Flu Vaccine Production: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Have you ever wondered how your tiny flu shots are prepared? And what goes into its manufacturing?
Well, you would be amazed to learn that flu vaccine production usually involves eggs. Yes, vaccine viruses are harvested in eggs. Besides this, this highly specialized process also involves sophisticated culturing approaches, purification methods, safety checks, quality checks, packaging, and more.
For all those interested readers, it’s time to dive deep into the science and artistry of flu vaccine production. In this FAQ guide, we’ll curate behind-the-scene production steps, ingredients, advantages, technologies, and challenges of flu vaccine production.
1.What is a flu vaccine? What’s its working action?
Flu Vaccine- Picture Courtesy: Monash Lense
What you might call the flu vaccine is also referred to as the influenza vaccine, flu shot, or flu jab. It is a preventive injection solution (sometimes nasal spray) to protect you against a frequent respiratory disease influenza or flu. It is developed to boost your immune system to fight against a particular flu viral type- likely to spread in the next flu season.
It lowers the risk of developing flu and makes your illness shorter and milder. It is integral in safeguarding vulnerable groups, such as infants, older adults, and, people with severe diseases.
Basically, the flu vaccine is inactivated, killed, weakened, or artificially created fragments of influenza virus. These viral elements don’t cause flu when injected into the body but are great in getting the attention of your body's defense mechanism (immune system).
Consequently, in response to these viral agents, your immunological system creates special proteins- antibodies that disable viruses directly and flag them for immune destruction.
2.How can you define flu vaccine production?
Flu Vaccine Production- Picture Courtesy: Crinti Medical Practise
Flu vaccine production encompasses the whole process of making flu vaccine. It is a biotechnology industrial operation in which flu vaccines are developed and prepared for use in individuals.
In this process, each step- from picking the right influenza strain to culturing, virus inactivation, purification, formulation, testing, and, packaging- is carefully timed and controlled so that people are kept protected from seasonal outbreaks of flu.
Different sets of specialized machines and innovative technologies are used in flu vaccine production to manufacture high-quality flu shot that fulfills every safety regulation set by health authorities.
3.What are the ingredients used in flu vaccine production?
It is a common misconception that a flu vaccine is just a flu virus. However, in reality, it has various ingredients besides the inactive influenza virus. All these components serve a specific role in this product formulation.
For your information, we’re describing every ingredient used in flu vaccine production in detail below:
Antigens
Antigen- Picture courtesy: Genetic Engineering
These are the active ingredients, mainly consisting of viral protein (like hemagglutinin) or flu viral strains. These antigens target the immune system and induce antibodies but don’t cause flu. In inactivated vaccines, generally killed viruses serve as antigens.
Whereas, the antigens in live attenuated flu vaccine are weakened virus strains. Conversely, recombinant vaccines employ lab-created flu proteins as antigens and don’t utilize the real virus.
Adjuvants
Adjuvants- Picture courtesy: Bioprocess International
These are the ingredients that are employed to enhance immunity in response to antigen and that’s why less antigen material is needed. They boost the potency of the vaccine and with adjuvants, you generally require smaller doses of vaccine. However, normally flu vaccines don’t have adjuvants unless stated.
Stabilizers
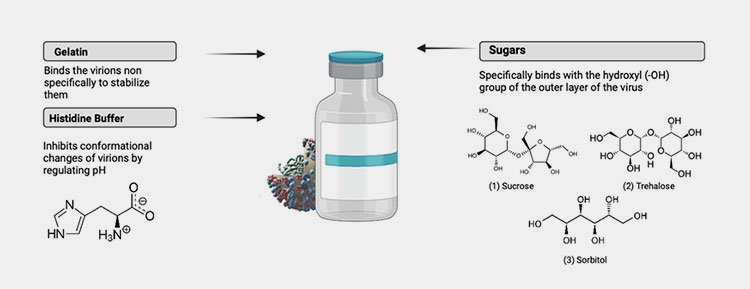
Stabilizer- Picture courtesy: MDPI
Flu vaccines are quite stable and are easily shipped across large distances. How is that possible? Well, flu vaccines have various kinds of stabilizers that aid in maintaining the stability of vaccines during their storage and shipment. Some common stabilizers examples in flu vaccines are table sugar, sorbitol (artificial sweetener), monosodium glutamate (MSG), histidine buffer, and gelatin.
Preservatives
Preservatives- Picture courtesy: Science
You’ll find preservatives in multi-dose vaccines to keep the latter safe from the growth of bacteria or viruses. For example, thimerosal (a mercury-containing compound) is found in very minute amounts in multiple administration vaccines. However, single-use vaccines don’t have thimerosal.
Manufacturing Trace Elements
Manufacturing Trace Elements- Picture courtesy: Health Engine Blog
Trace quantities of substances employed during flu vaccine production may remain in the final product. They might be egg protein, formaldehyde (inactivate virus or bacterial toxins), antibiotics, such as neomycin or kanamycin, emulsifiers, detergents, and salts (used for maintaining pH balance.
4.How do health sectors and patients benefit from flu vaccine production?
Beyond its massive financial returns for businesses, flu vaccine production has a positive contribution to the health sectors and the health of individuals. Because of the huge demand for flu vaccines all across the globe, many pharmaceutical and biotechnological manufacturers are creating their own formulations of flu vaccines.
Here we’re going to learn about various advantages of flu vaccine production to both health sectors and individual patients:
Eases Healthcare Demand

Eases Healthcare Demand- Picture courtesy: CIDRAP
In flu season, you’ll certainly hear about a high number of infected people, which pushes hospitals to their breaking point. However, flu vaccine production has a timely role in the formulation and distribution of vaccines before the flu outbreak, which helps in reducing the number of hospitalizations. This is because vaccinated people are less vulnerable to health complications needing urgent medical care.
Safeguards Sensitive Individuals
Safeguards Sensitive Individuals- Picture courtesy: University of Sydney
Every year flu vaccine production is customized to focus on particular viral strains that have higher chances of spreading around in the coming flu season. Hence with customized production, you’ll have targeted protection for kids below age 5, older people above 65 years, expecting mothers, and people with severe health problems (asthma, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases). These sensitive individuals are at greater risk for developing flu-related complications like pneumonia.
Lower Healthcare Costs

Lower Healthcare Costs- Picture courtesy: The Asutralian
With flu vaccine production, you can develop an efficient vaccine program that is effective in reducing the expenses of disease management. It does so by preventing long-term respiratory complications, minimizing hospital stays, and reducing medication use. It has been estimated that flu vaccines can save billions of dollars every year globally.
Increase Herd Immunity

Increase Herd Immunity- Picture courtesy: The ClearChain Health
Creation and mass distribution of flu vaccine because flu vaccine production aids in the prevention of virus transmission within the community. It is important because many people can’t receive flu shots owing to their age, allergies, or other underlying health problems. This mass vaccination creates a herd immunity in which unvaccinated people are indirectly protected against flu because the virus can’t spread from vaccinated individuals.
Lower Disruption in Routine Life
Lower Disruption in Routine Life- Picture courtesy: ABC News
Yes, you’ll probably be unable to attend school or work for at least one week if you catch the flu. Moreover, you are also at risk of transmitting the virus to others. But with the influenza vaccine, you’ll have a minimal chance of contracting the flu. Moreover, even if you develop flu, you’ll recover more quickly. This means less time away from your responsibilities, improved work quality, and a calmer household.
5.What are the primary steps that occur in flu vaccine production?

Flu Vaccine Production- Picture courtesy: RACGP
As you’ve guessed rightly, flu vaccine production is quite complicated, consisting of some advanced biotechnology techniques and pharmaceutical processes. Each of these stages is tightly regulated so that the final vaccine is safe and potent.
So, without delay, let’s walk through various stages occurring in flu vaccine production:
| Selection of Appropriate Strain | Due to the evolution of flu viruses, the vaccine produced in the last season is not effective for new strains. Thus, the WHO and national disease control centers work together to identify viral strains with the highest potential to circulate in the next flu season. Based on data, WHO recommends three or four influenza strains for vaccine production. |
| Viral Source Development | Now that target strains are selected, the next step is to develop a seed virus. This seed virus is a lab-synthetized virus with surface proteins, for instance, hemagglutinin and neuraminidase of selected flu strain. Also, this virus has a genetic makeup of virus that grows and reproduces more quickly in eggs or cells. After the creation of the viral strain, its safety is assessed by CDC or WHO collaborating centers. |
| Virus Culturing and Harvesting | It’s time to cultivate the seed virus, which is done on a large scale by manufacturers. Two main approaches- egg-based cultivation and cell-based culturing- are carried out for virus propagation.
When your desired quantity of seed virus is reproduced then fluid with the virus is gathered from egg or cell cultures. After that, you employ various filtration approaches to treat harvested fluid. In this way, it is free of egg-based debris or cell materials. |
| Virus Inactivation | After filtration, you’ll either inactivate or kill the viruses with chemicals. Sometimes, instead of inactivating the virus, it is weakened. This step results in the creation of viruses that don’t cause flu but can stimulate immune response. |
| Purification | After creating inactivated or attenuated viruses, you’ll clear out several impurities or contaminants, such as cellular proteins, viral debris, or chemicals. Diverse advanced procedures, for instance, centrifugation, membrane filtration, or chromatography are utilized to filter viral surface proteins, especially hemagglutinin (HA). The latter is the principal material that induces immunity. |
| Vaccine Preparation | As soon as you’ve purified your desired viral antigens, you need to mix them with different components, such as stabilizers, preservatives, adjuvants, and buffer solutions. For this, you require a fixed proportion of every ingredient material. Usually, a combination of three or four diverse HA antigens is blended to create trivalent or quadrivalent flu vaccines, respectively. |
| Filling and Packaging | After vaccine formulation, now comes the actual packaging step. For packaging vaccines, generally, you’ll use prefilled syringes, single-dose vials, or multi-dose vials. The filling and sealing steps are carried out in a sterile cleanroom environment, where there is no chance of contamination. After sealing, the packaging is labeled. |
| Quality Control Testing and Shipping | Then, each vaccine batch is stringently tested and its quality is assessed by various procedures, for example, sterility testing, potency assays, and purity inspections. Besides this, you’ll rigorously examine the safety of the product and ensure there are no endotoxins in vaccines.
Once, you get regulatory approval from the FDA or EMA, only then you can distribute and ship your vaccines for public use. For shipping and storage, always keep your vaccines at cold temperatures of 2–8°C. This aids in the prevention of vaccine spoilage. |
6.What machines are used in flu vaccine production?
Flu vaccine production is not possible without coordinated synchronization and precision of various equipment. These specialized systems have their own crucial role in every stage of flu vaccine production.
Here is a full list of vital machines found in flu vaccine production:
Bioreactors
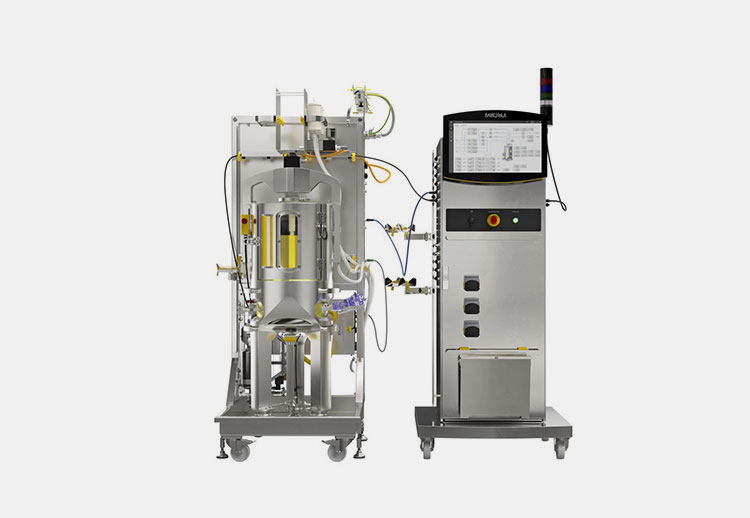

Bioreactor- Picture courtesy: Huck Institute
You can define this equipment as a vessel or system that is used for cultivating or sustaining biological cells or biochemically active substances. It mimics biologically active conditions like temperature, pH, and aeration to propagate mammalian or insect cells. This cell in turn produces viruses or generates viral proteins. It can be a stirred-tank bioreactor or a single-use bioreactor.
Virus Harvesting Systems

Virus Harvesting Systems- Picture courtesy: CEPI
As the name suggests, they’re the devices that isolate virus-containing allantoic fluid from eggs after specified incubation time. Generally, for harvesting, you can use egg decappers and suction devices. Their purpose is to amplify viral load and lower the chances of contamination.
Filtration System
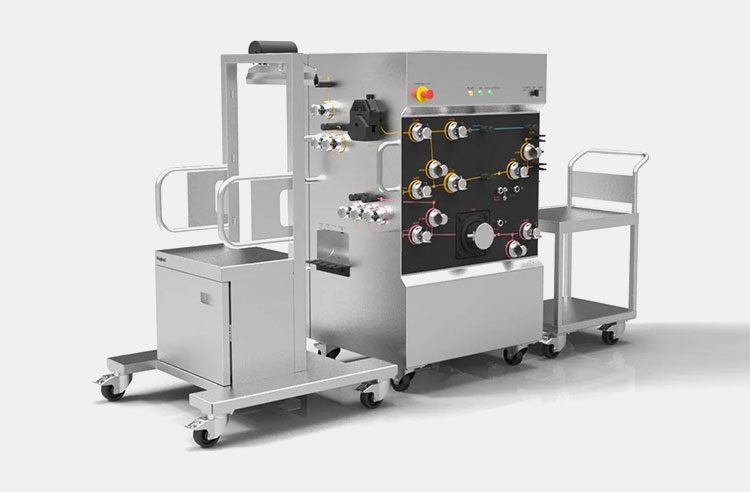

Filtration System- Picture courtesy: REUZEiT
As viral suspensions have a lot of egg products or cellular impurities, so in flu vaccine production, several types of filtration systems- for example, depth filters, microfilters, and ultrafilters- are used. They are integral in processing the viral fluids obtained from harvesting and extracting viral antigens and removing unwanted substances.
Chromatography Systems
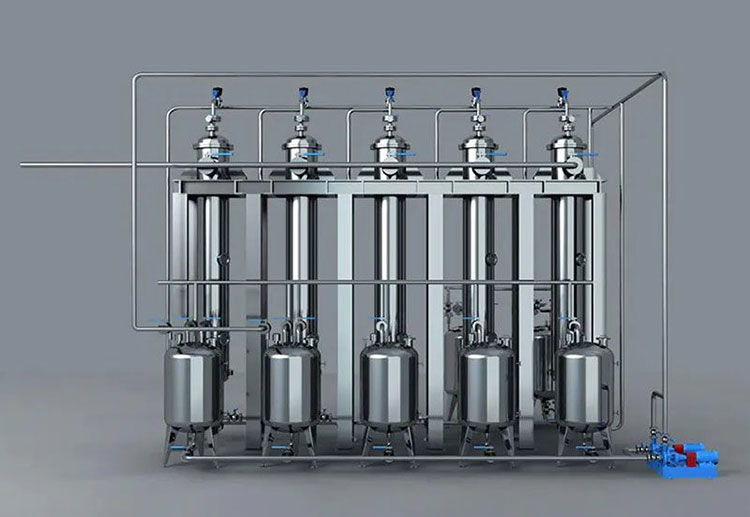

AIPAK ENGINEERING Chromatography Systems
As you know that usually flu vaccines are composed of viral proteins, particularly, hemagglutinin, so the latter must be separated from other viral components and proteins. For this, diverse chromatography systems, such as ion-exchange chromatography devices, column chromatography systems, and affinity chromatography are employed to filter out hemagglutinin on the basis of charge, size, and binding capability, respectively.
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer
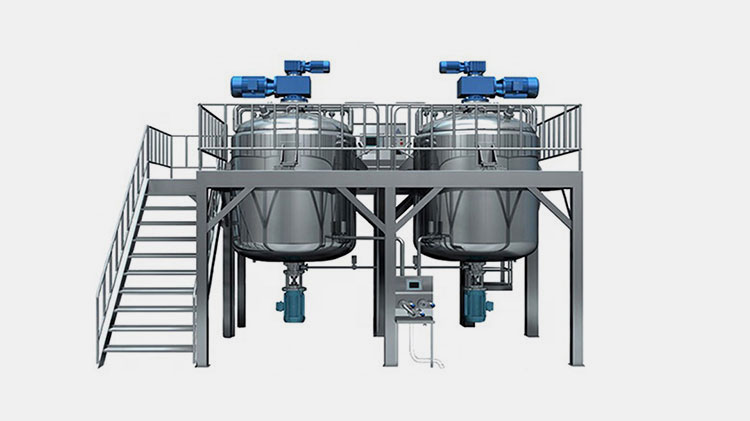

Vacuum emulsifying mixer plays pivotal in the uniform mixing of various ingredients, purified antigens, stabilizers, preservatives, and buffers. They are often gigantic tanks with different stirring and blending mechanisms to ascertain the thorough and even distribution of components within vaccine formulation under an enclosed system.
Quality Control Equipment
Quality test – Picture courtesy: Technology Network
A wide array of quality assessing instruments is used in the final stages of flu vaccine production to ensure the quality of the end product. For example, spectrophotometers, ELISA readers, PCR machines, pH meters, and, SRID machines are utilized for quantifying protein quantity, potency assessment, genetic testing, pH measurement, and identity investigation.
Aseptic Flu Vaccine Production Line

AIPAK ENGINEERING flu vaccine production line
As you are probably aware the sterile filling of flu vaccines is key to guarantee their safety. So, manufacturers employ aseptic filling systems, like vial filling and stoppering machines or pre-filled syringe filling devices to dispense the correct dose of formulated influenza vaccine in vials or syringes, respectively.
They work in a sterile environment and are integrated with a laminar airflow isolator. The production line is composed of vial washing machine, sterilization tunnel which helps in drying and sterilizing the filling material, unscrambler, filling, and sealing or a stoppering machine respectively.
Labeling and Packaging Systems
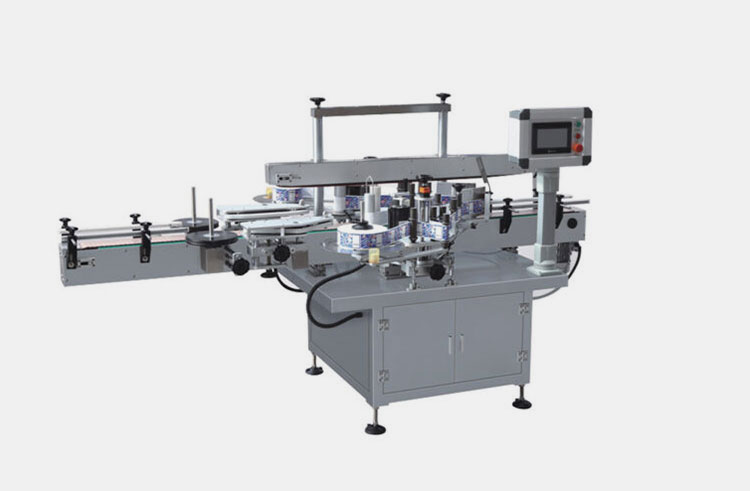

AIPAK Labeling Machine
Finally, after quality checking, labeling equipment puts information labels on syringes and vials. Lastly, your labeled flu vaccine containers are boxed, sealed, and stacked for distribution and storage.
7.What innovative technologies are used in flu vaccine production?
Flu vaccine production- Picture courtesy: NBC
However, egg-based flu vaccine production is still dominant even today. However, scientists have developed a wave of innovative technologies that are revolutionizing flu vaccine production. Hence, using these novel methods, you can get faster and more accurate outcomes. So, let’s take a closer look at these technologies:
| mRNA Platform | It is an advanced approach in which mRNA is used to provide cellular instructions for creating flu virus proteins, for example, hemagglutinin. mRNA acts as a template for cells and is followed for synthesizing flu vaccine antigens. One of the main benefits of this method is you can cut down manufacturing time by weeks instead of days.
Also, you don’t need an actual virus seed for creating antigens. Lastly, this procedure is easily modified if a new flu viral variety evolves. |
| Reverse Genetics | It creates a live-attenuated flu vaccine with the change of viral genome. In this technique, genetic fragments from different viruses are combined to make influenza vaccine. This results in lower disease-causing ability of viruses; however, they reproduce quickly to initiate an immune response.
It shortens the timing of creating vaccines and generates a vaccine candidate that provides increased protection and is safe to administrate. |
| Recombinant DNA Technology | It is the latest approach for synthesizing flu antigens by placing the said genes into baculoviruses. Subsequently, these viruses then go on to infect insect cells. This technology makes it unnecessary to propagate the whole virus, that’s why, only particular antigen proteins are generated.
This method is great for producing an egg-free flu vaccine that is suitable for egg-allergic patients. |
8.How viral strains are selected in flu vaccine production?
Flu vaccine production strains- Picture courtesy: Penn Medicine
For selecting viral strains in flu vaccine production, WHO’s Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS) gathers to collect and study several thousands of influenza virus specimens taken from infected individuals worldwide.
The virologists at these centers analyze mutation (tiny genetic changes) patterns, epidemiological data, and contagiousness and transmission rate of new viral variants. These strain selection meetings are held twice every year. Based on studied information, 3-4 strains are selected for flu vaccine production.
9.How long does it take flu vaccine to develop in flu vaccine production?

Flu vaccine production time- Picture courtesy: CYTIVA
Flu vaccine production is a tightly controlled and highly-synchronized operation that takes approximately 6-8 months to synthesize flu vaccine. Every year, starting in February, scientists at the World Health Organization (WHO) and other health agencies select and recommend strains for vaccine preparation.
Afterward, around March to May, pharmaceutical firms cultivate and grow viruses using diverse approaches. These propagation steps last for several months. Then from May to June viruses are inactivated, weakened, and purified.
Vaccine preparation and filling steps usually happen from June to July. After that, quality control, testing, and distribution steps take place from July to September.
10.Does flu vaccine production make different types of flu vaccines for different age groups?
Flu vaccine for population- Picture courtesy: Parents
Absolutely, yes! Flu vaccine production creates customized vaccines for various age groups and for individuals with various health conditions. In this manner, manufacturers can boost safety, immunity, and effectiveness.
For children from 6 to 36 months, a flu vaccine with smaller viral components is created. Because infants have delicate immune systems that are still being developed, therefore, they need a gentler vaccine dose of about 0.25 mL to 0.5 mL. On the other hand, 3 to 8-year-old children are administered nasal spray as the latter is less scary than injection but equally effective.
Flu vaccines mostly in inactivated or recombinant form are manufactured for adults aged 18-64 years. Older adults with 65+ age are injected with high doses of flu vaccine and are also immunized with adjuvant vaccines.
11.How does flu vaccine production differ from other vaccine manufacturing processes?
Flu vaccine production vs other vaccine- Picture courtesy: Johns Hopkins Bloom
The purpose of all vaccines is to trigger the body's defense system, which then identifies and neutralizes harmful pathogens. However, flu vaccine production is quite different than other vaccine manufacturing due to its exclusive characteristics and challenges. Here is a full breakdown of all the differences between these two manufacturing:
| Features | Flu Vaccine Production | Other Vaccine Manufacturing Processes |
| Seasonal Strain Choice | As the flu virus is constantly evolving this vaccine is updated every year to fight new viral strains. | On the other hand, other vaccines, for instance, MMR and Hepatitis B contain conversed protein antigens, so their one formulation provides immunity for several decades. |
| Time-Sensitive Production | Different disease-control centers chose flu viral targets approximately 6 months before the start of flu season. So, manufacturers will have tight and time-sensitive production windows. Because flu vaccines must be created and distributed before the outbreak of flu to prevent its transmission. | This manufacturing process has a longer production time because these vaccines are not linked to any particular time of year. |
| Egg-based Production | In flu vaccine production, mostly fertilized chicken eggs are still used for making flu vaccine. This process is more than 70 years old. | For synthesizing other vaccines, generally, cell cultures, recombinant DNA, or mRNA technologies are utilized. |
| Multitude of Formulations | Each year, you’ll have trivalent (targeting 3 viral variants) and quadrivalent (directed at 4 viral sub-types) versions of the flu vaccine. | In manufacturing other vaccines, the end products are intended to neutralize mostly one pathogen type. This process makes the same formulation every year. |
| Variable Potency | Since the flu virus quickly changes, so resultant influenza vaccine is only 40–60% effective. This effectiveness depends on the binding affinity between antibodies and viral strains. | Other vaccines offer long-term protection against pathogens and are mostly >90% effective. |
| Wastage Chance | As manufacturers have to prepare mass batches of flu vaccine within a brief duration, so if the demand for vaccine is low or viral strain in the vaccine and circulating viral type mismatches, then millions of doses would be wasted. | Other vaccines are stockpiled or stored after production to be used constantly for many years. |
12.What are some troubling challenges in flu vaccine production?
Indeed, flu vaccine production is full of challenges and even though it has been working as well-oiled machinery for many years, still you might have some problematic issues that can throw a wrench in operation.
So, let’s explore some main troubling challenges in flu vaccine production and learn about their practical solutions.
Viral Evolution

Viral strain- Picture courtesy: ABC News
You would’ve learned about virus biology and its rapid mutations. So, selecting a viral strain in advance might not correspond to one transmitted in a flu outbreak. This causes decreased vaccine response.
Solution
However, different innovative techniques are introduced to encounter this challenge. For example, now you have mRNA vaccine platforms that are easily adjusted to target new flu viral strains. Furthermore, universal flu vaccines are being developed that specifically attack conserved viral parts. This allows protection against multiple viral strains.
Nowadays, improved surveillance systems integrating AI technology and global viral databases are used to boost the prediction accuracy of flu virus types.
Mutation in flu Strains

Mutation- Picture courtesy: Al Jazeera
Viruses are prone to genetic alterations when they’re injected into chicken eggs. They generally change their genetic makeup to adapt to the egg environment. This in turn leads to alterations in vaccine antigen.
Solution
It is a very troubling issue but is easily resolved by growing viruses in mammalian-type cells. In this way, the antigen structure of the flu virus is conserved. Another approach to tackle this challenge is by producing desired viral antigens directly in insect cells via DNA cultivation approaches. This approach evades viruses completely.
Lengthy Production Duration
Lengthy Production Duration- Picture courtesy: The globe and mail
It is a significant problem, as production of flu vaccine is very slow and you can’t make last-minute changes in the vaccine.
Solution
To bypass this problem, advanced biotechnological methods, like mRNA platforms are adopted. This reduces month-long procedures to mere weeks. Also, currently, modular engineering plants are being developed with which you can alter production lines to combat evolving strains.
Conclusion
In summary, flu vaccine production is a powerful fusion of science, tactics, and, speed. This manufacturing is a very complicated process involving complicated steps, time-crunch approaches, global flu virus scrutiny, accurate strain selection, and the latest genetic and cellular approaches. It is a race against ever-changing viral genomics. Hopefully, after reading this blogpost, you would’ve got a complete knowhow about flu vaccine production. However, for your queries and purchase of machines related to flu vaccine manufacturing, get in touch with AIPAK Engineering. You can rely on us to deliver you high-quality machines for your projects.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours