Emulsion in Pharmaceutics: The Complete FAQ Guide in 2025
Has this question ever come to your mind how do your favorite creams remain smooth or how do dispersion dosage form remain stable? It is noteworthy that the solution to overcome the drug delivery challenges lies in mixing two liquids that seem immiscible with each other.
This is possible due to emulsion in pharmaceutics. It has taken charge of skincare products and newly developed pharmaceutical formulations to provide stable formulations of immiscible liquid ingredients. So, how does it work, and its application?
This study will ferret out the emulsions in pharmaceutics and every possible question that needs to be answered. We’ll discuss the method of preparation, challenges, and innovations that make them a vital part of modern healthcare. Further, we’ll get an insight into the differences between an emulsion in pharmaceutics and other liquid dosage forms.
1.What’s an emulsion in pharmaceutics?

Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Rheonics
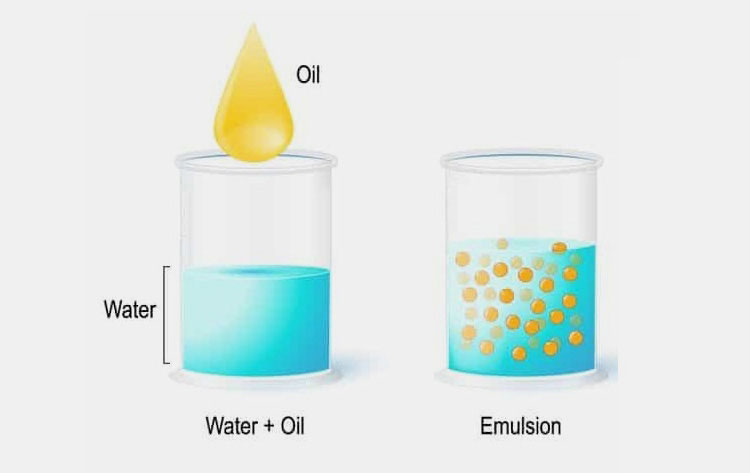
It’s quite obvious that water and oil are two liquids that never combine in normal circumstances. But emulsion in pharmaceutics is an exceptional biphasic liquid dosage form in which at least two immiscible liquids such as water and oil can be miscible.
The emulsion in pharmaceutics is a thermodynamically unstable formulation. Where one liquid forms tiny globules (internal/discontinuous phase) that are distributed throughout the second liquid which is the dispersion medium (external/continuous phase).
When it is lately developed, the dispersed phase is almost uniformly distributed in the dispersion medium. The formulation of emulsion in pharmaceutics incorporates emulsifying agents and provides mechanical agitation to stabilize the emulsion in pharmaceutics.
2.How do emulsions in pharmaceutics differ from a solution?

Emulsion VS Solution- Picture Courtesy: Carolina
The emulsion in pharmaceutics and the solution are both considered liquid dosage forms in pharmaceutical sciences but are entirely different in many aspects. Let's dive into the key differences.
Compatibility

Immiscible Liquids- Picture Courtesy: SciencephotoGallery
The emulsion in pharmaceutics is a mixture of two immiscible or partially miscible liquids i.e. dispersed phase and dispersion medium. For instance, oil and water. Whereas solution is formulated by completely miscible components i.e. solute and solvent. Such as alcohol and water.
Visual Attributes

Cloudy Appearance of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Biosmart
The emulsion in pharmaceutics has a cloudy appearance as the globules in dispersed phase scatter light. The diluted one may appear as bluish. On the other hand, the solutions appeared as transparent and homogenous, whereas solutes in solvent don’t scatter light.
Droplets size

Droplet Size Dimensions
The emulsion in pharmaceutics contains dispersed globules of larger size that form a dispersed phase. However, the solute in a solution is molecular size and comparatively smaller than droplets of emulsion.
Stability

Stability of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Borregaard
The formulation of emulsion in pharmaceutics always needed an emulsifying agent to stabilize the dispersed globules moreover to defend against separation or settling of the globules in the long run.
On the contrary, the solute of the solution is so uniformly distributed in the solvent that it doesn't settle down over time.
Phases

Biphasic System- Picture Courtesy: The Pharmaceutical Education
The emulsion in pharmaceutics is a biphasic dosage form having two discrete liquid phases dispersed in each other. Alternatively, the solution has a single phase formed by miscible substances i.e. solute dissolved in a solvent.
3.How do you differentiate between emulsion in pharmaceutics and suspension?

Emulsion in Pharmaceutics VS Suspension- Picture Courtesy: Cape Crystal Brands
The emulsion in pharmaceutics and suspension both have a dispersion system. Despite that, they significantly differ from each other in many respects. A clear understanding of the differences is key to the successful development of a drug delivery system. Let’s confer further about it:
Appearance

Cloudy Suspension- Picture Courtesy: Science Source
Emulsion in pharmaceutics have a cloudy or milky appearance due to the dispersed liquid droplets which scatter light. On the other hand, the suspension has an opaque appearance due to the dispersed insoluble solid particles but they don’t scatter light.
Droplets size

Microscopic Liquid Droplets- Picture Courtesy: Borregaard
The emulsion in pharmaceutics usually has smaller tiny droplets in dispersed passed as compared to suspension where the particles are larger. The droplets of emulsion in pharmaceutics are microscopic and usually not visible to the naked eye.
On the contrary, in suspension, the dispersed solid particles are visible to the naked eye or can be seen after slight magnification.
Phases

Phases of Emulsion- Picture Courtesy: Particle Technology Lab
Both the emulsion in pharmaceutics and suspension have two phases but the difference is in the type of substances the phases are composed of. In the case of emulsion in pharmaceutics, the two phases are always two immiscible liquids.
But in suspension, the two phases can be formed by two different immiscible substances i.e. solid, liquid, or gas.
Phases separation

Separation of Phases- Picture Courtesy: Shutter Stock
The two liquid phases of emulsion in pharmaceutics usually don’t separate over time and require specific techniques for the separation of phases. The emulsion in pharmaceutics is more stable due to the incorporation of emulsifying agents.
In the case of suspension sedimentation of the dispersed solid particles happens if left undisturbed. The solid particles of suspension are unstable and tend to aggregate or settle down.
Stabilization

Emulsion in Pharmaceutics Stabilization- Picture Courtesy: Food Crumbles
The emulsion in pharmaceutics uses emulsifying agents in its formulation. This addition provides stability to it. In contrast, suspension has temporary stability, achieved through external agitation. Therefore, phases separate quickly when left undisturbed.
4.What is meant by emulsifiers? What is its purpose in the development of emulsion in pharmaceutics?
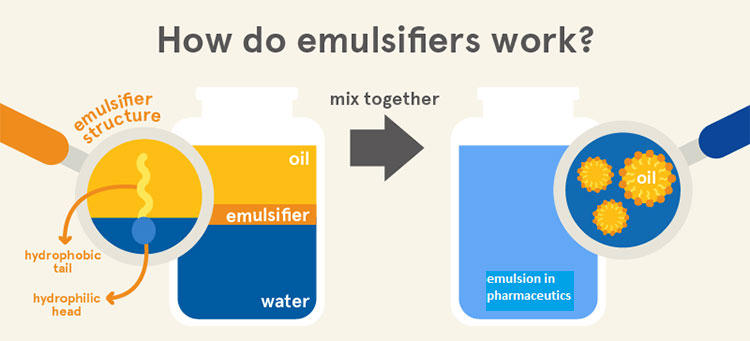
Principle of Emulsifiers- Picture Courtesy: Eufic
When we try to mix oil and water, they’ll never mix. If we provide mechanical agitation, they’ll mix temporarily. When the formulation is left undisturbed, the phases will separate eventually. Here we need an emulsifier for mixing these two immiscible liquids. The emulsifier has two parts:
- Hydrophilic head (water-loving).
- Lipophilic/ hydrophobic tail (oil-loving).
During the formulation of emulsion in pharmaceutics, the interfacial layer has formed (where two immiscible liquids separate). At this point, we incorporate an emulsifier. Its molecules adsorb themselves at the interfacial layer in this fashion, the hydrophilic end faces the water phase and its hydrophobic end faces the oil phase of emulsion in pharmaceutics.
By doing so, the emulsifiers reduce the tension of the interfacial system. As well as stabilize the formulation through homogenous dispersion of water and oil. This whole mechanism of emulsifiers is significant in preventing the separation of two phases providing smooth formulations.
- Some classic examples of emulsifiers are:
- Soy proteins
- Gum acacia
- Xanthan gum
- Gelatin
5.What are the possible advantages of emulsion in pharmaceutics as drug delivery system?
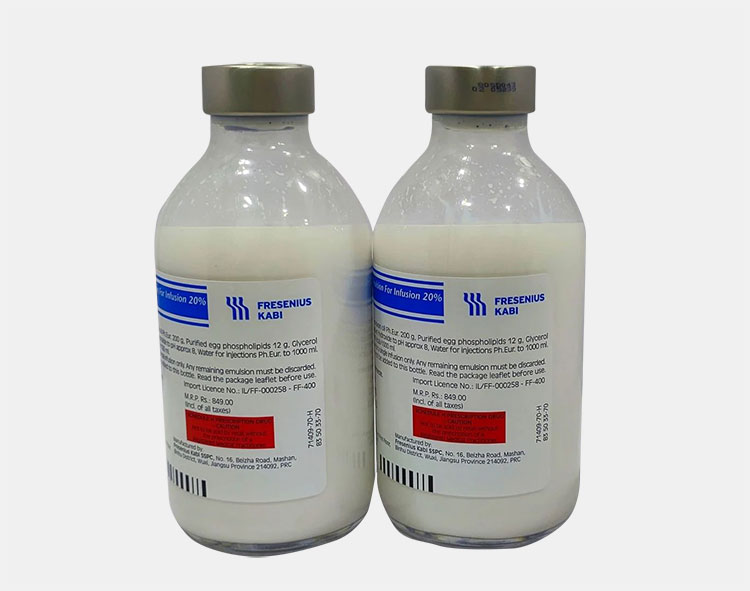

Fat Emulsion in Pharmaceutics
The emulsion in pharmaceutics has numerous applications in oral, rectal, and topical delivery of oil and oil-soluble drugs. Let's discuss each one by one.
Taste Masking of Oral Dosage Forms
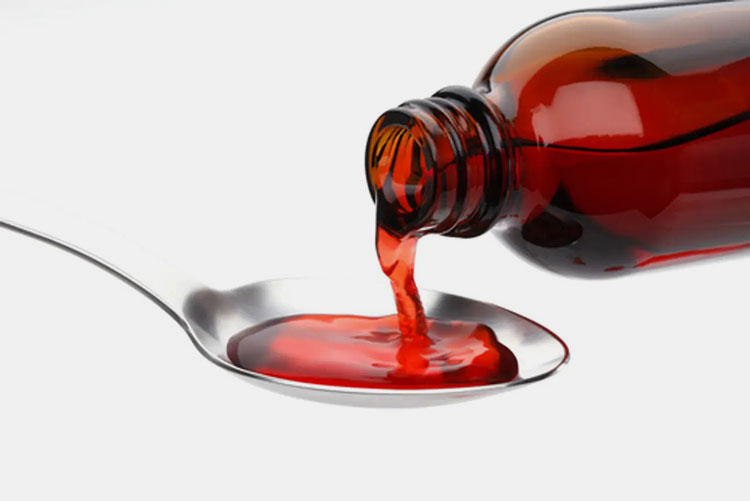

Taste Masking
It helps mask the unpleasant taste of active pharmaceutical ingredients. By incorporating it into the internal oil phase and adding sweeteners in the external water phase.
Drug Carrier for Low Aqueous Soluble Drugs

Enhanced Solubility
It helps deliver the drug with low aqueous solubility. The drug is absorbed easily in the body by dissolving it in the internal oil phase.
Enhanced Bioavailability and Absorption

Improves Drug Absorption
It improves the absorption and penetration of active ingredients. The globule size is relatively small, giving faster absorption and penetration.
Enhanced drug absorption increases the concentration of the drug in plasma for effective pharmacological action. Hence, improving the bioavailability of the drug.
Total Parenteral Nutrition
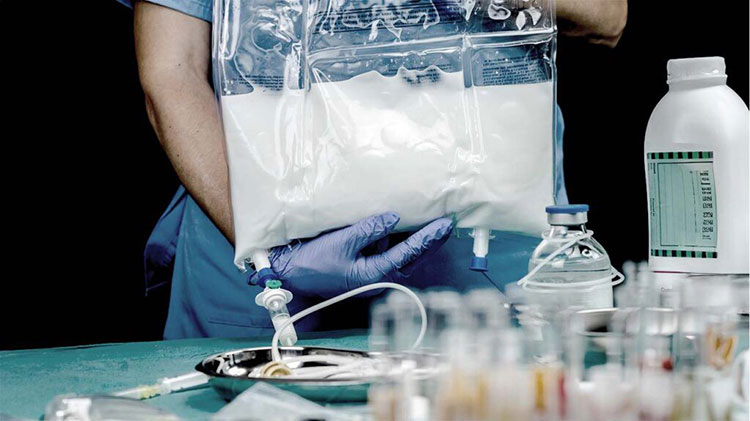
Total Parenteral Nutrition
It can be used for total parenteral nutrition. The intravenous emulsion in pharmaceutics is composed of fats, vitamins, and, carbohydrates as nutrition.
Reducing Irritability of Active ingredient

Total Parenteral Nutrition
Some topically applied pharmaceutical active ingredients are irritants to the skin. The irritability can be decreased by formulating them with emulsion in pharmaceutics.
Patient Compliance

Patient Compliance- Picture Courtesy: Avant
It provides a better alternative for drug delivery when patients feel difficulty swallowing the solid dosage forms.
Prolonged Drug Release

Vaccines- Picture Courtesy: OZ Biosciences
It has sustained release properties when administered parenterally. This property is beneficial for water-soluble drugs and vaccines.
6.What are the disadvantages of an emulsion in pharmaceutics as a drug delivery system?

Cons of An Emulsion in Pharmaceutics
Besides that, it’s an effective drug delivery system, but there are some cons of emulsion in pharmaceutics. Let’s understand them to have a clear picture before the formulation development of a drug.
Agitation

Oil Droplets in Water
It needs some external agitation before every use. Shaking is required before use for even distribution of the drug. If you don’t provide agitation, the dose accuracy will be affected.
Technical expertise

Technical Expertise- Picture Courtesy: Vialab
You need to calculate formulae and need other technical competence for the development of primary emulsion, for a stable formulation.
Storage

Storage Condition- Picture Courtesy: ACME
If it’s not stored as per requirements, it will disturb the disperse system. The improper storage conditions cause instability of dosage form.
Transportation

Container Breakage
We need plastic or glass containers for the storage of the emulsion in pharmaceutics. As it’s bulky, transportation is difficult and there is a risk of container breakage.
Microbial contamination
Microbes
It’s more prone to microbial contamination which can cause cracking.
7.What are the key factors to be considered for the stability of an emulsion in pharmaceutics?
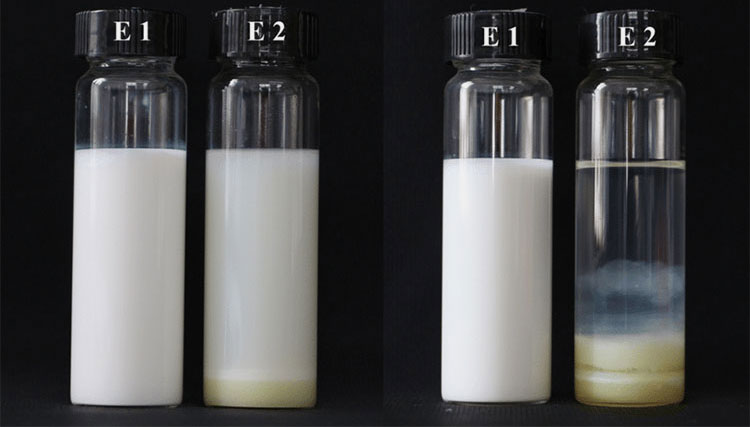

Stability of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Springer Nature Link
The emulsion in pharmaceutics is considered stable when its two immiscible phases resist separation during storage. Before developing a formulation, one should consider several key factors that can alter the stability. Let’s look into them.
Oil Globules Size

Globule of Oil in Water
The emulsion in pharmaceutics is kept stable by reducing the size of oil droplets inside it. Since they exhibited a lower tendency to form floccules (i.e. globules come closer to each other and form large clumps). Whereas Floccules settle down faster than the individual particles and affect the stability of it.
Emulsifying Agents
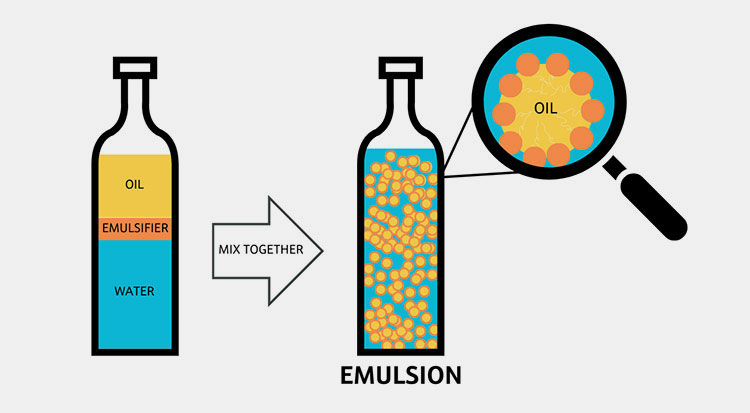
Role of Emulsifier- Picture Courtesy: Locus Ingredients
As we discussed earlier emulsifiers surround the droplets and create a protective barrier. These agents prevent emulsion in pharmaceutics from coalescence. Coalescence is the phenomenon used when there is separation of phases into distinct layers due to the breakage of emulsion in pharmaceutics. This is an irreversible process and can’t restore the stability.
The only way to overcome coalescence is the mixing of more emulsifiers as afterward pass through the emulsifying equipment.
Preservatives
Microbial degradation
There is a possibility of deterioration of the emulsion in pharmaceutics by microbes (e.g. bacteria, molds, yeast, etc.). That will cause the contamination of the water phase and rancidity of the oil phase.
The only solution to protect it from micro-organisms is the addition of a potent preservative. Such as the combination of parahydroxybenzoates of methyl ester and propyl ester is commonly used as a preservative.
Viscosity

Viscous System- Picture Courtesy: Viking Pump
By increasing the viscosity (i.e. thicker continuous phase), one can achieve stable emulsion in pharmaceutics. Because in the viscous system, the droplet movement speed becomes slower eventually resulting in stable formulation.
Other Factors

Rancidity- Picture Courtesy: Cookist
Emulsion in pharmaceutics should be protected from other factors too. Such as:
- Light exposure (affect color and odor).
- Too high/ too low temperature (causes breaking of emulsion in pharmaceutics).
- Rancidity (cause changes in odor and color).
8.How does an emulsion in pharmaceutics have industrial applications beyond pharmaceuticals?

Applications of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Rheonics
The emulsion in pharmaceutics has a broad spectrum of applications that are not limited to the pharmaceutical industry only. Let’s explore how these tiny globules in dispersion medium do wonders in different industrial sectors.
Food Emulsions

Emulsifying Food- Picture Courtesy: AAPS
The food industry is included in one of those sectors, where emulsion in pharmaceutics is being employed. It’s applicable for food products where emulsification is needed. Such as salad creams, mayonnaise, deserts, beverages, etc. emulsifiers are also added to increase the volume of cakes.
Cosmetic Emulsions

Beauty Enhancer- Picture Courtesy: VMI
Isn’t it surprising that most of the cosmetic and personal hygiene products are formulated as emulsion in pharmaceutics? These cover: Creams, lotions, scrubs, toothpaste, foundations, masks, sunscreen, body milk, zinc oxide, etc. ointments for babies Besides their different applications, they all have the same primary base, i.e. water and oil mixture.
Agrochemicals

Enhance Spraying Ability
It has its application in the agrochemical industry too. It is used as a vehicle for the delivery of pesticides, fungicides, and insecticides. It provides enhanced spraying ability to these products. examples are: self-emulsified oils, crop oil sprays, emulsion concentrates, etc.
Paint Industry

Paints- Picture Courtesy: Gellner Industrial
The emulsion in pharmaceutics has its role as emulsion polymer in the paint industry. They provide binding properties that are useful for primers for their adhesion. They also act as a protective film for paint against microbes and maintain the color.
9.How can you classify the emulsion in pharmaceutics?

Droplets of Oil in Water- Picture Courtesy: Differencebetween.com
You can classify the emulsion in pharmaceutics on either of the two bases.
Based on the internal phase.
- Oil-in-water (O/W)
- Water-in-oil (W/O)
- Multiple emulsion in pharmaceutics (O/W/O) / (W/O/W)
Based on the globule size
- Macro-emulsion in pharmaceutics
- Micro-emulsion in pharmaceutics
- Nano-emulsion in pharmaceutics
Based on the internal phase.
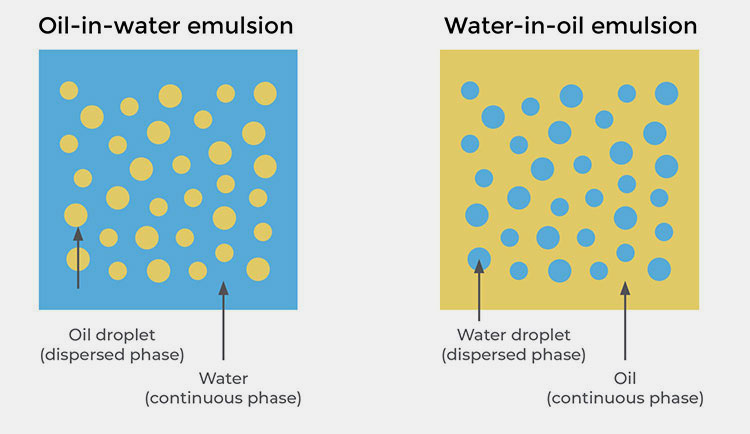
Classification of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: School of Natural Skincare
Oil-in-Water Emulsion in Pharmaceutics

Vanishing Cream (O/W) – Picture Courtesy: Besame
In this type of emulsion in pharmaceutics:
- The dispersed phase is composed of oil.
- Whereas water acts as a dispersion medium.
It can be used for topical as well as oral routes. The O/W emulsion in pharmaceutics is preferable for internal use because the unpleasant taste of oil can be easily masked. If the drug is water soluble, then it can be easily released from it.
It can be formulated topically for a cooling effect. Vanishing cream is an example of O/W emulsion in pharmaceutics. Non-greasy in texture so wash easily from the skin.
Water-in-Oil Emulsion in Pharmaceutics

Water in Oil Creams- Picture Courtesy: School of Natural Skincare
In this type of emulsion in pharmaceutics:
- The dispersed phase is water.
- The oil is served as a dispersion medium
It is suitable for topical formulations. The lotions and creams that we use in our daily lives are examples of W/O emulsion in pharmaceutics. It has a greasy texture and can't wash easily. Oil-soluble drugs have faster release from it.
Multiple emulsion in pharmaceutics (O/W/O) / (W/O/W)
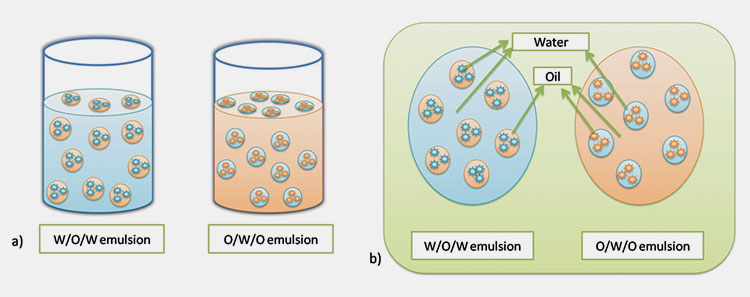
Multiple Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: SpringerLink
The multiple emulsion in pharmaceutics is a complex system. It’s also referred to as double emulsion in pharmaceutics. It’s a combination of both O/W and W/O types. It’s of two types.
- O/W/O
- W/O/W
In the case of O/W/O, the small oil globules are enclosed in large water globules which are dispersed in oil (oil is a continuous phase).
In contrast, W/O/W type, the water is enclosed as small globules in large oil globules. These are then dispersed in water, which is acting continuous phase.
These types of emulsion in pharmaceutics are suitable for the formulation developments of bioactive compounds. As well as where the controlled release of the drug is desirable.
Based on the globule size
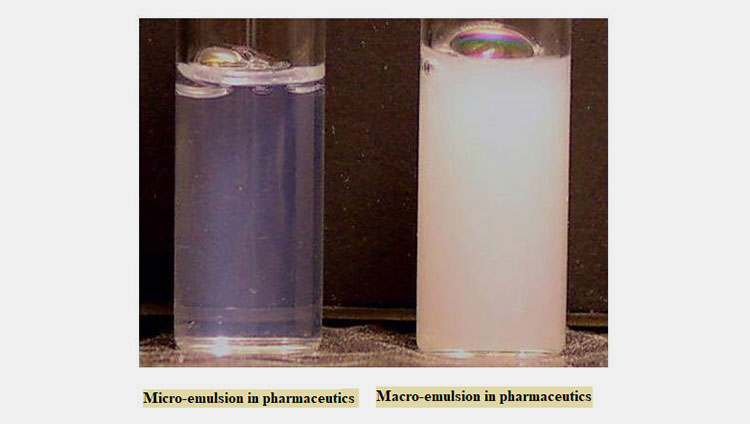
Micro-emulsion in Pharmaceutics VS Macro-emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: Michberk
Macro-emulsion in Pharmaceutics
It has a globule size of 0.5 to 100 µm. It’s thermodynamically unstable but kinetically stable. It has a turbid appearance.
Micro-emulsion in Pharmaceutics
The size of the globule ranges from 10-100 nm. It’s thermodynamically and kinetically stable. It has a transparent appearance,
Nano-emulsion in Pharmaceutics
The droplet size is < 100 nm. It is thermodynamically less stable as compared to micro-emulsion in pharmaceutics. It has s transparent or slightly turbid appearance.
10.What are the preparation methods for emulsion in pharmaceutics?

Formulation of Emulsion in Pharmaceutics-Picture Courtesy: Pharmacydpp1b1
On a commercial scale, the emulsion in pharmaceutics is prepared by mixing in a large volume tank with a high-speed impeller, and stability is achieved when it passes through the colloidal mills or homogenizer. On the other hand, small-scale methods are utilized for extemporaneous preparations. These are:
- Continental (dry gum) method.
- English (wet gum) method.
- Bottle (forbes) method.
These methods differ from each other based on the form of energy being utilized in the system. We’ll discuss each method here for better understanding:
Continental Method

Continental method
The continental method is also referred to as the “dry gum” method. The method basically starts with the preparation of primary emulsion which is formed from oil, water, and emulsifier (i.e. hydrocolloid or gum type such as gum acacia). The preparation is done in mortar. The process includes the following steps:
Hydraulic washing of 1 part of gum with 4 parts of oil. The process continues until the powder is wetted. After that 2 parts of water are added simultaneously. Then triturate the mixture vigorously. The process continues until the primary emulsion is formed (you can hear a crackling sound). This step takes 3-4 minutes.
Now solid substances are added including active ingredients, colors, preservatives, or flavors) as a solution into the primary emulsion. Meanwhile, oil-soluble excipients are added directly into the primary emulsion.
Some substances are potential risks for physical stability. They should be incorporated when the process is near completion. In this manner breaking of an emulsion in pharmaceutics can be resisted.
After all the ingredients are incorporated, the formulation is placed into the calibrated container to make up the final volume with the water.
Following that the formulation is homogenized to make a uniform mixture.
This method is more suitable for the preparation of an oil-in-water emulsion in pharmaceutics.
English method

English method- Picture Courtesy: RecNote
The English method is also known as the “wet method”. The method has the same proportion of oil, water, and emulsifier (4:2:1). But differs in terms of the mixing technique employed. The method is difficult to handle especially when oil has high viscosity even then it provided a more stable formulation. Let’s break the process into individual steps:
1 part of the emulsifier is incorporated with 2 parts of water and triturated until the mucilage formation. After that, the 4 parts of oil are added gradually and in small sections with continuous trituration. The trituration is continued for several minutes to obtain the primary emulsion.
Other steps are the same as the continental method.
This method is more suitable for the preparation of water-in-oil emulsion in pharmaceutics.
Bottle Method
Bottle method
The method is also called the Forbes method. This method is suitable for volatile oils and other oils with lesser viscosity. The method is the modified version of the dry gum method. Let’s come to the steps of the process:
- In a dry flask 1 part of the emulsifier and 4 parts of oil are added. Then cover the flask and shake it rigorously.
- Then the predetermined volume of water is added simultaneously. Then shake it until the primary emulsion is obtained.
- Finally, make up the volume with water.
11.What are the necessary types of equipment used for the preparation of emulsion in pharmaceutics?

Emulsion in Pharmaceutics- Picture Courtesy: VMI
The type of equipment chosen for the preparation of an emulsion in pharmaceutics depends upon the method of preparation. As well as according to the production scale i.e. small-scale or bulk-scale production.
For Small-Scale
Porcelain Mortar and Pestle
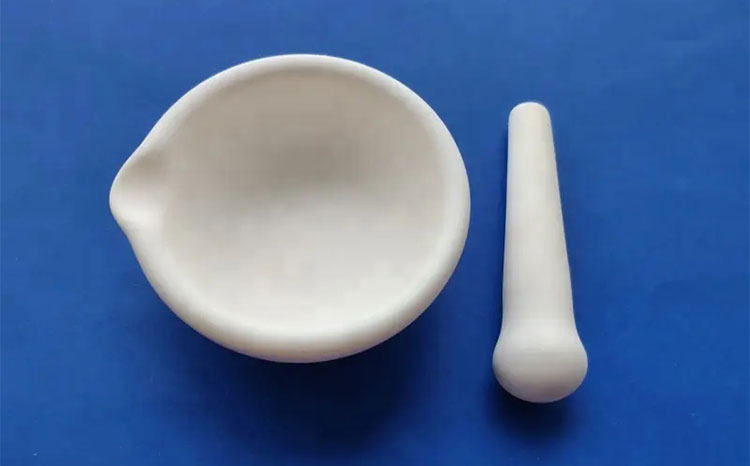

Mortar and Pestle
Porcelain mortar and pestle are used at a small scale for the preparation of emulsion in pharmaceutics. It’s used for the preparation of primary emulsion in the continental method and English method.
It is used for the trituration before the dilution of emulsion in pharmaceutics.
It has a glazed surface and is non-porous, making it ideal for the trituration steps in primary emulsion. Its non-porous nature helps prevent contamination and absorption of ingredients.
Hand Homogenizer
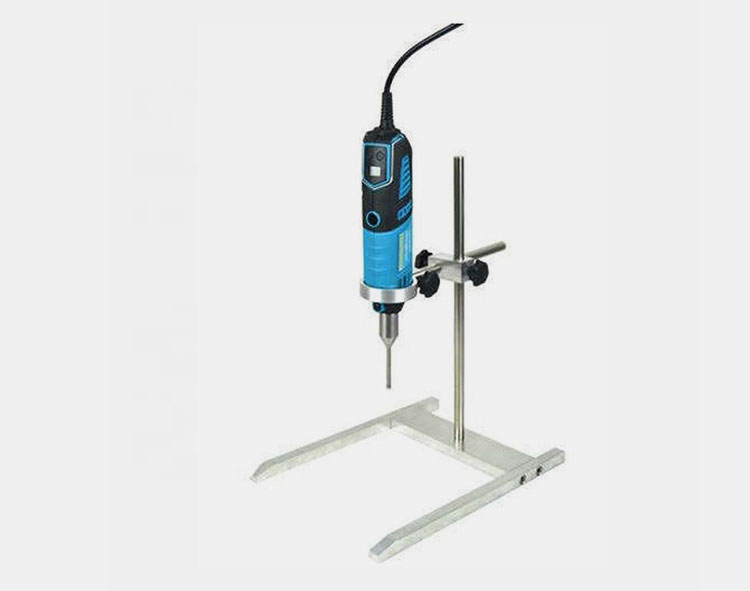

Hand Homogenizer
The hand homogenizer further aids in the reduction of globule size after the preparation of emulsion in pharmaceutics by other methods. It improves the formulation by passing it from a small aperture. The globule size can be minimized to 5 microns or less.
For Large-Scale
High-speed shear mixer
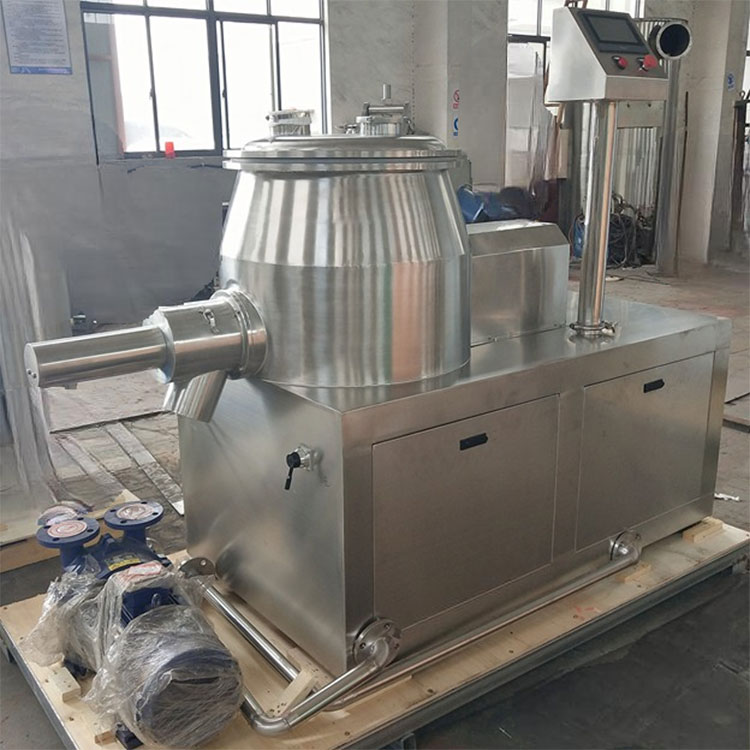

High-speed Shear Mixer- Picture Courtesy: Abster Equipments
The equipment is used for the reduction of globule size, blending of emulsifiers, and homogenization of an emulsion in pharmaceutics. It has a high-speed rotor stator the stator is immobilized which in contact with the moving rotor produces shear forces. It is suitable for mixing bulk volume and high-viscosity samples.
High-pressure homogenizer

AiPAK High-Pressure Homogenizer
It is an advanced equipment for producing formulation with more fine particles (results in a uniform blend of emulsion). It works by passing the liquids through a narrow tube at a high-pressure maximum of 2000 bar. It results in shear forces and cavitation which reduces larger globules into smaller ones.
Colloid Mills

Colloid Mills
The colloid mills work on the principle of rotor and stator, the same as the high-speed shear mixer. The liquids are passed through the rotor and stator having a narrow gap. The high shear forces reduce the liquid into fine droplets.
12.What types of physical instability challenges do you face in emulsion in pharmaceutics?
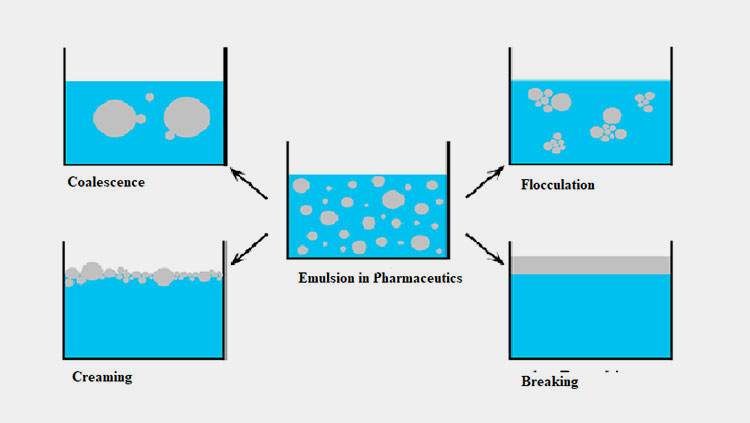
Instability Challenges- Picture Courtesy: ResearchGate
The development of an emulsion in pharmaceutics is an art in pharmaceutical science. With a minor handling or process error you could face major challenges, especially to maintain the stability of it. What could be the possible instability challenge aroused in emulsion in pharmaceutics? These are:
- Flocculation
- Creaming
- Coalescence
- Breaking
Flocculation
It’s a term used when a considerable portion of dispersed globules stick with each other and form aggregates. Aggregates are also termed as floccules. It’s a reversible process. The most important reason for flocculation is an insufficient quantity of an emulsifier. It can be reversed by:
- Mechanical agitation
- Increasing the amount of emulsifier.
- Adding other emulsifiers having high HLB (hydrophilic-lipophilic balance) value.
Creaming
It’s a condition where larger globules either move upward or downward and form a layer. It happened due to an increasing concentration gradient in the system. The creaming can be:
- Upward creaming
- Downward creaming
The term upward creaming refers to globules forming a layer on the upper surface of the system. It happens with particles of lower density. In contrast, the downward creaming happens with higher-density particles, forming a layer at the bottom of the system.
The reason could be the differences in the density of the globules or the effect of gravity on globules. This problem can be prevented by reducing the size of droplets, by minimizing the difference in density, and by making the continuous phase more viscous.
Coalescence
Coalescence is an irreversible process. It happens when two or more smaller globules come closer and form a globule of larger size. In this condition, the emulsifier film is damaged to some degree.
This condition is observed when:
- When the concentration of the emulsifier is insufficient
- When the partitioning of the emulsifier is changed,
- When incompatible emulsifiers are used in the system.
Breaking
The breaking of an emulsion in pharmaceutics happens when phases are separated into distinctive layers. This problem occurs when coalescence is increased. It’s an irreversible process and can’t be resolved by simply providing agitation or mixing.
The cause behind it can be:
- Increase coalescence
- High heat
- Freezing
- Incompatible emulsifiers
- Degradation of emulsifiers
- The breaking can be avoided using compatible emulsifying agents, preventing extreme temperatures, or adding preservatives to resist decomposition.
Conclusion:
The emulsion in pharmaceutics plays a significant role in the innovative drug delivery system. We have explored extended information relevant to the emulsion in pharmaceutics. In this post, you have found all possible information related to emulsion in pharmaceutics as well as associated parameters. Furthermore, if you are looking for efficient equipment for emulsion in pharmaceutics, AIPAK ENGINEERING gives you the best solution. Contact us for any further assistance.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours