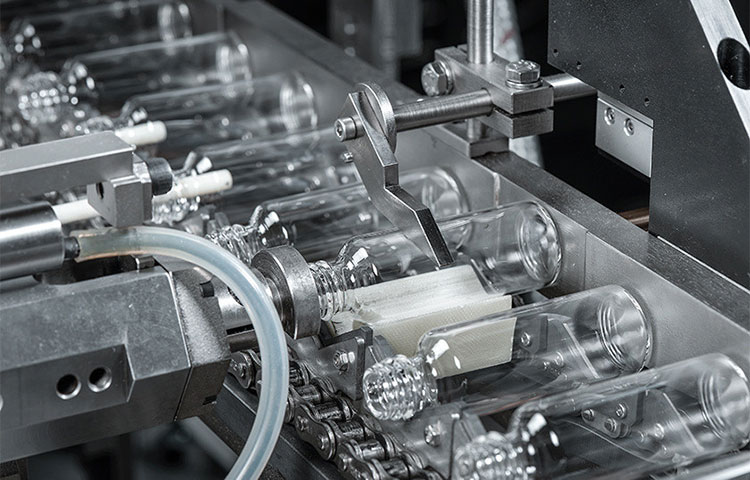
Vial Unscrambling- Picture Courtesy: Stevanato Group
The operation of the vial production line starts with the vial feeding by the vial unscrambling machine. Empty vials (deposited in hopper or feeding systems) are oriented in an upright position on the conveyor or rotatory turn wheel. The objective of this step is to ensure consistent vial supply for an undisrupted and seamless working.
Vial Washing
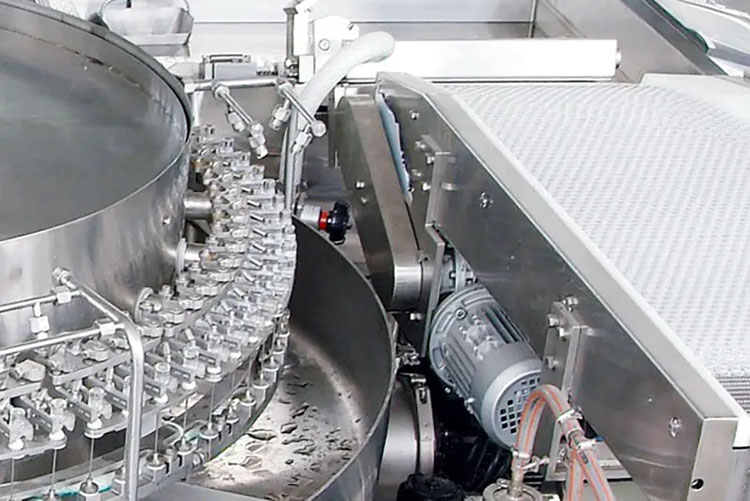

Vial Washing- Picture Courtesy: IVEN-Pharma
In the next step, the vial ultrasonic washing machine conducts thorough and meticulous washing of vials- both internally and externally- to dislodge and wash out sticky residues, dust particulates, microbial spores, or other contaminating agents using deionized water and ultrasonic waves. Injection needles are integral in introducing water and compressed air into vials to completely clean them. After washing, compressed air is loaded into vials for drying them.
Vial Sterilization
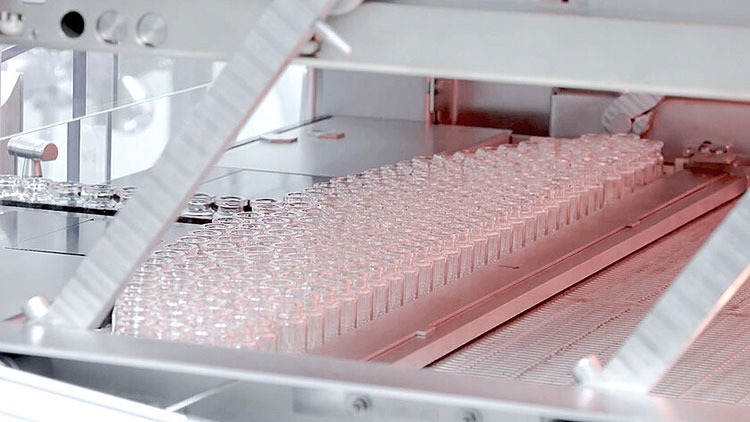

Vial Sterilization- Picture Courtesy: Groninger
The vials go through a depyrogenation tunnel, where they are exposed to exceedingly high temperatures for sterilization. It is carried out using dry heat or hot steam. It destroys and inhibits harmful fever-inducing pyrogens. In this way, the sterility of vials is ensured and now they are safe for parenteral and biopharmaceutical drugs.
Aseptic Vial Filling
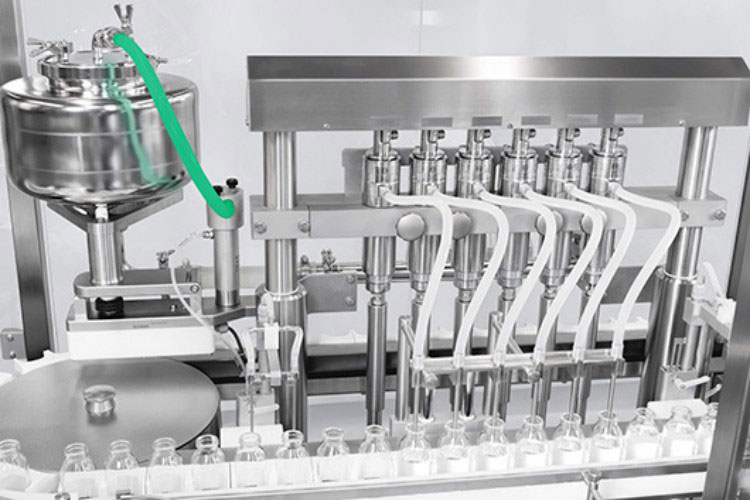

Aseptic Vial Filling- Picture Courtesy: Syntegon
This is a core step in the vial production line. To execute this step, vials are transferred to the filling station and are accurately loaded with different forms of medications through various filling mechanisms.
The dosing process is controlled through the feedback generated by the weighing cells. The filling machine is equipped with automatic weight-checking sensors to examine the weight of filled products. This step typically occurs in a sterile environment to avert any chance of pathogen entry in vials.
Stoppering
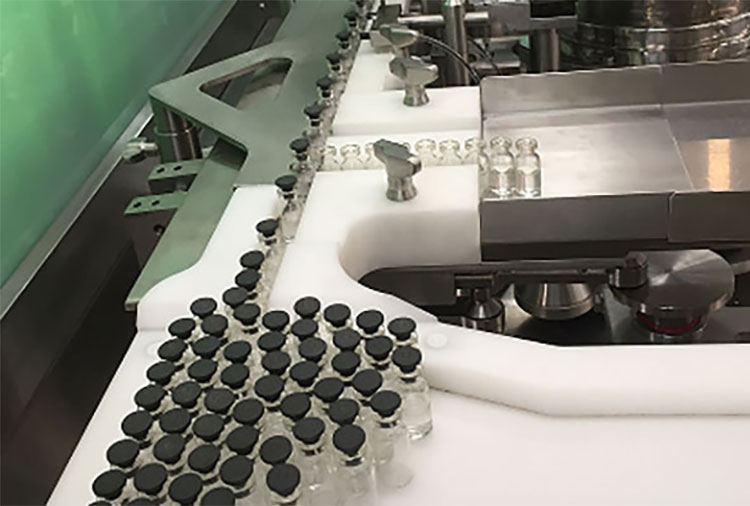

Stoppering of Vials- Picture Courtesy: IVEN-Pharma
The next step in the vial production line is the insertion of a rubber or lyophilized stopper on the vial mouth to completely secure pharmaceuticals and other biological products. These stoppers are lifted by the vacuum system and a robotic plunger arm puts them on vials. This step is essential in safeguarding samples from contamination and upholding their structural and functional integrity and potency.
Sealing
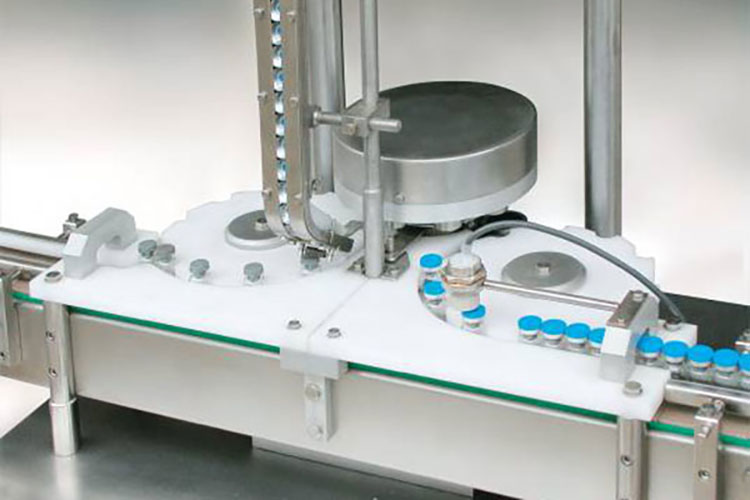

Sealing of Vials- Picture Courtesy: IVEN-Pharma
After stoppering, the aluminum or plastic crimping cap is dispensed over the vial stopper to fix and seal the latter in place. In some cases, a tear-off seal or flip-off cap is placed over the crimping caps to prevent any tamper-evident activities. This step ensures that caps are tightly secured and there is no chance of interference with a product and its leakage.
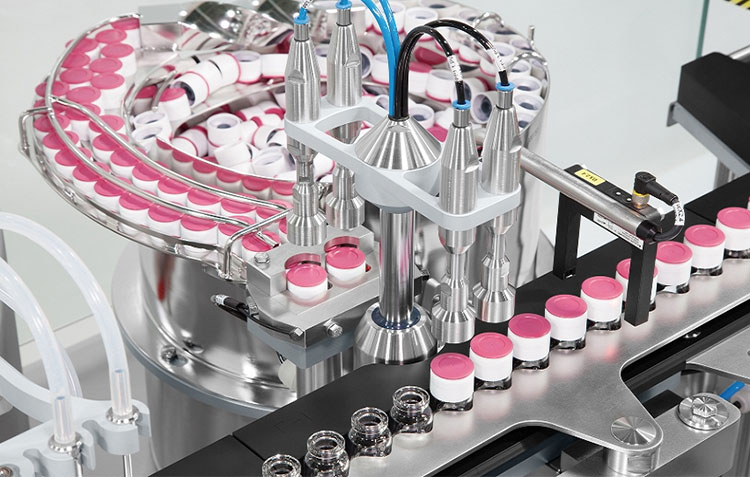
Inspection and Labeling
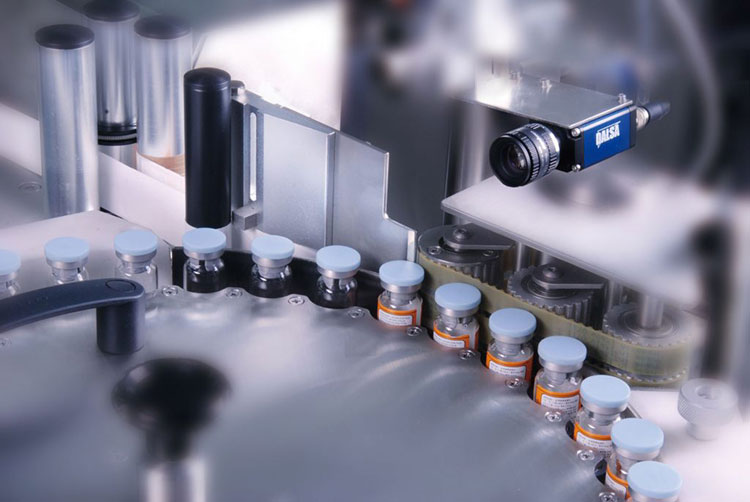

Vial Labeling- Picture Courtesy: Production Packaging Systems
Inspection of vials via various automated or manual systems is performed after stoppering step. It ensures manufacturers that there are no defects, damage, or blemishes present on the exterior or interior of vials and that they meet product quality and compliance criteria.
Afterward, the labeling machines are utilized for labeling a diverse kind of information, such as product name, serial number, expiry date, uses, and, manufacturing details on vials. This step is necessary for product tracing, tracking, and recognition.
Vial Discharge
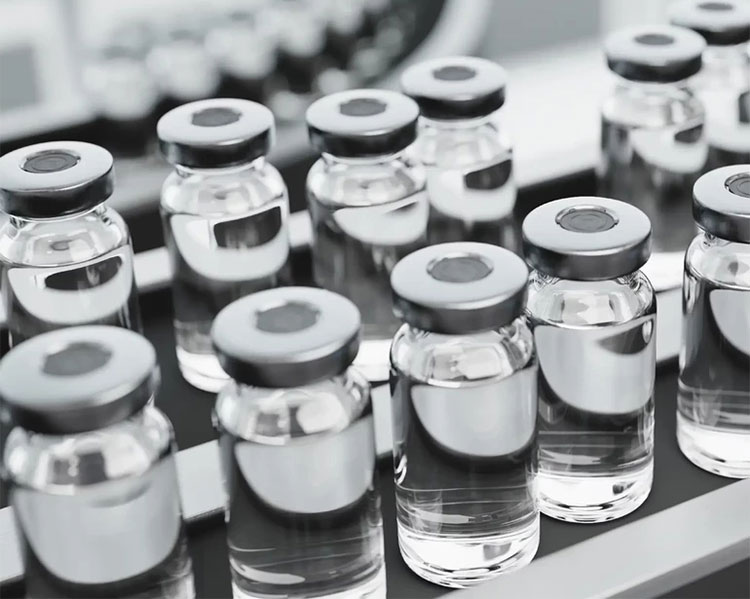

Vial Discharge- Picture Courtesy: BioPharmaReporter
Finally, after labeling, vials are now ready for discharge from the production line. They are held for final transportation or transferred to systems for further inspection.
4.What types of vials can be handled on a vial production line?
A wide array of vials houses pharmaceuticals, biotech, and diagnostic products all across the globe. Hence, the vial production line is designed to easily accommodate a diverse range of vial types. Some of the frequent types of vials handled by this production line are accounted for below:
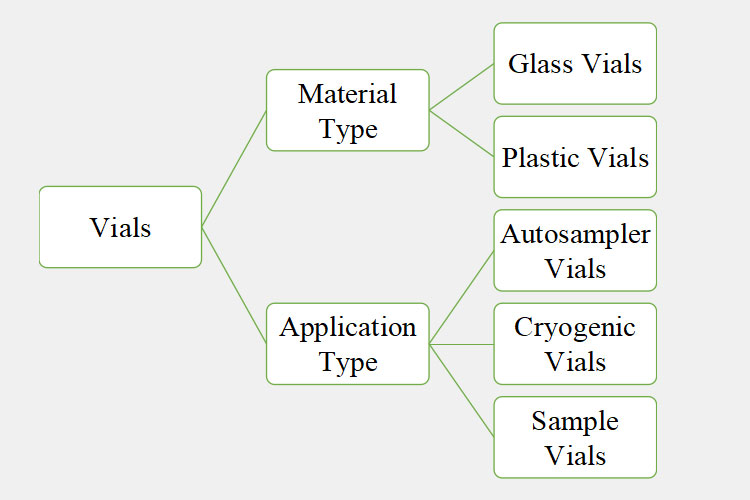
According to Material Type
Glass Vials
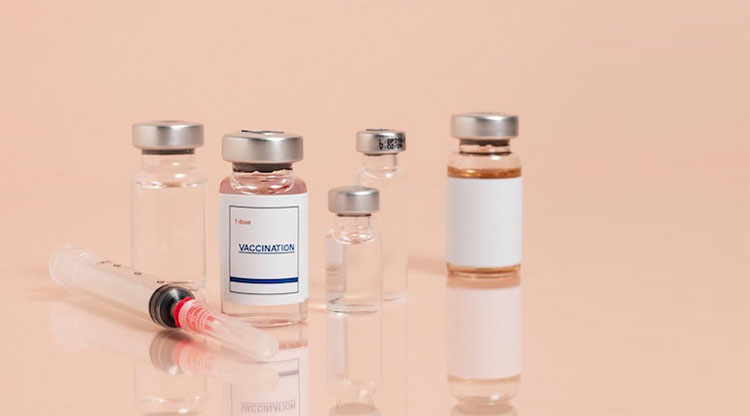
Glass Vials
Glass vials have been used since ancient civilizations. In earlier days, they held fragrances, oils, and tears. Today, glass is still regarded as the most appropriate material to pack sensitive medications, injectable compounds, and, laboratory samples. It keeps medicinal products protected from environmental agents- light, moisture, air- and extends their expiration date.
There are diverse types of glass vials- for instance, type I borosilicate glass vials, type II borosilicate glass vials, and type III borosilicate glass vials. Glass vials are preferred because of their clarity, non-porous nature, thermal resistance, and sustainability.
Plastic Vials
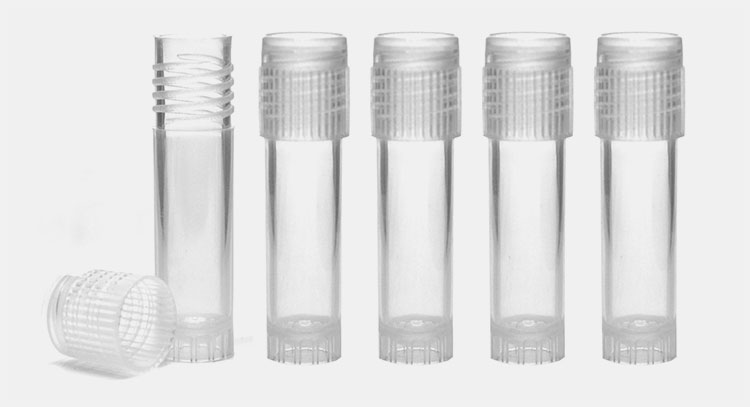

Plastic Vials- Picture Courtesy: Eisco Labs
Plastic vials usually hold cosmetic or fragrance samples, crime evidence, or laboratory reagents. They are manufactured from polypropylene or polyethylene. They have fairly low cost because their manufacturing expense is significantly less than other materials. Furthermore, plastic vials are well-regarded due to their lightweight and durable characteristics that make it easier to handle, ship, or deliver plastic vials to the market and patients.
According to the Application Type
Let’s discuss some basic kinds of vials, their uses, and advantages, based on their applications.
Autosampler Vials
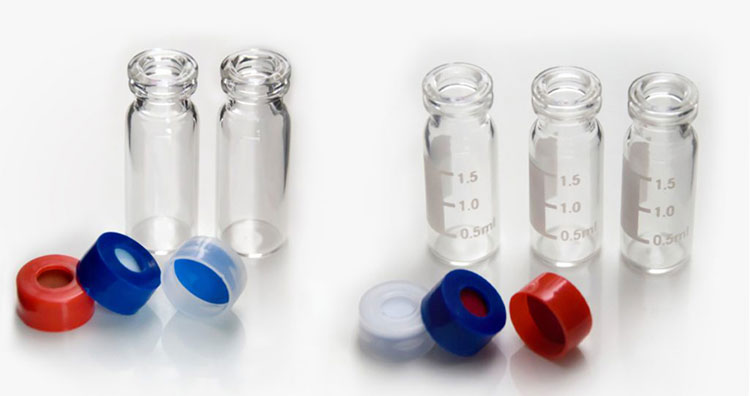
Autosampler Vials- Picture Courtesy: Moxcare
Autosamplers are instruments that are routinely used for automatically and precisely dispensing samples in the autosampler vials for evaluation. These vials are usually found in industries and laboratories to store samples for analysis, such as gas chromatography (GC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and mass spectrometry (MS). Therefore, it is crucial to use the right kind of autosampler vials, as neglecting this would cause sample degradation or wear and tear of the autosampler.
Cryogenic Vials
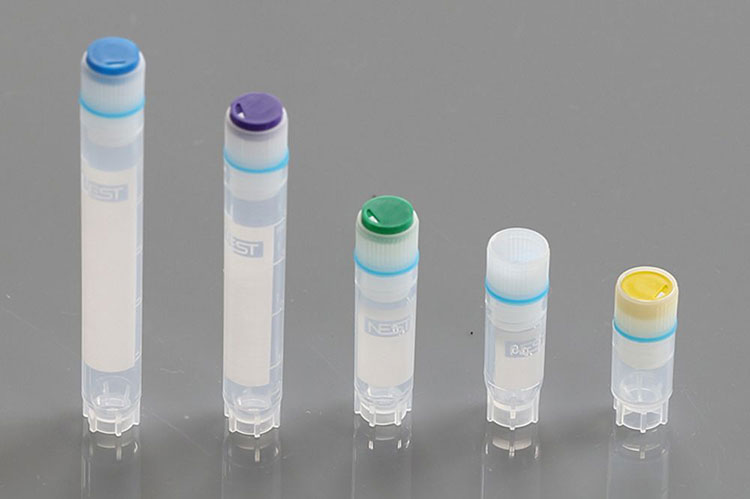
Cryogenic Vials- Picture Courtesy: DKSH
They are handled by the vial production line to enclose biological samples- for instance, cell culture, tissue samples, and other pharmaceuticals- at extremely cold temperatures of -196°C. Cryogenic vials are configured using sturdy materials, such as polypropylene and silicone O-rings that efficiently tolerate ultra-cold temperatures without breaking or cracking.
Sample Vials
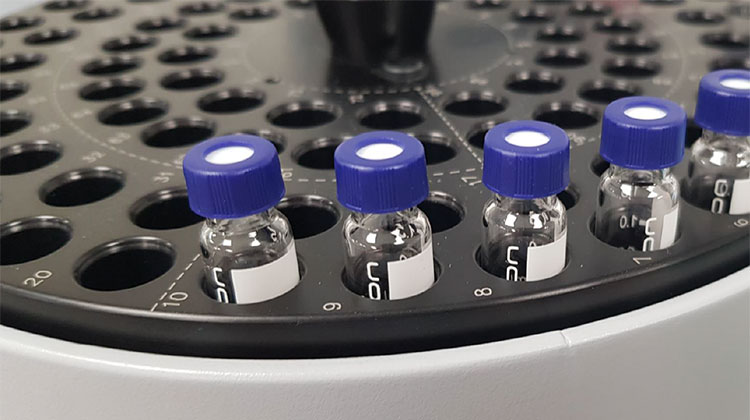

Sample Vials- Picture Courtesy: SICON Instruments
They are little vessels for storing various types of industrial and laboratory samples (plasma, blood, soil, hairs, and, fibers) for testing and analysis. They come in a huge variety like they may be clear, amber color, round-bottom, or flat-bottom, and manufactured using glass or plastic. They are usually available in pre-sterilized forms.
5.What are the minimum and maximum sizes of vials that can be processed by the vial production line?

Sizes of Vials- Picture Courtesy: Stevanato Group
Vials are available in a variety of sizes to accommodate samples- ranging from minor amounts to larger loads. So, a vial production line is flexible, when it comes to processing minimal and maximal volumes. Its various models have their standard minimum and maximum dosing volume capabilities. However, in general, the minimum volume is as small as 0.2 ml and the production lines are adjusted to process micro vials, depending upon the product need.
Furthermore, some versions of the production line can handle larger sizes of vials up to 500 ml, but these sophisticated processing lines are constructed with bigger capping and filling systems.
6.What product types are filled by a vial production line?
A vial production line easily doses a vast assortment of products in vials for medical, research, and cosmetic purposes. Some product types loaded by this production line are mentioned in the following table.
| Pharmaceutical Products
Vials are a highly popular means for storing a huge diversity of pharmaceutical products, such as chemotherapy drugs, parenteral medications, hormones, antibiotics, anesthesia, and sterile water. |
 |
| Diagnostic Reagents
With the revolution in the diagnostic field, nowadays, diagnostic agents like anticoagulants or buffers come in the vial packaging. Also, enzyme diagnostic kits- for evaluating clinical samples- and other clinical screening agents are housed in vials for secure distribution. |
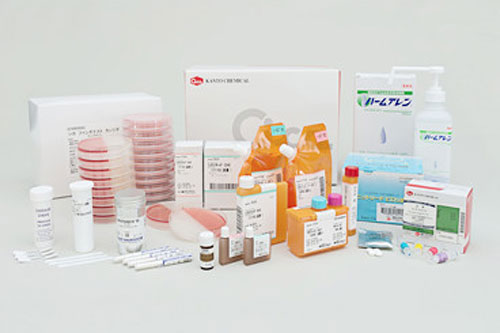
Diagnostic Reagents- Picture Courtesy: Kanto Chemicals |
| Immunization Therapies
Today, single or multi-dose vaccines (flu, whopping cough, rabies, and, hepatitis) are typically available in both small and large vials. Besides this, serum and antitoxins for supporting immune functions are dosed in vials for accuracy and sterility. |
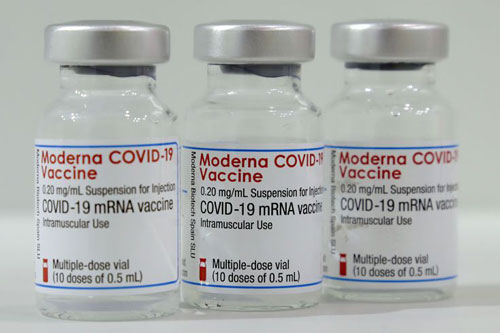
Immunization Products- Picture Courtesy: Verywell Health |
| Analytical Products
Vials also store different types of chemical reagents, such as alkalis, solvents, and acids. They are routinely used during testing, analysis, and, research in laboratories and industries. |

Analytical Products- Picture Courtesy: Phenomenex |
| Lyophilized Products
These products are formed through the technique of dehydrating under vacuum conditions. These freeze-dried materials include biologics, proteins, and, vaccines. They are usually reconstituted before administration. |
Specialty Chemicals- Picture Courtesy: GEA |
| Chemicals
In chemical industries, certain specialty chemicals like resins, pigments, lacquers, waxes, and binders are loaded in the vials to improve the performance, appearance, and finishing of certain construction products. |

Specialty Chemicals- Picture Courtesy: Bruker |
| Cosmetic Serums and Oils
Various kinds of luxe and high-end beauty potions, like facial serums, anti-aging solutions, skin care essences, and essential oils are filled in vials for daily skincare and body care routines. |

Picture Courtesy: Jarsking |
| Bio storage Liquids
This production line is featured with cryogenic devices to safely fill bio-storage and cryogenic products, such as DNA, tissue materials, monoclonal antibodies, and, cell cultures. |

Picture Courtesy: M2 Scientifics |
7.What types of closures are fixed on vials by the vial production line?
A vial production line utilizes various kinds of closure to uphold the integrity and antisepsis of inner vial contents. These inert and airtight closures protect contents from leaks, contamination, and evaporation. Some of the fundamental types of vial closures are listed below:
Rubber Stopper

Rubber Stopper- Picture Courtesy: Aptar
They are also termed elastomeric stoppers. They are typically preferred for pharmaceutical samples like injectable therapies. They offer airtight closure and also provide a site for the insertion of a needle to draw the drug from vials. Some stoppers can accommodate multiple punctures and do not interact with sensitive compounds.
Aluminum Crimps

Aluminum Crimps- Picture Courtesy: Fisher Scientific
They are made of aluminum and vial necks are secured by them to firmly lock the stopper in place. They are also integral in preventing the tampering of products. It tightly forces the stopper between the vial neck and cap, resulting in a high-quality seal and decreased evaporation risk.
Plastic Screw Caps
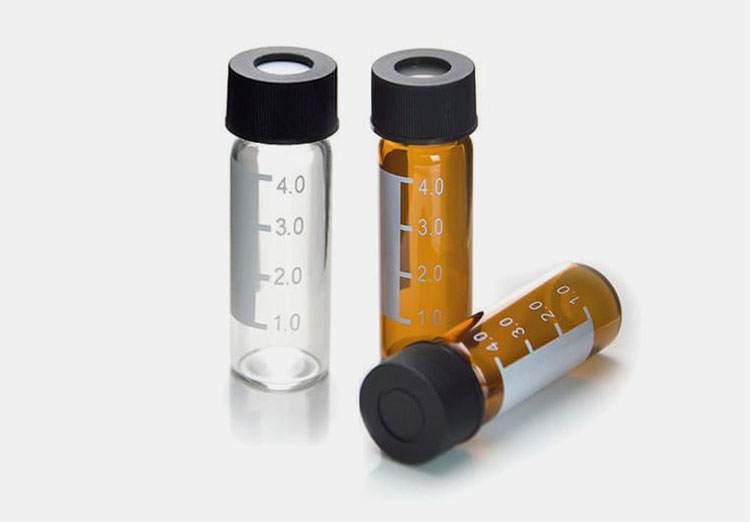

Plastic Screw Caps- Picture Courtesy: Vials
They are usually manufactured from polypropylene and secure non-injectable and non-sterile reagents and diagnostic essays. Plastic screw caps are rotated for opening vials and reclosed upon use. They are ideal for reusing and may come with tamper-evident features.
Snap Caps

Snap Caps- Picture Courtesy: ISO-MED
It offers a mild seal but does not need specialized devices for putting caps onto the vial rim, as they are snapped on and removed manually. Snap caps offer a convenient way to open and close vials.
Double Vented and Slotted Stopper
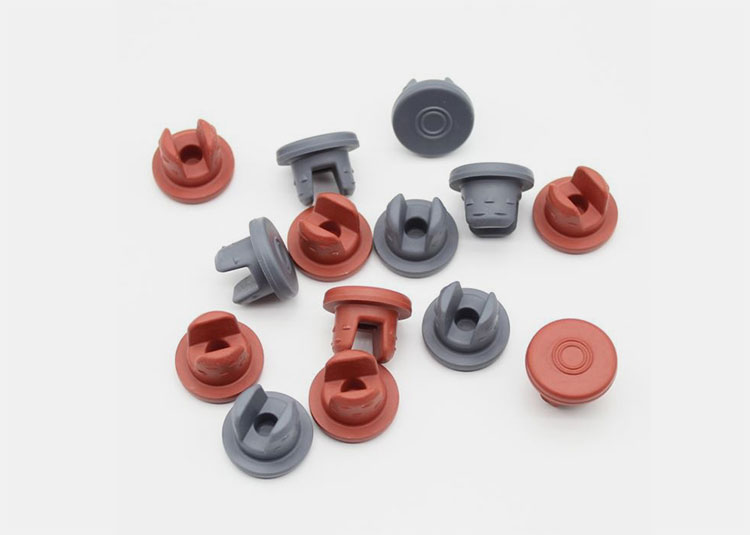

Double Vented and Slotted Stopper
They are particularly developed for freeze-drying vials and contain slots or holes for gas flow and vapor evaporation during drying. They can be completely fitted into vials to attain a hermetic seal.
8.What are the challenges and solutions of the vial production line?
The vial production line is a series of trailblazing machines that assiduously handle and dose vials. In certain settings, unfortunate incidents arise in this production line, significantly jeopardizing the throughput rate and precision of the system. However, these challenges are effortlessly addressed by careful planning and operator training. Let’s review some common challenges and solutions of the vial production line:
Precision in Filling Rates

Precision in Filling Rates- Picture Courtesy: PharmTech
It is extremely pivotal to attain precise and uniform dosing, particularly for micro-volumes for parenteral medications. There should be no errors of overfilling and underfilling, as they are usually the reason for product recall, wastage, dosing accuracies, and, legal penalties from regulatory bodies.
Solutions
This challenge can be overcome using sophisticated and high-end filling systems like peristaltic pumps or time-pressure-based filling devices. They have advanced and highly precise sensors and weight-checking systems for detecting minor differences in loading volumes, leading to the verification of fill volumes.
Seal Integrity

Seal Integrity
Poor sealing of pharmaceutical and diagnostic vials poses a major challenge in the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector, as ineffective capping, crimping, or stoppering, negatively impacts product integrity, leads to biological, chemical, and physical contamination, and also causes product spillage.
Solution
Manufacturers deal with this issue by incorporating innovative capping, crimping, and stoppering units for exerting optimized forces on different sealing closures to effectively and firmly secure vials. Moreover, these devices are routinely calibrated and maintained to prevent sealing anomalies.
Particulate Control

Particulate Control
Different varieties of particles, for example, dust, debris, tiny glass shards, leachable, and, others may contaminate the vials before, during, and after product dosing.
Solution
It is imperative to equip the vial washing machine with highly effective particulate washing mechanisms to avoid contamination before product dosing. Secondly, there should be strict quantity control measures across every checkpoint of the vial production line to avert the chances of impurity of products. Lastly, this production line should be operated in a cleanroom environment having HEPA filters to filter out dangerous airborne particulates from vials.
Breaking or Cracking of Vials

Breaking or Cracking of Vials- Picture Courtesy: Tecnosoft
Vial breakage or cracking is a huge challenge faced in manufacturing lines, causing product wastage, interruption in production workflow, and safety hazards for workers.
Solution
To avoid this issue, the vial production line should be equipped with precision handling systems- for example, soft grippers, conveyors, and robotics- to avoid the vial breaking possibility. Moreover, automatic vial inspection systems like vision cameras and image analysis software should be integrated into this production line to check the quality and appearance of vials- for damages, like crack lines and chips. These systems help in the rejection of defective vials.
Maintaining Sterility

Maintaining Sterility- Picture Courtesy: Garvey Conveyors
Upholding sterility has foremost importance because, without sterility, products become contaminated due to environmental agents, carelessness of operators, and, interaction with unclean machinery.
Solution
To resolve this problem, it is advised to integrate sterility devices, such as isolator technology or restricted access barrier systems (RABS) in the filling and sealing sectors to cut down the risk of contamination. Moreover, scheduled cleaning and sterilization approaches in conjunction with real-time hygiene inspection and frequent quality control checks are ideal ways to ensure absolute sterility of products and systems.
Conclusion
The vial production line is an assembly of continuously operated machines that guarantee safe, sterile, and, clean operation with no chance of contamination. It is developed to enhance aseptic filling quality and minimize vial packaging intricacies. It opens up vast arenas of profitability through its potential to accommodate large batch sizes and versatility, Today, manufacturers all across the globe have introduced their versions of vial production line. However, the sophistication and high quality offered by AIPAK Engineering in their vial production lines are beyond comparison. So, without waiting, immediately contact us for the best deals.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours