Tincture In Pharmaceutics: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Do you use tincture for antiseptic purposes or as inhalant? Did you know tincture is the oldest form of pharmaceutics?
A tincture is a keystone of pharmaceutical technology and acts as a bridge between old remedies and modern medicine. They are generally herbal extracts in alcohol. And they are the easiest method to administer plant-based medicines. Why tincture is still preferred as a mode of drug delivery in recent times? Well, because they are easy to prepare, have longer shelf-life, and quickly absorb through mucosal linings. Do you want to learn about the ins and outs of pharmaceutical tincture manufacturing?
This FAQ guide “Tincture In Pharmaceutics” is exclusively catered to mollify the inquisitive minds of pharmaceutical manufacturers or researchers. It will unravel hidden secrets by explaining in detail concepts related to the formulation principle of tincture, fundamental equipment, and frequent challenges. Let’s get right into the extraordinary world of tincture in pharmaceutics.
1.What is tincture in pharmaceutics?

Tincture in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Crystal Health & Beauty
In pharmaceutics, tincture is described as a liquid preparation, devised by dissolving various medicinal, chemical, or botanical compounds in diverse types of solvents- whether alcohol, water, or their combination. In most cases, tinctures are utilized to conserve active constituents of plants like alkaloids, glycosides, and essential oils.
It serves various purposes, such as a vehicle for solubilizing active components, and helps in preparing different potencies of fresh and dried herbal extracts. It has the advantage of extended shelf-life and boosts absorption of components when delivered orally, sublingually, or, topically.
2.What are the fundamental components of tincture in pharmaceutics?
The two main components of tincture in pharmaceutics are solvents or plant or chemical-based molecules but other substances are also added to tincture in small amounts to maintain its consistency, stability, color, and flavor Now, we are going to explain various fundamental components of tincture in pharmaceutics:
Active Ingredients Typically Consisting of Medicinal Components

Active Ingredients- Picture Courtesy: MedlinePlus
They are the core chunk of the tincture- extracted from the source material and basically involved in its therapeutic relief. It is a solute component in tincture preparations. They could be phytochemicals or other particular chemicals. Some active ingredients include:
| Plant Extracts | These materials are prepared from herbs (dried or fresh), bark, roots, flowers, leaves, fruits, or, other parts of the plant. They are composed of bioactive substances, for instance, alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, oils, or phenolic acids. |
| Animal Substances | They originate from animal sources, for instance, tissues, organs, membranes, or secretions. Animal extracts are typically comprised of hormones, enzymes, or proteins. However, they are less frequently utilized in modern pharmaceutics and are mostly replaced by plant extracts or chemicals. |
| Synthetic Chemicals | They are synthetically made in laboratories or industries to boost the characteristics of natural substances. They are prepared to offer medicinal relief. They are highly pure and can be tailored to elicit a particular therapeutic response. |
Solvent: Liquid Phase

Solvent- Picture Courtesy: Craftly US
It acts as a liquid phase or medium for dispersing active medicinal components. Solvents are about 25-60% of tincture but can go as high as 90%. One of the most frequent solvents is ethyl alcohol or ethanol. It is mixed with water and is used in herbal medicine. Different amounts of ethanol are present in the alcoholic tinctures.
Ethanol is preferred in tincture in pharmaceutics because it can dissolve both acidic and basic components.
Preservatives For Stability

Preservatives- Picture Courtesy: Kidsapo
Alcohol not only behaves as a solvent in tinctures but also has a role as a natural preservative; however, pharmaceutical manufacturers also incorporate extra preservatives to stabilize formulations and lengthen their expiry period.
Flavoring Agent: Adding Characteristic Flavor

Flavoring Agent
They are optional substances and can be included in tinctures to disguise the bitter or potent taste of some active ingredients. They are mostly utilized in oral use tinctures and can be naturally sourced or artificially manufactured. Some of their examples are mint, honey, or essential oils.
Additives

Additives- Picture Courtesy: Lab Alley
They are auxiliary materials incorporated in tincture preparation as a stabilizer, viscosity modifying agents, solubilizers, and pH adjusters. They are usually used for improving the solubility of solutes, altering the texture of tinctures, and, maintaining the chemical composition of tincture with time.
3.What are the advantages of using tincture in pharmaceutics?
Why tincture in pharmaceutics is still a favorite among manufacturers? Because their production has various advantages. If you want to learn its benefits, then continue reading the next section:
Efficient Solubility of Active Components

Efficient Solubility of Active Components- Picture Courtesy: Ongrok
Yes, tincture in pharmaceutics is highly regarded because of its remarkable dissolution properties. It can readily dissolve a wide range of both water and fat-soluble bioactive molecules, for instance, terpenes, phenols, flavonoids, and more. This translates into higher therapeutic efficacy of tincture.
Wide Array of Utility

Wide Array of Utility- Picture Courtesy: Ferry-Morse
Tincture is one of the pharmaceutical products that is administered in a wide variety of ways. You can take tincture orally without any beverage or diluted with water or juices. Moreover, it is dispensed sublingually for quick absorption in systematic circulation and thus offers a faster therapeutic outcome. You can utilize it tropically for disinfecting wounds and analgesic purposes.
Customizable Dose Intake

Customizable Dose Intake- Picture Courtesy: 420 Central
Are you aware that tincture dosages are modified based on patient needs? You can alter its dosage by dropper and accommodate individual patient health requirements. Furthermore, you can create your personalized treatment regime by mixing several tinctures.
Faster Therapeutic Relief

Faster Therapeutic Relief- Picture Courtesy: Zen Mailtri
Why do patients take medication? Well, to obtain therapeutic relief. Hence, tinctures are favored by individuals over tablets or capsules due to their rapid absorption through oral or sublingual routes. Meaning that it provides quick relief from the disease state.
Easy Portability

Easy Portability- Picture Courtesy: UkHerbals
One of the significant benefits is its easy usage. There is no need for extra preparation steps, such as brewing teas or decoctions, usually performed with other herbal extracts. Also, they come in lightweight and portable containers that are carried out and stored conveniently.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing

Cost-Effective Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Culinary Solvent
Producers always wish to save money and tincture in pharmaceutics comes with optimal money-saving advantage. This formulation is simple and cheap to produce in contrast with new dosage forms, like syrups or emulsions. Why is that? This is due to its minimal processing steps and requirements of less excipients.
4.What types of medicines or active ingredients are frequently formulated as tincture in pharmaceutics?
As is known, tinctures in pharmaceutics have a wide range of applications due to their diverse composition. Hence, it is utilized for a multitude of healing functions. We are explaining some frequently prepared tinctures and their active ingredients.
Plant-Based Medicines

Plant-Based Medicines- Picture Courtesy: UkHerbals
These types of tinctures have a variety of herbal components, for example, echinacea, valerian root, ginseng, chamomile, and peppermint. They have different health benefits, like supporting immunity, promoting good sleep, relieving anxiety, providing stress relief, and soothing digestive discomfort. You can also use opium tincture for alleviating pain and belladonna tincture as an antispasmodic agent.
Antiseptic Treatment

Antiseptic Treatment- Picture Courtesy: Harmonics Arts
Tincture in pharmaceutics holds an integral task as an antiseptic and skin disinfectant. For example, iodine tincture disinfects superficial and internal wounds. It prepares the skin by clearing debris or microbes for the application of topical medications. While thymol or phenol tinctures are ideal for preventing antifungal infections.
Pain Relief Aid

Pain Relief Aid- Picture Courtesy: Essentially Natural
Pain treatment is a major utility of tincture in pharmaceutics. Capsaicin tincture prepared from extracts of chili pepper is dispensed for localized pain management. You can also calm muscular pain by applying menthol or camphor-based tinctures on the skin.
Digestive Support Therapy

Digestive Support Therapy- Picture Courtesy: Healthline
Herbal-based tinctures are commonly used as a digestive aid by stimulating digestive metabolism and improving appetite. Gentian root tincture is excellent for soothing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Similarly, dandelion tincture is the perfect remedy for liver and gallbladder disorders. For relieving constipation, you can take cascara sagrada tincture.
Nerve and Heart Tonics

Nerve and Heart Tonics- Picture Courtesy: Healthline
Today, people are opting for solutions to boost their heart and nerve health and tincture is one of them. Like, hawthorn berry tincture is both a traditional and modern treatment approach to sustain heart and blood well-being. Also, the high prevalence of anxiety and stress disorders has led to increased application of passionflower tincture, cannabis tincture, and kava tincture.
5.What are the operational steps of manufacturing tincture in pharmaceutics?
Before manufacturing tincture, the first step is to learn about its different operational stages. You can carefully control these stages to achieve thorough extraction, optimized preparation, and superior-quality yield. So, let’s delve into the description of the operational steps involved in manufacturing tincture in pharmaceutics.
Selection of Raw Source Material

Selection of Raw Source Material- Picture Courtesy: GrowHub
First, to make tincture in pharmaceutics, you need plant materials, animal matter, synthetic chemicals, for instance, iodine. These source materials before being processed, are first checked for quality and purity.
Preparation of Source Feed and Solvent

Preparation of Source Feed and Solvent- Picture Courtesy: Stockcake
After inspection, you are required to clean the source material by removing various dust, stones, debris, and large substances from the source feed. Afterward, it is pulverized with a grinder or millers to chop and crush it into smaller pieces. This helps in increasing surface area and boosting extraction yield. You can also dry fresh plant substances to attain optimal moisture content.
You must select a suitable solvent and process it so that it is void of any impurity. Mix various solvents together by adjusting their solvent quantities.
Extraction
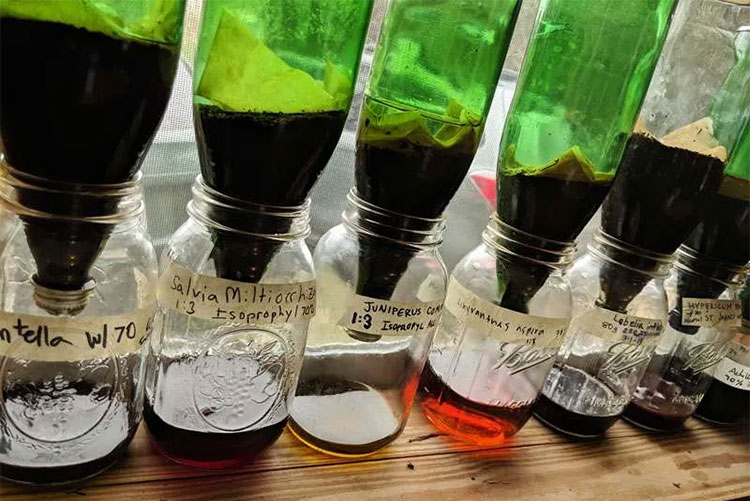

Extraction- Picture Courtesy: Herbal Medics Academy
The extraction step is dependent upon the extraction technique. For example, in maceration, the source material is placed in the solvent for a certain amount of time, normally several days or weeks, with seldom and gentle stirring. While in percolation, you pass the solvent through a column of raw feed, resulting in continuous and faster extraction. You can also use ultrasonic waves to improve the discharge of active components from source material by disrupting cell walls.
Filtration

Filtration- Picture Courtesy: Brother Filtration
After extraction, the insoluble particulates or other contaminants are eliminated through suitable filtration approaches to obtain a highly pure and clear tincture.
Mixing and Homogenization

Mixing and Homogenization
Additional solvents, preservatives, additives, or stabilizers are added to the final filtrate extract according to the recipe for tincture preparation. Various types of mixing approaches are utilized to achieve smooth and even solutions for all ingredients.
Packaging
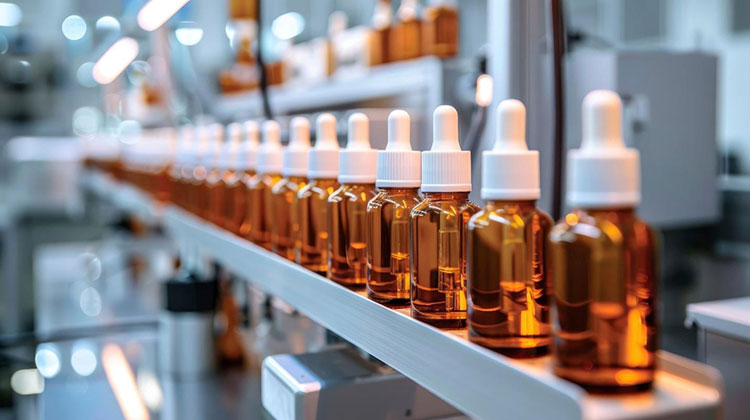

Packaging- Picture Courtesy: Pravada Private Label
Finally, the tinctures are packed in sterile containers to ensure inner contents remain sterile and safe throughout the distribution chain. They are also sealed with airtight caps, stoppers, or seals. Lastly, you label the tincture products with various information details like dosage instructions, warnings, ingredient quantities, expiry period, and more.
6.What is the key equipment for manufacturing tincture in pharmaceutics?
It is an important question that is central to the work of pharmaceutical manufacturers and research technicians. This manufacturing protocol needs different kinds of specialized instruments and other supplementary accessories to produce high-quality tinctures in pharmaceutics. The selection of these devices is dependent on the production scale and composition of active substances. Here is a detailed guide to equipment for your knowledge:
Mixing Equipment
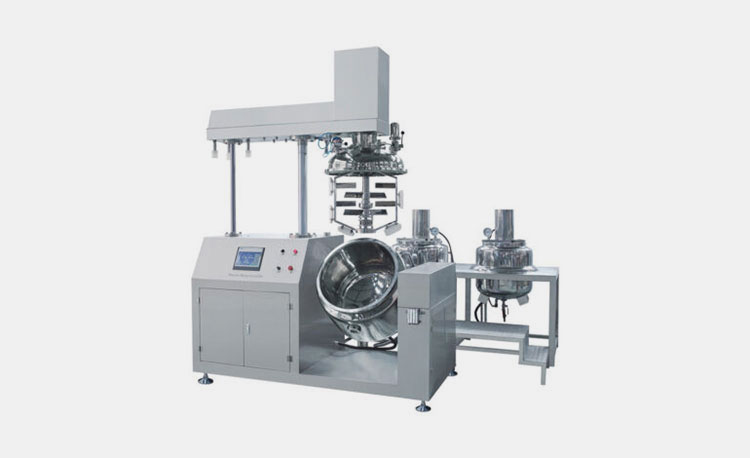

AIPAK Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
They either consist of mixers or homogenizers that blend or mix desired substances, solvents, and additives thoroughly. They are typically incorporated in the tincture manufacturing line to obtain stable and homogenous solutions of poorly soluble compounds. They also have heat-exchange systems or cooling mechanisms to improve mixing efficiency.
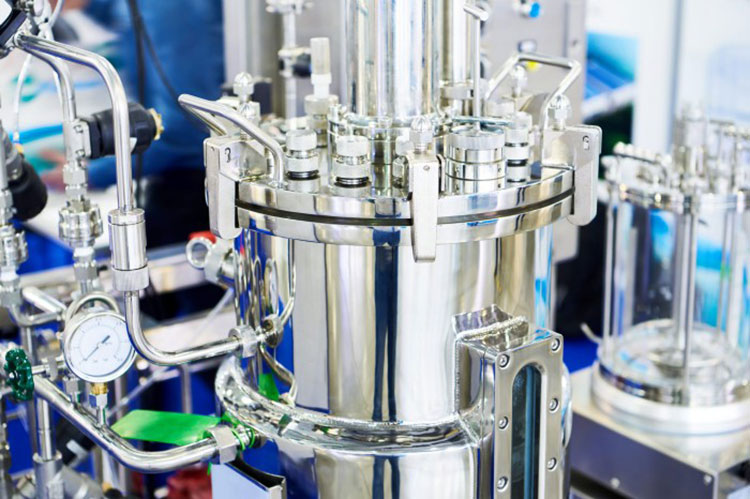
Extraction Equipment
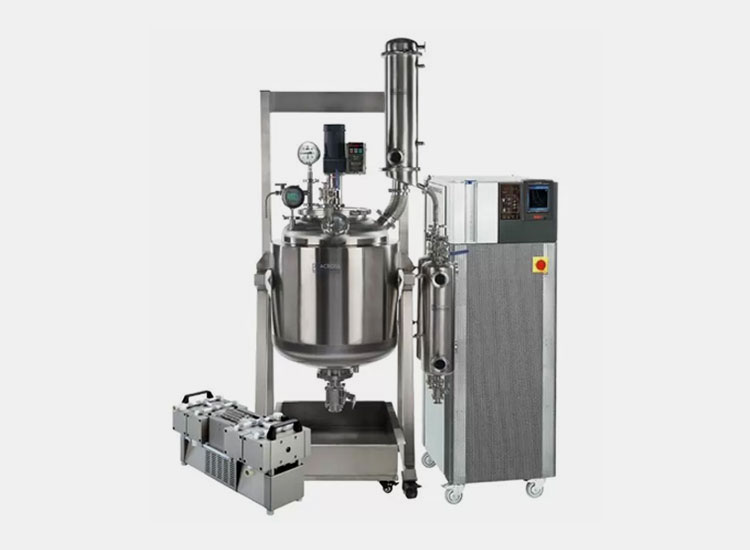

Extraction Equipment- Picture Courtesy: Making
They form the core part of the preparation of tincture in pharmaceutics and are containers or vessels to extract required compounds from source matter. Their function is to hold plant parts and solvents for extraction of therapeutic components. They are usually composed of inert or non-reactive materials, for instance, glass or stainless steel. It has various types like:
| Maceration Vessel | It is a kind of closed container employed to draw out various active remedial components from raw materials. The latter are placed in this vessel and solvents are poured over these materials. Then the mixture is left for a certain time about 36 hours and sometimes stirred or agitated to speed up the extraction. Afterwards, the solvent is filtered and residual solid or marc is squeezed to retrieve left-over solvent. |
| Percolators | It is a large glass container that has a cone-like structure, with an opening at the top and a stopcock at the lower part. The raw ingredients are placed in the percolator and solvent is poured over the top. Then the mixture is allowed to sit for about 24 hours after which the bottom opening is opened and liquid gradually drips out of it. This vessel is employed for continuous extraction. |
| Soxhlet | This vessel is a type of laboratory apparatus, engineered for the extraction of material with limited solubility in a solvent. It has three major parts: a percolator, thimble, and siphon mechanism. The solvent is heated and vapors move into the chamber containing thimble (filter paper). Then desired components are solubilized in water and after that Soxhlet chamber is drained through a siphon. |
Filtration Systems
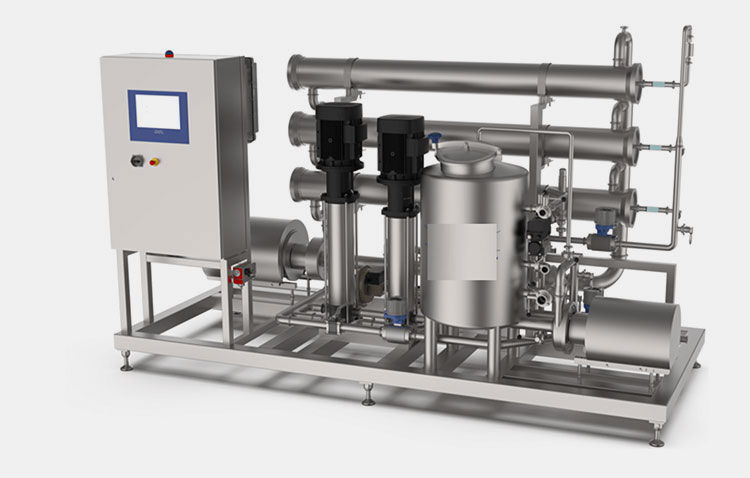

Filtration Systems- Picture Courtesy: Alfa Laval
This device has an integral function in clearing out various types of solid residues from the tincture preparation after the extraction process. This helps to attain a clear and impurities-free tincture. There is a wide array of filter systems including:
| Sieve Filters | They are composed of sieves or membranes (made from stainless steel or nylon), employed for eliminating large deposits or debris after initial extraction. |
| Cartridge Filters | They come with disposable filter cartridges that have an aperture size of 0.2–10 microns. Their job is to remove tiny particulates from the tincture to achieve a high degree of clarity. |
| Membrane Filters | They are an advanced system of filter units and are ideal for ultra-pure filtration. With the help of small-pore-sized membranes, they are excellent for removing bacteria, fungi, or viruses from tincture preparation. They are frequently employed at the last steps in tincture manufacturing. |
Quality Control Systems

Quality Control Systems
They are typically employed before filling and packaging. What’s their purpose? Pharmaceutical manufacturers often incorporate various quality control systems, such as spectrophotometers, pH meters, and refractometers to ensure tinctures in pharmaceutics have the best quality, the desired concentration of active compounds, stability, effectiveness, and potency.
Packaging Solutions
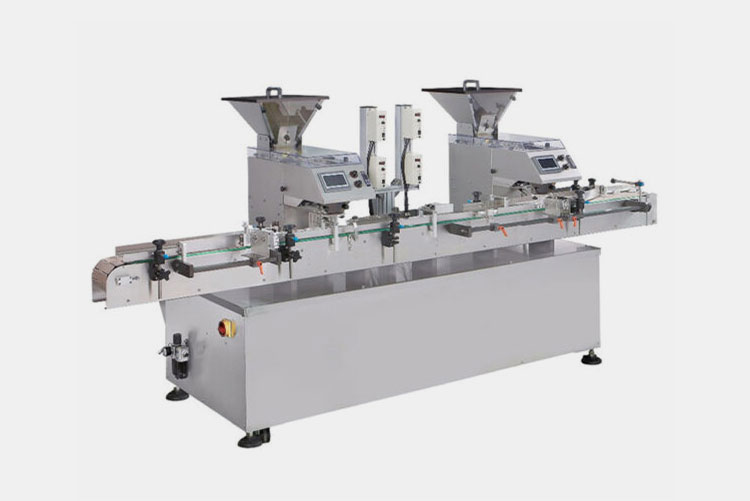

AIPAK Capping Machine
To ensure superior purity and stability, diverse types of packaging devices, like vial filling machines, bottle filling machines, etc. are integrated into tincture manufacturing in pharmaceutics. They accurately and exactly dispense tincture in bottles or vials. After filling, sealing devices, such as capping sealing machines or crimp sealing machines are present to airtightly seal containers to avoid contamination of contents. Finally, labeling machines prepare tincture containers for retailing or distribution by sticking information labels on them.
7.How is tincture in pharmaceutics different from other liquid dosage forms like syrups or suspensions?

Differences Between Tincture, Syrup, and Suspension- Picture Courtesy: PTCB Test Prep
Liquid dosage forms include tincture, syrup, and suspension but they vastly differ from each other due to their dissimilar ingredients, manufacturing, and applications. Now, let’s discuss some important differences between tincture, syrup, and, suspension:
| Features | Tincture | Syrup | Suspension |
| Solvent Type | Generally, tinctures are formulated with alcohol or a combination of alcohol and water. | It is made with a high amount of sugar or sugar derivatives that easily solubilize in water. | Water or other liquid phase is utilized for dispersing solute particles in suspension. Stabilizers or suspension agents are also incorporated in suspension to avert sedimentation of particles. |
| Active Ingredient Properties | It is composed of plant or animal-derived ingredients as well as synthetic chemicals fully soluble in solvents. | It has water-soluble active components together with sweeteners. | It is prepared by insoluble active compounds as finely dispersed particles. |
| Preparation Technique | It is widely devised by maceration, percolation, or other alcohol-based extraction approach. | It is formulated by solubilizing various components in hot water. | Suspensions are generally manufactured by suspending fine particulates into the liquid phase. |
| Stability | Usually with alcohol, a long shelf of tincture is attained due to the inhibition of microbial growth. | A high amount of sugar in syrup is linked with some sort of stability but it has more tendency of microbial development. | It needs stabilizers or preservatives to prolong its shelf-life and avert the chance of microbial contamination. |
| Usage | A tincture is administered through oral, sublingual, or topical drug delivery modes. It serves antiseptic or analgesic functions. | Syrups have ideal ease of use and are mainly utilized for cough-easing purposes. | It has mostly oral or injectable modes of administration. |
| Flavor Profile | It has an intense alcohol-like taste, which is unappealing for some patients. | It has a sugary or sweet flavor. | It often has no taste and sometimes needs flavoring agents to disguise the bitter taste of components. |
| Onset of Action | It is absorbed rapidly, so has a faster onset of action. | Syrups have moderate bioavailability and slower therapeutic action than tinctures. | Its onset is variable owing to solubility and particle size distribution of ingredients. |
| Dosage Precision | It needs precise dosing through a stopper. | Usually, spoons or measuring cups are required for dosing large volumes of syrups. | You will have to shake the suspension before use to attain dosing accuracy. |
8.Are there alcohol-free alternatives to traditional tincture in pharmaceutics?
Individuals, who avoid using alcohol for medical, religious, or personal reasons, typically ask this question. The answer is yes. These alcohol-free alternatives maintain the full healing potential of tinctures. Some alcohol-free advantages are:
Glycerites

Glycerites- Picture Courtesy: Monterey Bay Herb Company
These are glycerin-based tinctures that employ glycerin as a solvent. It is a sweet and viscous liquid and is combined with water to attain maximum solubility. It has excellent taste-masking traits thus, glycerites are administered in children and sensitive users.
Vinegar-Based Extracts

Vinegar-Based Extracts- Picture Courtesy: Chuckling Goats
It incorporates apple cider vinegar or distilled vinegar as solvent alkaloids, minerals, and, other phytochemicals. Vinegar is excellent for extracting compounds from calcium-rich herbs. Vinegar has antimicrobial traits, so acts as a natural preservative.
Infusion or Decoctions

Infusion or Decoctions- Picture Courtesy: Botany Culture
They are formulated with water by soaking or boiling herbs. Infusion or decoctions are widely accepted because of their pure and alcohol-free nature. It is safe for consumption in every age group as well as expecting mothers and infants. However, they have a short expiry period and need refrigeration.
Oil-based Tinctures

Oil-based Tinctures- Picture Courtesy: Forbes
In these tinctures, you can employ oils, such as olive oil, coconut oils, or MCT oil to draw out fat-soluble active ingredients, for instance, cannabinoids, carotenoids, and some vitamins. They have a longer expiry period.
Honey-Based Formulations

Honey-Based Formulations- Picture Courtesy: Mickelberry Gardens
They are prepared with honey as a solvent base. Herbal extracts with honey are extra sugary and long preservation period because of the excellent antimicrobial traits of honey. These formulations are ideal for treating colds and coughs.
9.Does tincture in pharmaceutics have a specific shelf life? What are the storage conditions to maintain its potency?
It is very important to learn about the shelf-life of tinctures in pharmaceutics because their composition can alter after a certain period and produce health-deteriorating byproducts, which could be hazardous to your health.
Shelf-life of Tincture in Pharmaceutics

Shelf-life of Tincture in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Ongrok
Alcohol-based tinctures are well-accepted in the healthcare world due to their longer expiry period of about 2-5 years. They could last even longer if they are properly stored. Why is that? Because alcohol is a natural preservative, consequently inhibiting microbial contamination and chemical reactivity.
Conversely, glycerin or vinegar-based tinctures have a serviceable life of 6 months to 1 year and 1 to 3 years, respectively. The lack of alcohol in these formulations renders them more vulnerable to microbial proliferation.
Storage Conditions for Tinctures

Storage Conditions for Tinctures- Picture Courtesy: Jessie Martelhof
To extend the consumption time of the tincture in pharmaceutics, experts advised users to place tincture containers in cool and dry places with temperatures of 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F). It is better to use amber or tinted glass bottles for holding tinctures because the shading of glass blocks the UV light.
Also, you are recommended to tightly capped tincture containers after use to reduce air contact and inhibit the vaporization of solvents. Do not place tinctures in high-humid regions, for example, bathrooms or kitchens. Because moisture is the pivotal cause of microbial development in non-alcoholic tinctures.
Conclusion
In summary, you can think of tincture in pharmaceutics as a perfect fusion of historical practice and modernization. Its use is rooted in ancient times and now this liquid dosage form has evolved into a highly sophisticated and scientifically approved treatment approach. Both alcohol-based or alcohol-free alternatives serve as versatile treatment and health support aids in a variety of malfunctions in the body from heart disorders to psychological illnesses. Hopefully, after reviewing this blog post about tinctures in pharmaceutics, you now have a solid understanding of applications, advantages, production steps, equipment, shelf-life, and storage requirements. Get in touch with AIPAK ENGINEERING if you need anything else.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours