Enzymes Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Have you ever heard about the term biological catalyst? Are you familiar with their definition or how do they work? If not- they’re small biological protein molecules called enzymes. Nowadays they’re used in quite a lot of industrial processes, like drug synthesis, food processing, textile treatment, and more.
Now you must be thinking- if they’re so important, how do manufacturers make them in their production plants? Does enzymes manufacturing require specialized machines or specific preparation conditions?
In this blog post “Enzymes Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025”, we’ll help you understand all the key aspects of enzymes manufacturing, for instance, its operational stages, equipment, conditions, etc. needed to prepare enzymes on a large scale. Let’s get ready for an informative ride!
1.What are enzymes?
Enzymes
Enzymes which is a protein known as catalysts that function in living beings. Like other chemical catalysts, they exist to accelerate the speed of reaction without being consumed themselves during chemical reactions. They’re used over and over.
In most cases, enzymes are basically proteins but RNA enzymes have also been discovered. The bodies of living organisms from the smallest bacteria to humans have enzymes to make biochemical processes occur at a quicker rate. These processes are breaking food substances, building cellular structures, assisting cell division, metabolizing drugs, and regulating muscle movement.
2.How can you define enzymes manufacturing?

Enzyme manufacturing- Picture courtesy: Creative Enzyme
Certainly, enzymes are made in living bodies naturally, but you can also synthesize them in industry using microbial, plant, or animal cell cultures. These small factories work under controlled conditions to prepare large quantities of functional and stable enzymes for you. This preparation of enzymes in industries is called enzymes manufacturing.
This systematic process involves a number of steps, like cell cultivation, fermentation, harvesting, purification, and, product preparation. Also, you should know that this manufacturing can’t proceed without sterile equipment and specific operating conditions.
3.Why do you need enzymes manufacturing?
Perhaps, you’re likely wondering why enzymes manufacturing is a big deal in industries. Well, the answer is very simple by making these proteins, you achieve unparalleled efficiency in production without negatively harming the environment and breaking the bank. Here are more details of benefits for those of you who’re interested:

Benefits of enzyme manufacturing- Picture courtesy: Creative Enzyme
| Works Faster and Better | One reason why enzyme manufacturing has become popular in industries is because they’re unbelievably powerful catalysts. This means that by using them, you can dramatically improve your reaction speed. As a result, you can lower your operational time and acquire high product yields. And the best part is they don’t get consumed in reaction, consequently could be used again. |
| Very Specific to Certain Reaction | No wonder a chemical catalyst can be used in many different reactions. Consequently, they create a lot more extra byproducts, needing various purification approaches to have purer products. However, with enzymes manufacturing, you can avoid these problems altogether because they only bind to particular molecules and catalyze specific reactions. In this manner, you’ll get a cleaner product with less waste, saving you headaches at the purification step. |
| More Cost Cutting | For many manufacturers operational cost and utility bills are major issues. So, they prefer to use enzymes, as they operate best under moderate temperatures and pressure. This is a big win because traditional catalysts usually need high temperatures or pressure to work. This consumes a lot of energy. So, with enzymes you can’t only save your time but also your money. |
| Greener Approach | Needless to say, with enzymes manufacturing, you could contribute heaps to current sustainability efforts. It is because for one- less energy is used to carry out operations involving enzymes. Another thing is that they minimize chemical waste more drastically than possible with chemicals. And lastly, they are recycled and biodegradable. So, all these points make your production more sustainable. |
4.Where are enzymes manufacturing mainly required?
Due to the countless benefits of enzymes manufacturing, you’ll certainly find its presence in almost every world industry. So, without delay, let’s detail some significant industrial uses of this manufacturing type:
Pharmaceutical Industry

Pharmaceutical Industry
No pharmaceutical industry exists without the utility of enzymes. Not only do they create drugs in the right way but they’re also used for purifying active substances from unwanted impurities. In some cases, you can utilize them to transform your desired drug. Also, you would be amazed to learn that enzymes also serve as key ingredients in many medicines.
Biotechnology Industry

Biotechnology industry- Picture courtesy: Iberdola
Besides being the lead industry involved in enzymes manufacturing, it also heavily relies on enzymes for making advances in research. You may have heard about the use of restriction enzymes, ligases, polymerases, etc. in genetic editing and modification to clone and create recombinant proteins, antigens, and DNA.
Medical Industry
Medical Industry- Picture courtesy: AMSBIO
Enzymes manufacturing also has a significant contribution to healthcare. Wondering how? Well, nowadays, enzymes are being employed as biosensors in diagnostics, like detecting glucose in blood or ELISA test kits. Furthermore, they’re also used in enzyme replacement therapies to treat cystic fibrosis, metabolic disorders, lactose intolerance, and remove dead tumors or tissues from the body.
Food Industry

Food Industry- Picture courtesy: Campden BRI
The uses of enzymes manufacturing are far and wide in the food industry. For producing common food products, enzymes often act as processing aids. For example, you can use them to extract juices from fruits, such as grapes. Tenderizing of meats, kneading of dough for bread, and generation of cheese and yogurt from milk are some of the chief applications of enzymes in food processing.
Chemical Industry

Chemical Industry
In the chemical industries, thousands of reactions happen daily to generate and transform diverse compounds. To make reactions faster, often you turn to enzymes manufacturing. Why? Because enzymes are the most effective catalysts on planet Earth with high specificity and eco-friendliness. That’s why, you see them in the preparation of agrochemicals, fragrances, artificial flavors, biopolymers, and other specialty chemicals.
Textile Industry

Textile
Don’t be surprised! You’re reading it right. Enzymes have also found their utility in the textile and detergent industry. With their help, you can soften your fabrics, improve the finishing of denim, remove fuzz from clothes, bleach or decolor materials, and remove stains from laundry.
Biofuel Industry

Biofuel Industry
Interested as to how enzymes manufacturing come into play in biofuel processing. Typically, enzymes break down materials so, they’re used to change biomass into sugar. In this way, ethanol is produced and used as an energy source.
Waste Management Industry
Waste Management- Picture courtesy: EMBL
Pollution has become the biggest problem of the modern era. To tackle this many governments and private waste management companies are now embracing enzymes for cleaner and smarter waste treatment alternatives. You can use enzyme manufacturing for breaking down organic matter, treating wastewater, and increasing bioremediation speed.
5.What are the major steps of enzymes manufacturing?
Perhaps, now you’re curious about the steps of commercial enzymes manufacturing. There is no doubt that enzyme production has come a long way in the past century. For your information, we’re penning details of the major steps of enzymes manufacturing below:
Selection of Desired Organism

Selection- Picture courtesy: Jordan Crowe
Enzymes manufacturing often begins with the search for the right organism that produces enzymes of the desired composition in required quantities in the shortest time possible. Often genetic modification is done to clone enzyme genes in the selected organisms. In most of the production lines, bacterial or fungal species are used for generating enzymes but in some cases, manufacturers might cultivate plant or animal cells for preparing required enzymes.
Upstream Operations

Upstream Processes of Enzymes Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Bio-Techne
| Media Preparation | Now that you’ve selected the strain and changed its genetic composition, the next step in enzymes manufacturing is to prepare media for the culturing and growth of organisms. Mostly you’ll need sugar and nitrogen compounds for media. Then, you simply load your media and organism cell in a fermentation tank. |
| Fermentation | In this step, cells are grown in large volumes to express enzymes. Two types of fermentation techniques are mostly utilized for enzyme manufacturing. In solid-state fermentation, you grow fungi on solid wet media with small quantities of free-flowing water. While, in submerged fermentation, microbes are cultivated in liquid media containing nutrients. |
| Harvesting | Once attaining the desired quantity of cells, your next step would be to harvest cultures by draining the fermenter tanks. |
Recovery Operations

Recovery Operations- Picture Courtesy: Evolve Ltd
| Cell Disruption | In recovery processes, the first step is often to disrupt microbial cell cultures to extract enzymes from inside the cells using chemicals or homogenizers. On the other hand, harsh disruption approaches like sonication or enzymatic lysis are used to digest cell walls and cell membranes of plant and animal cells. |
| Centrifugation | In order to separate enzymes from the rest of the liquid media, you’ve to use different techniques, such as centrifugation. It helps in fractionating substances based on their molecular weight. Heavier components settle in the bottle while lighter substances are present in the upper layers after centrifugation. Consequently, you’ll be able to filter out heavier impurities, like cell debris, unbroken cells, or other solid particles. |
| Filtration | The clarified liquid obtained from the centrifugation step is further purified by filtration techniques. They remove DNA, unwanted waste, impurities, cell wall fragments, and proteins that are still found in this clarified broth. |
| Chromatography | Certainly, it is considered one of the chief purification steps when it comes to enzymes manufacturing. Using various types (size, net charge, polarity, or binding affinity) of chromatography columns allows you ease in isolating your specific enzymes from the huge array of proteins. As the liquid broth travels through columns various mixture components flow at different speeds depending upon their interaction with resin material. |
| Enzyme Concentration | Once you’ve purified the enzyme, your next step would be to increase its concentration in solvent. You can do this by clearing out surplus water and other solvents. |
Formulation
Enzyme Formulation- Picture Courtesy: The Conversation
After the completion of downstream processing, now enzyme formulation is prepared. Typically, enzymes are stabilized using preservatives and stabilizers like ascorbic acid. Also, diluents are included in preparation to standardize enzyme activity. In some cases, carrier agents are also added to facilitate enzyme use by lowering enzyme powder sticking and clumping.
In industrial operations, enzymes are mostly used as liquid concentrates. But to increase their stability for storage and transportation, they’re often converted into powder using spray-drying or freeze-drying. Sometimes, enzyme granules are also formed by the agglomeration of powder.
Filling & Sealing
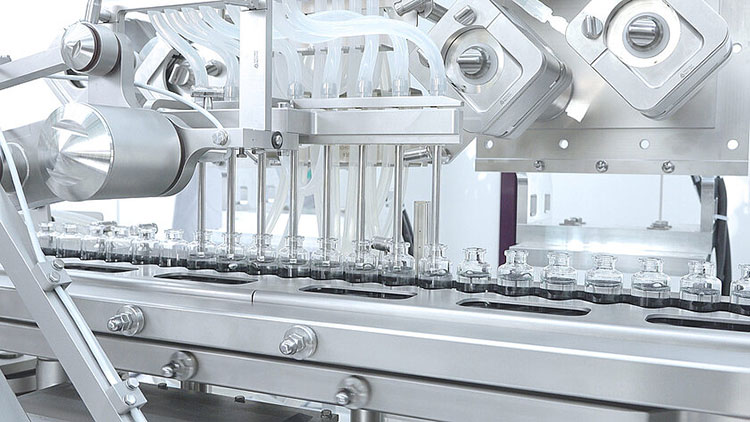

Vial Filling- Picture Courtesy: Groninger
Seeing as the enzyme formulation is achieved in the above step, you can start the filling step. Normally, you can employ precise filling machines at this step and dispense enzyme preparation in various containers, bottles, pouches, drums, or vials. Subsequently, sealing devices secure the opening of containers by adding caps, stoppers, or other types of closures.
Labeling & Cartoning
Labeling- Picture Courtesy: Avantor
Finally, labels are affixed on sealed enzyme packaging to inform users about essential product information. In the end, your containers are safely stored in cartons made using paperboard or cardboard materials.
6.What kinds of enzymes can you make from enzymes manufacturing?
A variety of enzymes can be produced from enzymes manufacturing, such as:
| Oxidoreductase | As the name suggests, these enzymes are involved in oxidation-reduction reactions in which the transfer of electrons occurs. These include glucose oxidase which is used in baking or food packaging to remove oxygen from containers. | 
Food grade glucose oxidase enzymes for baking |
| Hydrolases | Are you aware that these are the most common enzyme types made from enzymes manufacturing? They carry out the breakdown of larger compounds with the addition of water. They include proteases, amylases, and cellulates that catabolize proteins, starch, and cellulose, respectively. | 
Hydrolase |
| Transferases | Shift functional groups from one molecule to another. Transglutaminases enhance the texture of meat and dairy products by joining proteins in them. | 
Transglutaminase enzymes |
| Lyses | Spilt the bonding between compounds without the use of water or redox reactions. Mostly creates new molecules by forming double bonds. Asparaginase is their ideal example and is utilized for cancer treatment and the creation of baked goods. | 
Asparaginase -anti cancer manufacturer |
| Isomerases | Arrange the configuration of atoms within the same molecules to form isomers. One of its key subtypes glucose isomerases is utilized in the manufacturing of high-fructose corn syrup. | 
High-fructose corn syrup- health impacts |
| Ligases | Act as a molecular glue by joining two separate molecules with the help of ATP energy. | 
Molecular glues are shaping drug development |
7.Can you give an explanation of systems used in enzymes manufacturing?
As you would expect enzymes manufacturing is not possible with a single device. Rather a diverse array of machines are used to purify, process, and pack your enzyme formulation. If you’re interested in knowing its various systems, read the following section:
Bioreactors
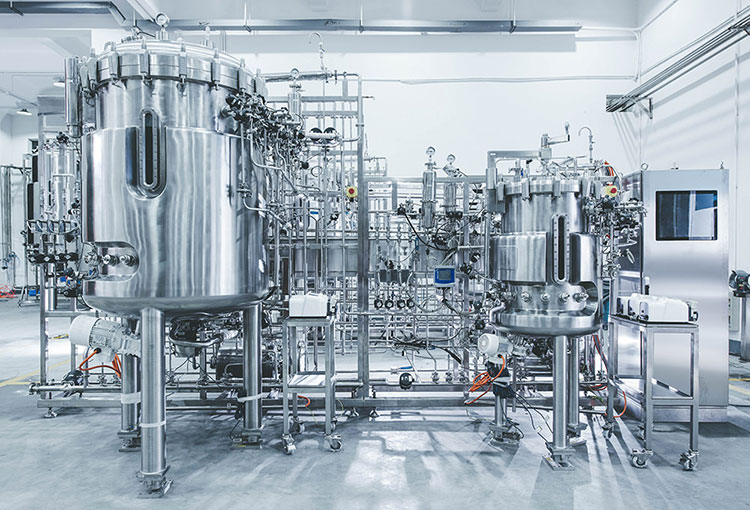

Fermenters- Picture Courtesy: BIOTOP
You’re right! Fermentation is impossible without bioreactors. These are devices where you grow your selected cells to generate enzymes. Usually, they are the core vessels consisting of large stainless-steel tanks. And often can hold a few liters to a hundred thousand liters of media. For mixing cells and nutrient media, impellers or stirrers are also present in the bioreactors.
Cell Disruption Systems

High-Pressure Homogenizers- Picture Courtesy: LEWA
Mostly utilized in scenarios when you’re dealing with intracellular enzymes. Cell walls or cell membranes are broken open using these systems. In this way, the enzymes expressed inside the cell are released in the solution. High-pressure homogenizers are the more common cell disruption devices seen in enzyme manufacturing.
Water Treatment Plant
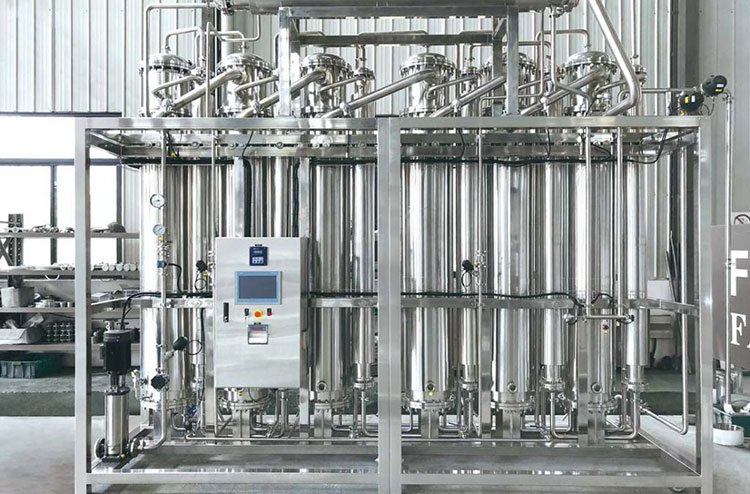

AIPAK Engineering Water Distiller
To prepare the formulation, you will always require water medium for various steps. In this way a water treatment plant must be installed in facility to bring pure and sterile water. The system ensure that water is passed through multiple levels of sterility including level 3 centrifugal separation. This ultimately gives clear and clean water suitable for processing the manufacturing protocols.
Centrifuge Device
Centrifuge Device- Picture Courtesy: Moglix
Mainly a clarification device. Quite useful in removing bulk contaminants, larger impurities, and unwanted debris from enzyme solutions. Sedimentation of particles occurs based on their densities after spinning at high RPM.
Filtration Devices
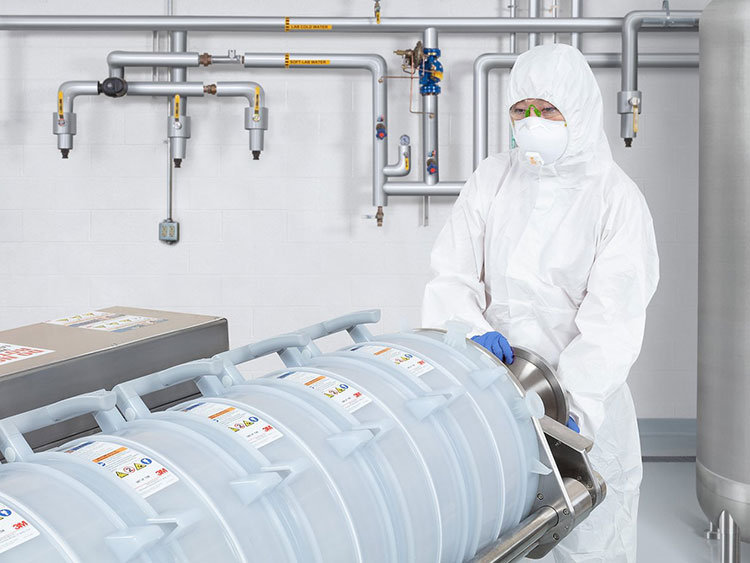

Depth Filters- Picture Courtesy: Solventum
In these systems, different forms of filter media are utilized for removing suspended impurities from your fermentation liquid. Depth, ultra, and, microfiltration systems are used for filtration. Depth filters are generally used to capture larger particles, whereas, microfilters are best for filtering fine cell materials and proteins.
Chromatography Columns
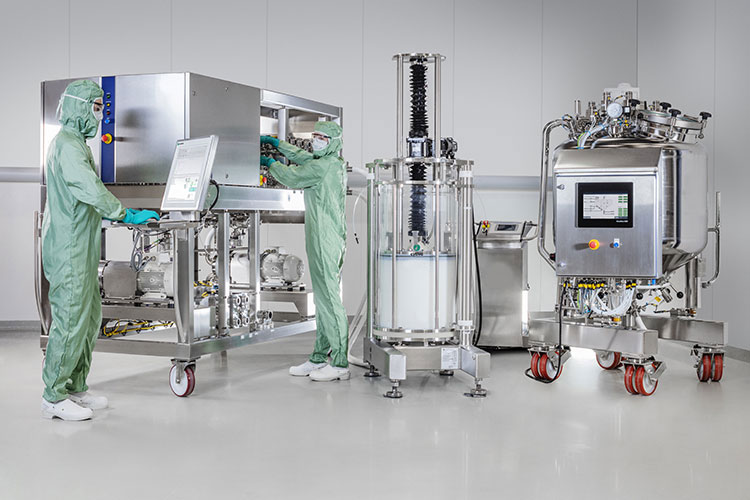

Chromatography Columns- Picture Courtesy: The Chemical Engineer
To obtain higher levels of purified enzymes, you can employ chromatography devices in your enzymes manufacturing. Think of them as specialized columns packed with resin beads. Each is designed to interact with molecules in solution in a specific way. They also have pumps that are integral in moving enzyme solution down the column.
Concentration Equipment
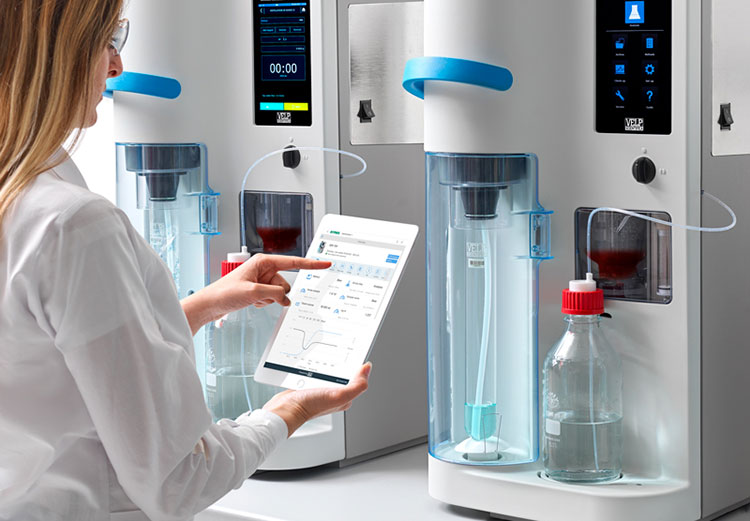

Concentrator- Picture courtesy: VELP
In many instances, the concentration of enzymes is very little, which can’t offer the right effectiveness. What should you do in this case? With the help of concertation equipment like ultra-filtration systems or vacuum evaporator concentrators, you can increase the quantity of enzymes in solutions. Semi-permeable membranes or evaporation are utilized to remove water and other solutes, such as salt from enzymes, thus, concentrating its solution.
Drying System
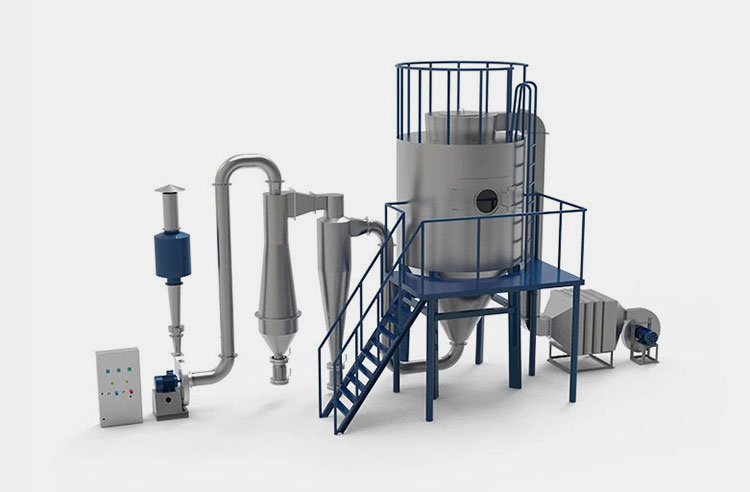

AIPAK Engineering Centrifugal Spray Dryer
To boost the stability of enzyme preparation, you’ve to change them into a powdery or granular state. For this purpose, you can use spray dryers, lyophilizers, and, fluid bed granulators. The liquid is evaporated using heating conditions and a vacuum in these instruments, which leaves behind dry enzymes.
While, in fluid bed granulators, enzyme powder is suspended via air inside the granulating chamber. Simultaneously, binding liquid is sprayed onto powders, which leads to their agglomeration.
Vial Filling Line

AIPAK Engineering Vial Filling Line
When it comes to enzyme packaging, the vial filling line is generally regarded as the core component. You would be surprised to learn that this system is not just one machine but several units integrated together to attain precise filling and sealing of vials. These units are:
Washing System
Vital component, as it clears impurities both from the surface and interior of vials. After the unscrambling unit, the washing system processes vials by spraying high-pressure jets or striking ultrasonic waves on them, which rinse them and dislodge particles sticking to them.
Sterilization Tunnel
Once vials are washed, they’re moved to the sterilization tunnel. Where hot air and heat are used to kill any remaining microbes on vials. Not only does it remove microbes but also destroys their byproducts, for example, spores or toxins present on and in vials.
Filling & Stoppering Device
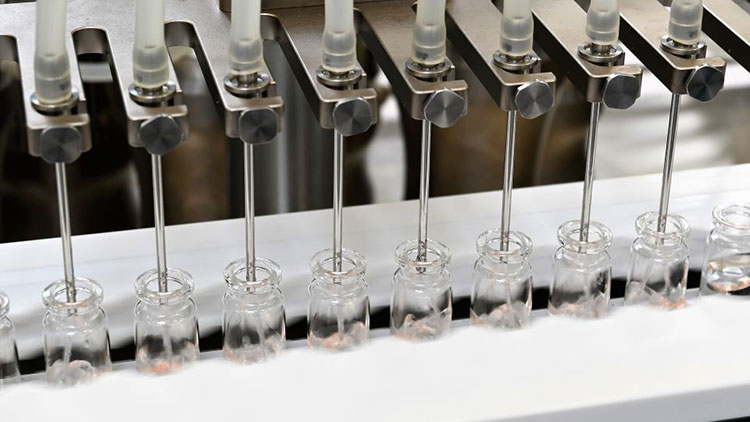

Filling and stoppering unit
It is the central system in the vial filling line. Its task is to load accurate quantities of enzymes in vials. For this, it uses filling pumps, pistons, as well as weight-checking sensors to prevent over- and under-filling. Lastly, the stoppering unit adds a stopper on vials to close and seal them.
Labeling Unit
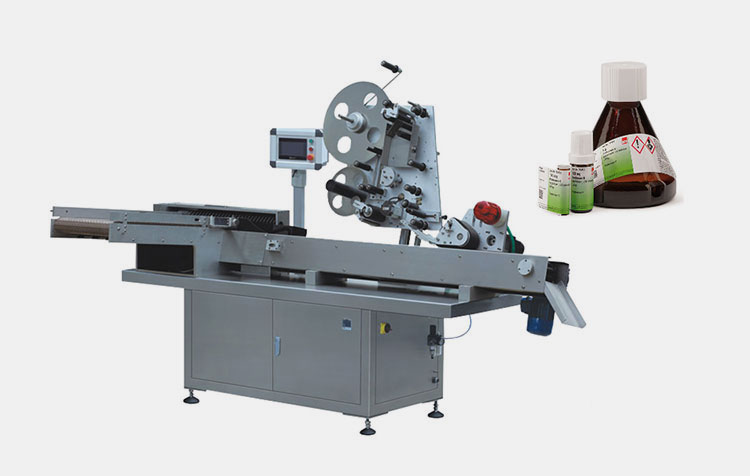

AIPAK Labeling Unit
Labeling is key to notifying users about the product. So, you can’t find even a single vial without labeling. That’s why you see labeling machine in your manufacturing plants. Its job is to stick labels using pre-adhesive labels on vials or other containers. Some of its kind also apply hot-met or wet glue to labels to bond them with vials.
Cartoner
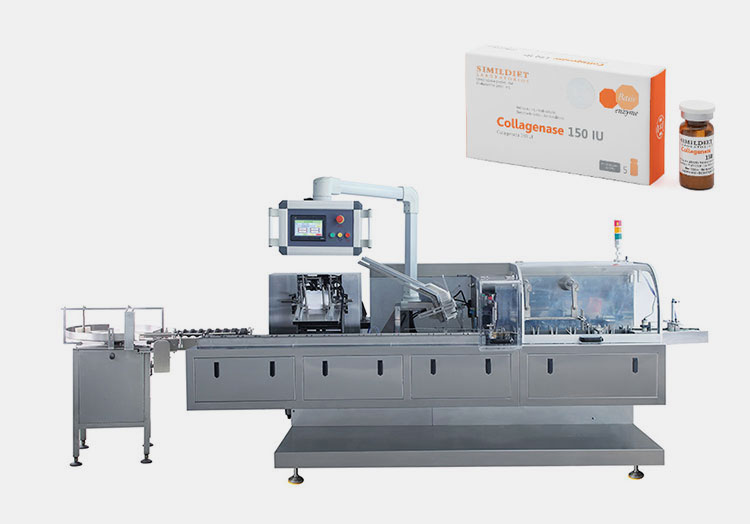

AIPAK Cartoner
A cartoning or cartoner is used for boxing of your enzyme containers. Yes, it has various carton gripping, erecting, folding, container loading, and sealing stations to pack containers in durable cartons. Now your cartons are ready for shipment.
Pharmaceutical Autoclave
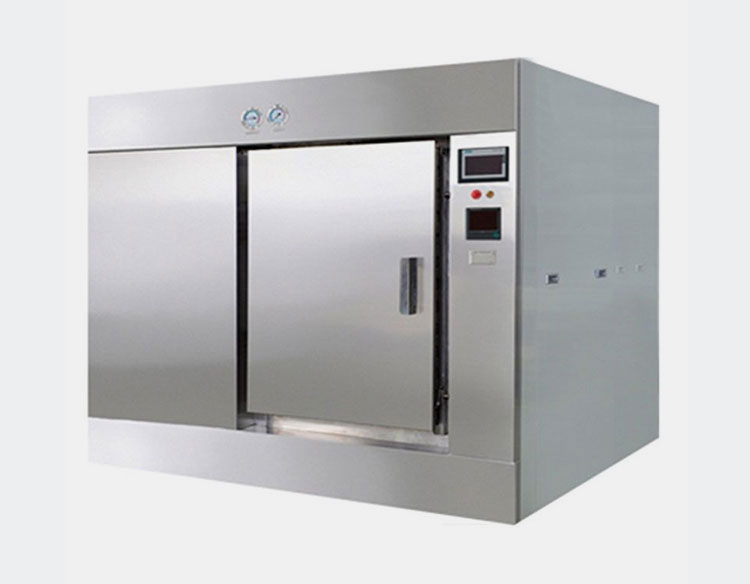

AIPAK Engineering Pharmaceutical Autoclave
The pharmaceutical autoclave is responsible for sterilization of prepared enzyme using temperature scale of 80 till 126℃. This limitation is considered as ideal for decline the presence of microbial content if present in the formulation or surrounding the packaging material such as vials. This machine utilizes temperature, vacuum and high pressure to make the product sterile and safe.
8.Are there certain environmental conditions (temperature, pH, moisture) for enzymes manufacturing?

Environmental Conditions for Enzymes Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Biocatalyst
In short answer? Yes. Enzymes are very picky molecules to produce. Their manufacturing demands that the production environment must be right. Some of the right environmental conditions for enzymes manufacturing are discussed below:
| Temperature | Like other proteins, enzymes perform well at moderate temperatures of about 30-40°C. However, if you increase the temperature beyond that, your enzymes will get damaged. And if the temperature is decreased below the above range, you’ll see enzymes becoming slow and inactive. |
| Moisture | When carrying out solid-state fermentation, the liquid level in tanks should be around 60-70%. While in submerged or liquid fermentation, water is the main medium component, still, you should maintain its right ratio in tanks to prevent foaming or viscosity problems. |
| pH | Right pH means the flawless working of enzymes. Definitely, they will stop working, if they face too high or too low pH. Bacterial enzymes often favor an environment with a pH of 6.5 to 8. Contrary, fungal enzymes exhibit optimal activity on pH conditions of 4.5-6.5. |
| Air | For the culturing of aerobic bacteria optimal supply of oxygen is essential. |
9.Can you differentiate between intracellular and extracellular enzymes manufacturing?

Enzymes Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Amano Enzyme
Both intracellular and extracellular enzymes are made by enzymes manufacturing. However, you may find it shocking that both these manufacturing vastly differ from each other on the basis of enzyme extraction and purification. Some of their key differences are found in the table below:
| Aspects | Intracellular Enzymes Manufacturing | Extracellular Enzymes Manufacturing |
| Location | These are expressed by microbial cells and after that, they remain inside cells. | After their production, they’re secreted into the fermentation medium. |
| Extraction | Typically needs an extra step of cell disruption to disrupt cells so that they release their enzyme products. | Quite easily extracted from fermentation liquid without using cell-breaking approaches. |
| Purification | A bit more complicated owing to the presence of smaller and larger cell debris, waste, and other intracellular components. | Very simple and cost-cutting purification steps. |
| Product Examples | Catalase, transaminase | Amylase, cellulase |
| Organism | Often utilize organisms that are genetically changed to overexpress the desired enzyme. | Use microbes that naturally secrete enzymes, for example, Aspergillus, Bacillus, and others. |
10.What should be the storage for products formed by enzymes manufacturing?

Enzymes manufacturing
You certainly won’t want to lose the functioning of enzymes, once you’ve gone through all the time-consuming and complicated processes of making and purifying them. So, your main objective is to properly store them- right? Some storage tips are described in the following section to help you improve the shelf-life and performance of enzymes:
| Enzyme Forms | Storing Guidelines |
| Liquid Solution | As it is a very sensitive enzyme formulation type, so, you must keep it in your refrigerators at a temperature of 4°C. Preservatives must be included in these solutions to stop microbes from growing. Many people perform repeated freeze-thaw cycles; however, it is not safe to do so. As this causes decrease in enzyme catalytic ability. |
| Dry Powders | Absolutely, dry enzyme powders are more tolerant to changes in their environment, hence, you can store them at room temperature (15–25°C). Bear in mind that your storage place must be cool and have low humidity. Why? Because moisture is a sneaky culprit that ruins your powders. |
| Granules or Tablets | Simply, place them in settings that are out of reach of sunlight and heat. Also, for their storage, you should use moisture-proof containers. |
11.What are the major problems encountered when running enzymes manufacturing?
While being a fruitful venture, enzymes manufacturing- just like other industrial operations- is a complex feat full of challenging hurdles. These problems can happen at any step of production but you can easily encounter them with proper planning and training. So, for your information, some of the frequent issues along with their solutions are explained below:
Foaming in Bioreactors

Industrial enzymes- Picture Courtesy: AMANO Enzymes
Have you ever noticed excessive foam formation in your bioreactor tanks? It could be due to microbial growth and activity during fermentation. This may cut down oxygen flow in tanks and may also result in their overflow.
Solutions
To get around this issue, here is what you can do: first you can use pharmaceutical or food-grade antifoaming agents in your tanks to put a stop to foam formation without damaging cells in any way. Also, you may install foam sensors in your systems and connect the sensors to automatic antifoam units. The foam production can also be reduced by changing airflow and impeller speed as well as the design of bioreactors.
Inactivation of Enzymes

Activation and Inactivation of enzymes reactions
Well as you are probably aware enzymes are proteins and therefore very delicate in nature. Extreme chemical or physical changes in the environment may lead to the loss of their structural composition, denaturing, and inactivation.
Solutions
Although it is a very serious problem, however, there are some easy fixes for it. Such as buffers or stabilizers could be included during preparation to safeguard enzymes from harsh conditions. Moreover, make sure to maintain mild conditions of temperature and pH so that enzymes remain stable. It is recommended to use gentle drying approaches, such as spray drying or freeze-drying.
Enzyme Clumping Together
Enzymes sticking together
Yes, certain enzyme products have a tendency to stick together, resulting in their agglomeration during purification steps or storage.
Solutions
Don’t worry, you can tackle this issue with the use of stabilizers, for example, trehalose, glycerol, or mild surfactants in formulation. Secondly, buffers included in your preparation should have accurate pH and salt concentration. Last but not least, keep in mind to store enzymes in chilly settings.
Ineffective Drying

Enzymes Drying- Picture Courtesy: Tou Food
Sometimes, your drying procedures make enzymes inactive due to high-temperature inputs. In addition, desiccation may cause a reduction in enzyme performance.
Solutions
The following suggestions will help you to remedy this problem: fine-tune the inlet and outlet temperatures of your drying systems to limit heat exposure. The inclusion of protective agents, such as sugars protects enzymes during drying. Lastly, it is best to consider freeze-drying for heat-liable enzymes.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve reached the end of this FAQ guide, surely, you’ve learned about what, why, how, and when of enzymes manufacturing by reading this guide. But remember that enzyme manufacturing isn’t just about concocting proteins in tanks, it’s also about creating cleaner, safer, greener, and, faster solutions for many industries around the world. Have more questions about enzymes manufacturing on your mind? Or maybe you’re ready to invest in equipment for your own enzyme production. Either way, we’re here for it! Contact AIPAK ENGINEERING today. Our expert team is always on standby to help you bring your production line to life.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours