BCG Vaccine Production: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Do you know what is the only approved vaccine for TB? The world is striving harder for eradication of TB strain which is a global challenge. Today the topic of our blog is all about it! The BCG vaccination and its production. If you’re a scientist, manufacturer, or student, this informative discussion is related to history, composition, indication, and how the production of BCG vaccine takes place. Not just this, there are various challenges associated with its manufacturing, therefore, from start to end, the article highlights all basic factors.
Don’t go anywhere, just scroll down to find and discover the knowledge related to BCG vaccine production.
1.What is the BCG vaccine production?
BCG Vaccine- Picture courtesy: News-Medical
BCG is derived from termed Bacille Calmette-Guérin. These are live attenuated microorganisms of Mycobacterium bovis that are specifically protected from strains of tuberculosis or TB. It is the mild and weak form that results in the progression of TB in cattle. In humans, the main cause of TB is Mycobacterium tuberculosis. So, these two strains are somewhat similar to each other. That’s why upon administrating these vaccinations, your body starts an immune response and makes you safe against progressing the disease.
The BCG production is composed of a series of steps involved in the designing, making, and packaging of the formulation. The purpose of this is to slow down or eradicate the progression of TB’s intensity in special populations such as pediatrics and make them safe from other associated pathogens such as meningitis.
2.When first BCG vaccine production take place?

History of BCG Vaccine- Picture courtesy: Wikimedia Commons
The story began around 3000 & 2400 BC from Egyptian mummies where spinal tuberculosis was recognized. However, the first strain was identified in Heidelberg in the bone of Neolithic. Those days such a disease remained a mystery and was called an ‘unidentified infection’ to mankind. The scientist Robert Koch caught the strain that causes disease and identified it as Mycobacterium-um tuberculosis or TB in 1882.
The BCG vaccine is known as the oldest one with huge popularity across the globe. Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin were the pioneers who created the miracle solution for TB vaccination in the early 1900s by separating the strain from Mycobacterium bovis. It was first tested on the human body in 1921 once passed from average clinical studies but not on an advanced scale. It was administered to an infant infected with TB whose mother suffered and expired from a similar strain soon after delivery.
The studies were carried out for around 6 months by exposing the baby to BCG and in this way, many other studies were performed on infants with and without the pathogen with good results. So, in this way, a huge population of children was immunized in France in around the period of 1924 to 1927. The vaccination is propagated high with more advancement and development from that period till the 1960s.
3.What BCG vaccine production is composed of?
The BCG vaccine mainly contains the living strains of Mycobacterium bovis. Today it has many different strains that are developed by blessing and striving of research and biotechnology methods to minimize the intense response of pathogens and boost high immunity response. Due to minor genetic variation and strain phenotype, you can find a series of strains available worldwide.

The ingredients of BCG vaccine production- Picture courtesy: RACGP
Active Strains of BCG
Active Strains of BCG- Picture courtesy: News-Medical.net
This is the active ingredient of the BCG vaccine which is added in the vaccine in a smaller amount such as 0.1 to 0.2 mg and it is also based on country protocol or formulary and manufacturer drug design. The composition of BCG vaccine is mainly composed of WHO-approved strains such as:
| Pasteur 1173 P2 | This is an effective and highly potent strain mainly used in areas with greater pressure of TB. |
| Danish 1331 | This is the most popular strain used worldwide due to reliable immunogenicity. |
| Glaxo 1077 | The originated version is from the Danish strain. |
| Tokyo 172-1 | Its name shows its popularity in Japan and related Asian countries. |
| Russian BCG-I | mainly used and available in Russian and European regions. |
| Moreau RDJ | It was introduced by Brazil and implemented in Latin USA regions. |
Stabilizers

Stabilizer- Picture courtesy: The medicine maker
To keep the active ingredient in a stable form, the stabilizer is added to keep its integrity well-maintained. There are various stabilizers available that are pharmaceutically protective and commonly used in BCG vaccine production. For example, trehalose, lactose, mannitol, etc. They are added in the formulation thus preserving the viability of the product.
Additionally, glycerol is present in the BCG vaccine to improve cryoprotectant properties and make the product stable against the degradation process for a longer time.
Trace Elements

Trace Element- Picture courtesy: Farm Advisory Service
The BCG vaccine production is composed of some trace elements such as zinc, and polysorbate 80 for supporting the active ingredients and inducing an ideal immune response in your body.
Water for Reconstitution

Water for Reconstitution – Picture courtesy: Pharmco
This is provided separately to dilute the medication. The simple plain water is passed through treatment plants to make it more sterile and purified and palatable for parenteral preparations. Also, this is also available in the form of saline water, phosphate water, dextrose water and simple water for injection that has no additional components or preservatives.
4.How does BCG vaccine production take place?
BCG vaccine production- Picture courtesy: JoVE
Contrary to popular belief, BCG vaccine production is not a single-stage process; the reality is quite different. In fact, several steps are responsible for developing quality BCG vaccines. Moreover, there is constant harmony between these stages, which ensures consistency and reproducibility in every product batch.
So, let’s explore various stages in BCG vaccine production:
| Choosing the Right Strain | Before starting the production operation, the right strain of Mycobacterium bovis is selected. This step is essential as this vaccine is composed of live attenuated strains and the choice of appropriate strain is pivotal for the effectiveness of the final vaccine.
Thereafter, you’ll develop a master seed lot in accordance with strict GMP procedures. Then, you’ll prepare a working seed lot (WSL) from this master seed lot. WSL is the preparation used in real-time vaccine formulation. This reduces genetic instability and mutation rate. Afterward, you’ve to store your working seed at -80°C or in liquid nitrogen to maintain its cellular structure. |
| Culture Medium Formulation | After the preparation of WSL, the next step is to develop a culture medium. Normally, a sauton medium is used for the cultivation of bacteria. It is a synthetic and protein-free medium consisting of important nutrients, such as glycerol, citric acid, magnesium sulfate, ammonium sulfate, potassium phosphate, and iron salts.
Remember to sterilize this medium by filtration to reduce the entry of contaminants. However, nutrients are not destroyed by this technique. |
| Bacterial Culturing & Harvesting | Now that you’ve prepared the culture medium, you will then restore and inoculate WSL into the sterile medium. This bacterial culture is cultivated and propagated in various steps to slowly increase the volume of seeds.
Ultimately, this culture is moved into bioreactors or fermentation tanks for mass-scale manufacturing. This fermentation step occurs at 37°C and a pH of 6.8–7.4. Furthermore, you’ve got to regulate aeration and stirring to prevent agglomeration. This step takes about 2-3 weeks owing to the slow reproduction cycle of bacteria. Once your desired viable cell count is attained, then you’ve to harvest culture. This is performed by centrifugation or filtration techniques that aid in collecting bacterial cells. After that, this biomass is rinsed and dispersed in a stabilizing buffer consisting of glutamate buffer. |
| Vaccine Formulation | After that, you’ll mix this stabilization suspension with different ingredients, for instance, stabilizers, buffers, etc. It is an important stage in which you’ll ensure that every dose has a precise number of viable bacteria typically 0.1–0.2 mL = 2–8 × 10⁵ CFU. |
| Inline Quality Control | When your vaccine is formulated, then you have to conduct a quality control assessment to stringently test its quality, effectiveness, and purity using different established protocols. You’ll check its purity, pH, osmolality, and water content. Furthermore, the viable count of bacteria in the vaccine is assessed by measuring colony-forming units per dose and Ziehl–Neelsen staining, respectively. |
| Filling | Having passed all the quality control checks, the approved vaccine batch is transferred to filling systems. Here a precise volume of BCG vaccine formulation is loaded in Type-I glass vials. Next, these vials are stoppered halfway. These stages occur in a cleanroom environment in which air is continuously ventilated to prevent ingress of impurities and biological contaminants. |
| Freeze Drying | Following the filling stage, the vials are lyophilized by freeze-drying the filled BCG vaccine preparation. It is done by subjecting these containers to a lyophilizer. In this procedure, the temperature dropped below -40°C to form ice crystals. Afterward, in the primary drying stage, vacuum pumps are utilized to lower pressure, which starts the evaporation of water molecules. After that, secondary drying is performed to remove the rest of the moisture. A final freeze-dried vaccine has <3% water content. |
| Sealing & Labeling | After successful freeze-drying, the vials are completely stoppered and capped via a capping machine. The capping head presses the cap on the vial and rotates so the cap is tightly sealed to the vial opening. Subsequently, vials are transported to the labeling machine via a conveyor belt. This device then labels vaccine information, its formula, expiry date, usage guidelines, and company information on vials. |
|
Packaging & Cartoning |
In a separate vial or ampoule, the diluent is packed. Following this, the diluent packaging is conveyed to the cartoning machine for boxing where it is enclosed in sturdy carton boxes along with freeze-dried BCG vaccine and leaflet instructions. |
| Quality Control Checkup | Before batch distribution, it is once again subjected to quality control checkups, where its potency, sterility, and stability are tested. Moreover, manufacturers also check the endotoxin levels in freeze-dried vials. Only after you’ve received the necessary quality approvals by these tests then you’re cleared to ship and distribute the product batches. |
5.What machines do you need for BCG vaccine production?
The BCG vaccine production is composed of a complex set of machines. Each unit has a significant responsibility to generate a potent vaccine for your use. You can see below the enlisted machines and their working.
Controlled & Clean Rooms

AIPAK ENGINEERING clean rooms
This is the first setup of the production where various machines and technicians work in high-quality quality controlled and clean rooms. These rooms are specialized areas designed with GMP and international regulations implemented by WHO. The purpose of utilizing is to enjoy stress stress-free and hygienic environment for BCG vaccine production which is mandatory for it. Here, it offers controlled temperature, pressure, and humidity with particle air flow and particle sizes of air. Hence, the overall environment is aseptic with low chances of contamination.
Biosafety Cabinet
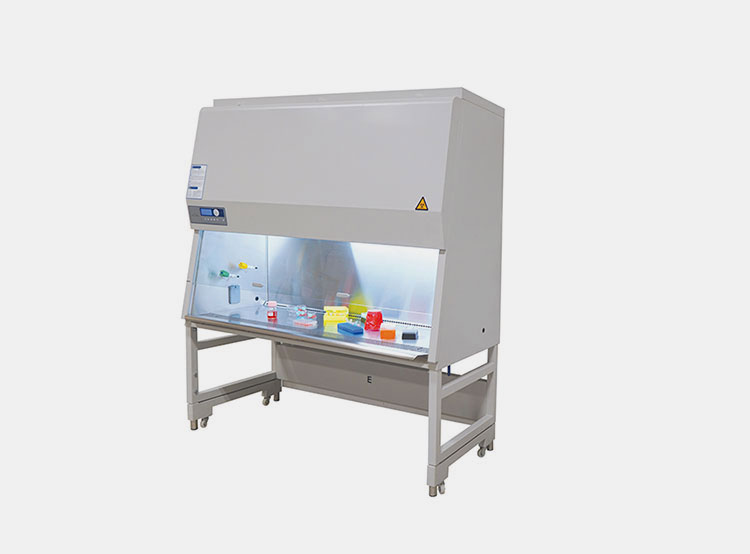

Biosafety Cabinet- Picture Courtesy: Airclean System
This is an essential unit to carry out sterile processing and making of dilutions. The machine runs by offering a laminar airflow with filtered particles by using a HEPA filter system that is highly recommended for the operator as well as your product to keep it sterile.
Fermenter
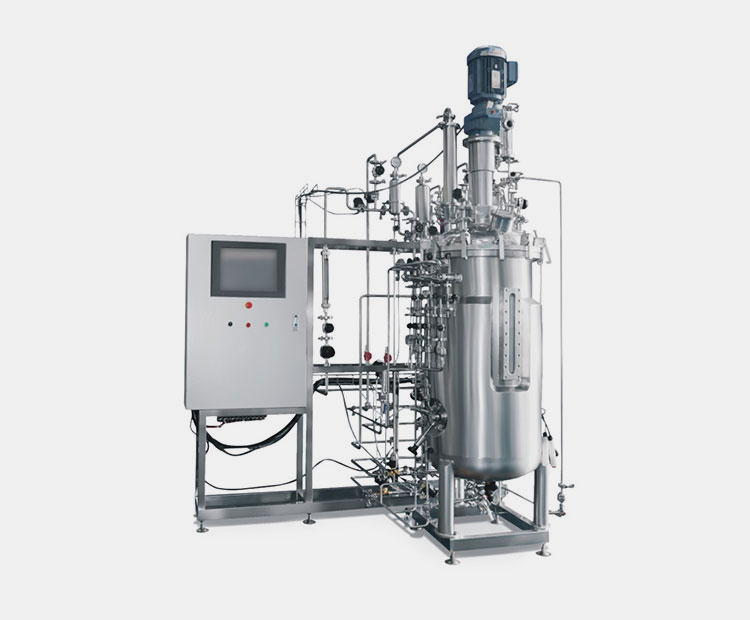

Fermenter- Picture courtesy: BaiLun Biotechnology
The story of BCG production starts with its cultivation. The bacterial colony is cultivated in a controlled condition and in a flask with nutritional ingredients to initiate the process. Along with the flask, a fermenter is used to boost the fermentation. The ideal temperature of the fermenter is 37°C. In the meantime, flasks are automatically shaken to support the media, and the process of growth mainly takes ten to fourteen days.
Harvesting Machine
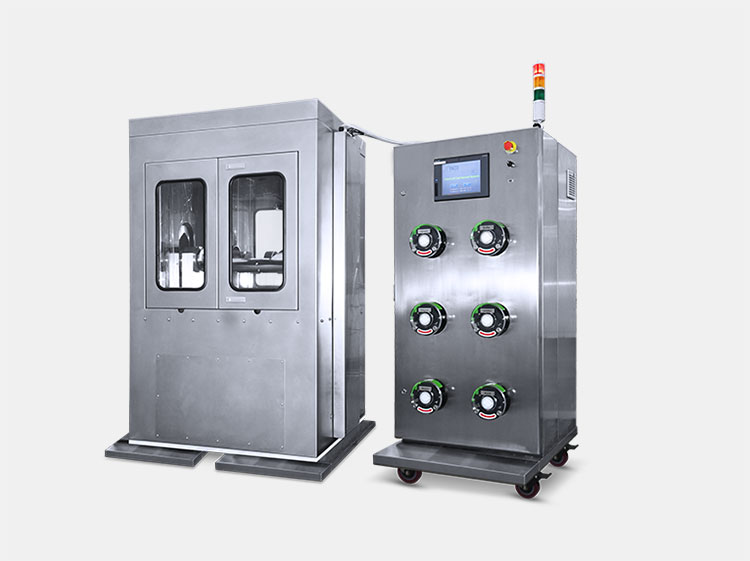

Harvesting Machine- Picture courtesy: ESCO
This is a powerful unit that is capable of harvesting the pellicle which is a kind of tough layer over the fermentation media. The machine is designed with an enclosed system where contamination cannot take place and a clear harvesting method occurs with removal and washing to provide a clean medium.
Centrifuge Machine
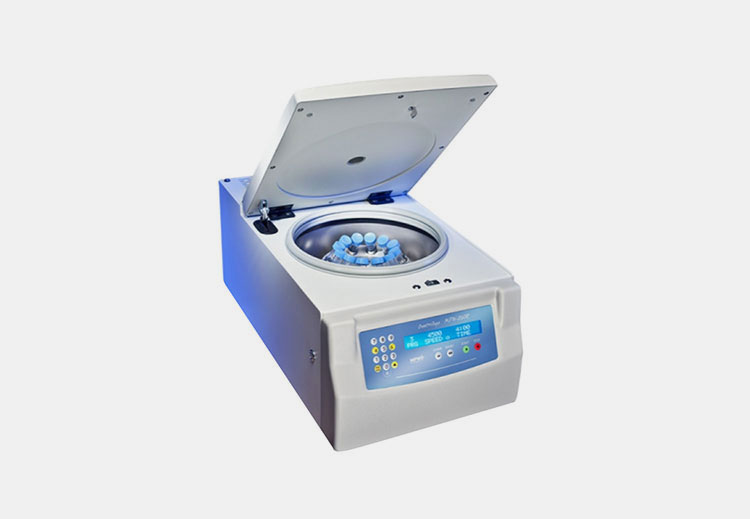

Centrifuge machine- Picture courtesy: Profilab
The liquid mixture of the BCG vaccine is subjected to a centrifuge machine where separation of layers is obtained with the help of intense centrifugal force which is approximately thousands of revolutions per minute. This machine is helpful in the harvesting of BCG cells and separating protein nuclei from the mixture.
Filtration
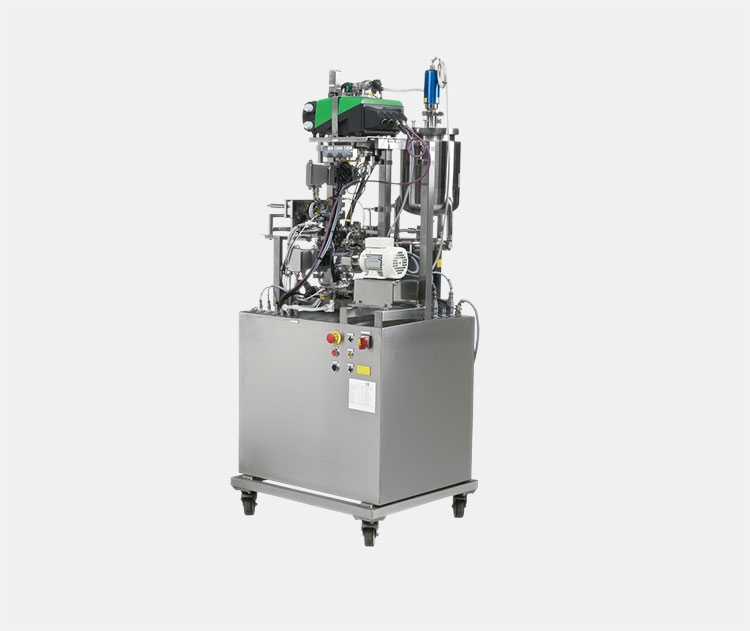

Filtration
This is the significant machine used for cleaning and purifying the cells from unwanted content. In this regard, ultrafiltration devices are used that ensure uninterrupted workflow of filtration and are integrated with other units to facilitate fast and efficient operation.
Lyophilization (Freeze-Drying)
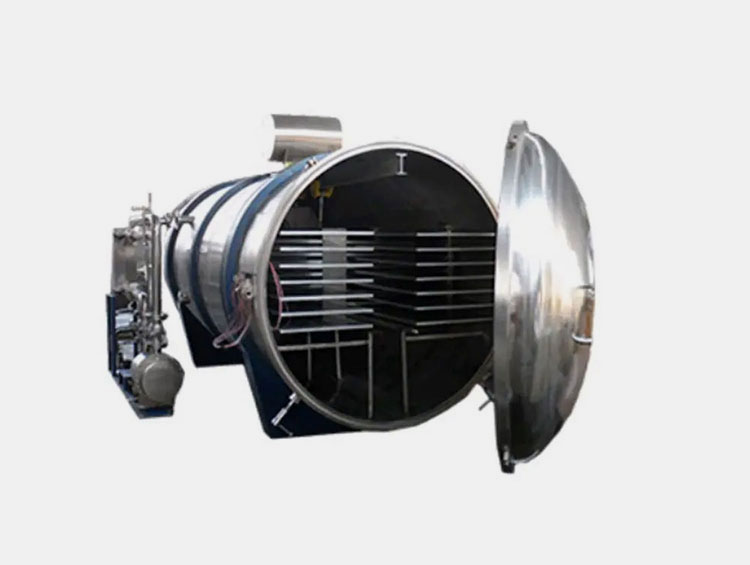

AIPAK food-grade lyophilization freeze-drying machine
The alive harvested active ingredients must be potent and away from moisture. For this purpose, a lyophilizer is used to evaporate the presence of moisture content in the material. The machine works by freezing of material followed by a sublimation process then simultaneously drying. In this way, fluffy and porous dried ingredients are formed. With the help of this machine, a stable, extended shelf life and potent vaccine powder are formed.
Milling Machine
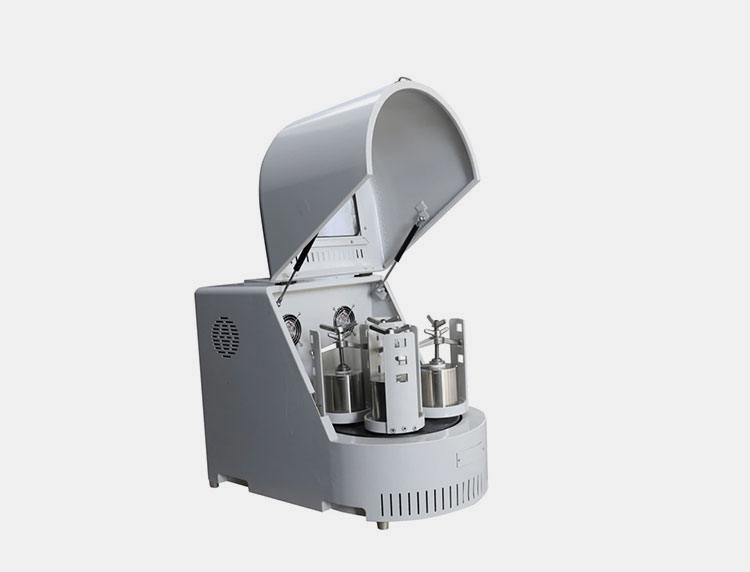

Ball Mill- Picture courtesy: kindle-tech.
For grinding or milling of the pellicle, the grinder is used which helps in the sophisticated milling of the material into the finest powder. The material is introduced into the machine which is designed with several balls that are heavy in weight and help in the milling of particles. The material also circulates and in the meantime, the ball's impact force ensures an ideal reduction of the size by involving cutting as well as chopping. This machine is safe and is used in various biological sectors for suitable results.
Water Treatment Plants
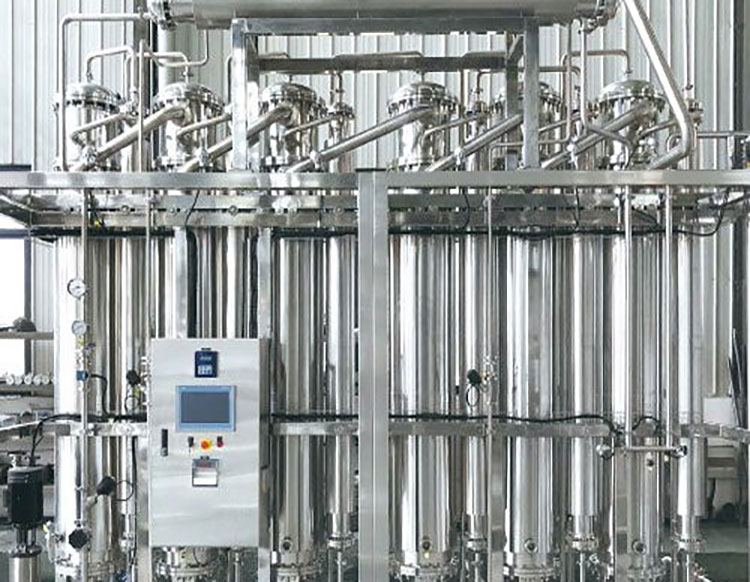

AIPAK ENGINEERING Water Treatment Plant
The water treatment plant is required to provide water with ultra purity and regulated with WHO requirements. This mostly includes a distillation unit, reverse osmosis unit, and deionized water machine. Such units are essential to install to obtain water with 99.9% purity and clear from foreign particles to avoid interruption or contamination.
Vial Filling and Stoppering Production Line

AIPAK ENGINEERING vial filling and stoppering line
An automatic vial filling and stoppering production line for the BCG vaccine is ideal for final manufacturing formalities. This is an absolute solution that is composed of around five major integrated units. When you set up this unit, it will offer a vial-washing process by rinsing and washing all over the vial and corners. The next unit is a sterilization tunnel that is designed to blow hot air flow which dries the vials and makes them sterile by killing the presence of microbes around the vial’s edges.
The unscrambler machine is integrated to provide a uniform and oriented flow of vials toward the vial filling machine. The accurate portion of the BCG vaccine is flowed and filled in the vials by an automatic sensing system for the pre-nitrogen and post-nitrogen filling action. The sealing and stoppering machine firmly affix the cork and stopper over the neck of the vials and secures the entire formulation.
Labeling & Cartoning Machine

AIPAK labeling and cartoning machine
An automatic labeling machine is used to label the required information over the edges of vials in a particular pattern. The prepared BCG vaccines are positioned and secured in cartons by using a cartoning machine that automatically detects the presence of the product and positions them in a carton which is made up of a flat sheet by the machine.
6.How do you store formulation from BCG vaccine production?

Storage- Picture courtesy: QCPP
As you’re dealing with live attenuated bacteria, therefore; you’ve to carefully store the product from BCG vaccine production. Here are three different stages employed for storing and using BCG vaccines:
| Storage of Large Vaccine Batch | It usually occurs before the freeze-drying of the BCG vaccine. To store it, you typically place its packaging at 2–8°C. This stage happens only for a small duration because the vaccine n doesn’t have much stability in liquid form for longer intervals. Therefore, you’ve to constantly check it to avoid microbial contamination and loss of live bacteria. |
| Post-Lyophilization Storage | It’s a storage step after the freeze-drying of the BCG vaccine and it is safe to store it in the refrigerator at 2–8°C because now it is in powdery form and has more stability against contamination. Its shelf-life is around 2 to 3 years if you keep it in the refrigerator and away from direct sunlight and moisture. Humidity control is a must at this stage because if bacteria encounter even a tiny drop of moisture they lose their viability. |
| Storage of Reconstituted Vaccine | Once you reconstitute the vaccine by adding a sterile diluent, then it must be administered instantly or within 6 hours only if you keep it at 2–8°C. You must always remember to discard leftover vaccine after 6 hours as it is not safe to use after this period. |
7.What are common doses of BCG vaccine production?
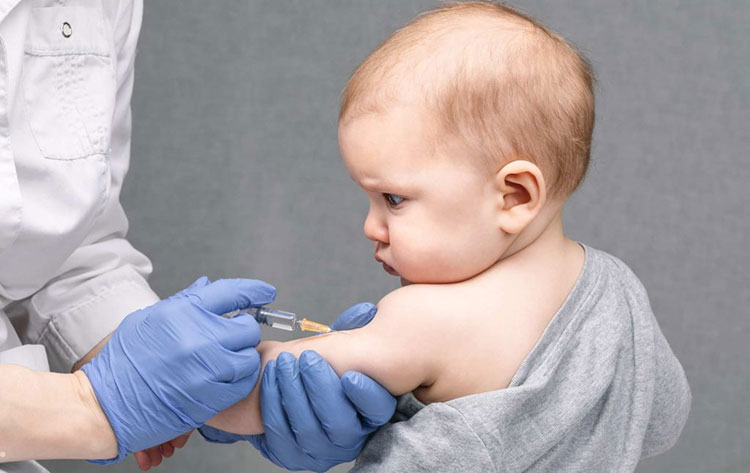
Doses of BCG Vaccine- Picture courtesy: Supernova Medical
The dose of your BCG vaccine must be precise and higher doses are harmful to the immune system whereas, lower doses are ineffective and don’t offer the desired immune response. Let’s explore some common doses employed in BCG vaccine production and how they’re suitable for different age groups:
| Typical Pediatric Dose | It is usually administered to infants under 12 months and is approximately 0.05 ml after reconstituting with diluent. It has about 0.05–0.1 mg of live TB bacteria. |
| Dose for Older Kids and Adults | They are administered 0.1 ml of BCG vaccine that has around 0.1–0.2 mg of BCG formulation. |
8.What are the routes of administration of BCG vaccine production?
You would probably be thinking about how the BCG vaccine enters the body. Well, the route of administration is the delivery method by which live attenuated bacterium safely and effectively go inside the body. Let’s read about different routes of administration of BCG vaccine production:
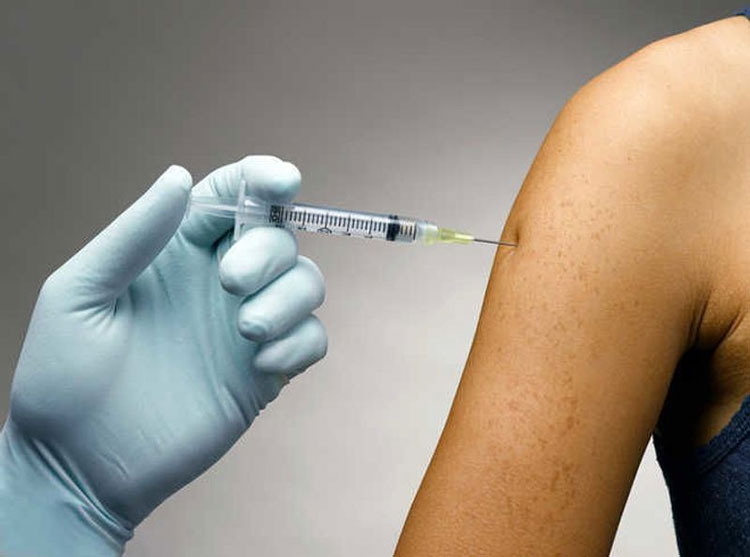
Route of Administration- Picture courtesy: The Tribune
| Intradermal Route | It is the primary route for dispensing BCG vaccines to both children and adults. WHO recommends this route for delivering this vaccine. Usually, a skilled person administers this shot in the deltoid region of the left upper arm. It is injected by a minute fine-gauge needle (26G or 27G).
It is the most frequently used route because your dermal tissues have lots of immune cells. This allows maximum response from your immune system without the vaccine getting into systematic circulation. |
| Percutaneous Route | It is known by the name of the multiple puncture method and is less commonly utilized for administering the BCG vaccine. In Japan, South Africa, and the United Kingdom, a device like a heat gun is utilized for puncturing skin at multiple sites for injecting the BCG vaccine. It often causes scarring at the site of injection. |
| Oral Route | It is considered the oldest route for delivering BCG vaccine as this vaccine was originally made for oral administration in the 1920s. Nevertheless, this mode of delivery was discontinued because it results in inconsistent immune response and a large proportion of bacteria being degraded by stomach acid. |
| Intravenous Route | This mode of administration is still in the experimental stages and is being tested in animal studies and early-stage human trials. Although, with this delivery method, you have a stronger immunity against TB bacteria, however; it also comes with huge risks, so still not safe for the public. |
9.What are the available packaging types for BCG vaccine production?
Although, BCG vaccines are formulated in minute doses, however, its stylish and sterile packaging. You can say that its potency, dose precision, and, safety depend upon its packaging. Below are some of the common packaging formats in BCG vaccine production:
Vials
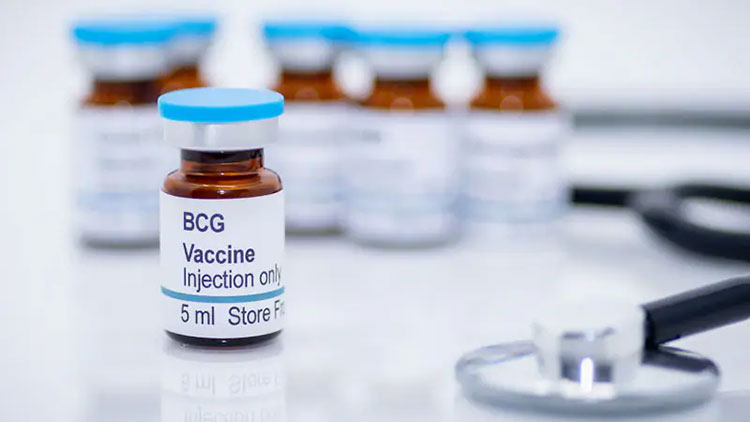
Vial- Picture courtesy: Medscape
It is the vastly utilized packaging and has the best airproof protection of the freeze-dried BCG vaccine. This vial is created from type I borosilicate glass and is quite popular because of its excellent thermal resistance and chemical inertness. They are often sealed with rubber stoppers and aluminum flip-off caps.
Ampoule
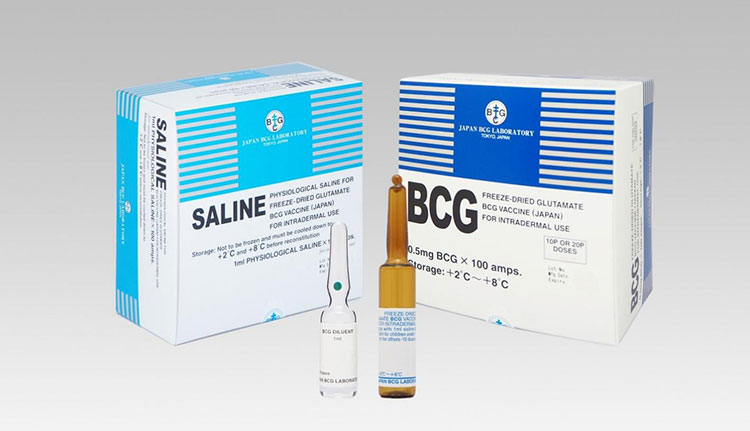
BCG Ampoule
Generally, you’ll find diluents and vaccines in glass ampoules. The ampoules are often broken by snapping their top half. While vials with rubber stoppers are frequently preferred because of their ease of usage and no cutting risk. The ampoule stores a small volume of vaccine and is best known for its single dose option.
10.What are the challenges and consideration factors of BCG vaccine production?
BCG vaccine production is a high-tech manufacturing process in which various technical issues may arise. These problems might seriously compromise the quality and efficacy of vaccine creation in addition to leading to drastic financial loss.
Some of the common challenges for BCG vaccine production and their solutions are detailed in the following section:
BCG Vaccine- Picture courtesy: esaic
| Slow Propagation of BCG Bacteria | As you already have learned the growth time of BCG Bacteria is very slow and it grows in culture media in 2-3 weeks. This increases the duration of BCG vaccine production. |
| Solution
To overcome this challenge, you’ll need optimized growth media, for instance, Sauton medium. It is enriched with key nutrients, such as glycerol and amino acids, which improve the growth rate of bacteria. Additionally, with the use of automated bioreactor tanks, you’ll have better control over growth conditions, which in turn leads to faster growth. Lastly, it is best to plan production in overlapping batches. This leads to continuity in bacterial supply. |
|
| Inadequate Sterilization Options | Bacteria is needed to stay alive to produce an effective BCG vaccine. Hence, you can’t utilize heating, autoclaving, or chemical sterilization in this live attenuated vaccine. This certainly compromises the safety of vaccines. |
| Solution
To boost the safety of BCG vaccines, manufacturers generally implement various aseptic manufacturing practices. These techniques allow high-level biosafety (BSL-2 or higher). Besides this, BCG vaccine production is carried out in HEPA-filtered cleanrooms in which media is sterility filtered, and working personnel must follow hygienic practices. |
|
| Reconstitution Issues | It is a severe matter, as incorrect reconstitution, for instance, use of incorrect diluent and taking time after mixing could significantly impact the potency or safety of the vaccine. |
| Solution
To solve this troubling problem, it is required by health regulatory authorities that manufacturers must pack diluent along with BCG vaccine packaging. This diluent should have the required volume to reconstitute BCG vaccines. In addition to this, they must include leaflets with clear instructions and training materials for hospital staff in vaccine carton boxes. It aids healthcare workers in correctly reconstituting vaccines. Furthermore, they must state on the vaccine container that it must be used within 6 hours of reconstitution. |
|
Conclusion
BCG vaccine production is indeed a complex process that requires careful handling, protocols, last but not least an excellent and advanced set of types of machinery. Are you looking for a reliable one-stop solution? AIPAK ENGINEERING is a solution. We welcome you to discuss your budget, the type of vaccine you’re planning, and production capacity. You will be happy to communicate with us as we have a broad solution to your problems related to BCG vaccine production. Why not contact us right now? You will get a fast reply from us!
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours