Antitoxin Vaccine: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Have you ever imagined how does a quick, targeted and ready to action force, rushing down to destroy or neutralize the lethal chemical weapon looks like, well that’s the core thought process behind antitoxin vaccines.
We are living in a world where infections are evolving faster than the treatments, and toxins are a constant threat of these infections. Sometimes the bacterial infection itself is not lethal but it leaves behind the toxins that can go unnoticed and produced life threatening conditions. This is where the antitoxin vaccines make their way.
They are prepared to prevent any kind of this threat from the start before any delay. Antitoxin vaccines are designed to neutralize harmful toxins directly. These vaccines are playing an important role in the global health, whether they are used in emergency medicine, routine immunization or bio manufacturing.
The following article will help you explore more about the antitoxin vaccines; lets inject some knowledge through these FAQS!
1.What is an antitoxin vaccine?
Antigen antibody reaction in the body
Antitoxin vaccine can be defined as a prepared product for immunization, which contains specific type of antitoxins, which are modified antibodies or can be inactivated toxoids which are specifically prepared to fight against the harmful effects of the specific toxin. They are designed to provide immediate action and also for long lasting protection from that specific toxin. They provide immunity against the toxins directly produced by the bacteria or viruses.
They are formulated in way for direct use without any need of further preparation. The type of immunity these vaccines provide is called the passive immunity, because these antitoxins are prepared by injecting a specifically modified, a very weak or dead toxin into the blood of an animal, usually a horse, or it can be a human. As a result that organism produces antitoxin to neutralize that specific toxin.
2.Where do antitoxin vaccines come from?
Vaccines a sign of hope for the patients-picture courtesy: cedars Sinai
Antitoxin vaccines come from inactivated bacterial toxins, which are termed as toxoids. These antitoxin vaccines have come a long way from early serum therapies to modern bio-tech based formulations, which provide safe and target specific protection against the toxin mediated disease.
Historical origin:
In the treatment of human infections, antitoxin vaccines are typically derived from an animal source, among which the most commonly used and the first ever antitoxin was made from horse.
These antitoxins, which are actually antibodies that are produced in response to the exposure of repeated controlled small amount of toxins in the host animal, until a high concentration of the antitoxin builds up in the body.
The serum from these animals, which has a high concentration of antitoxins is called antiserum, is extracted and goes through an extensive procedure of purification and separation for human use.
The first antitoxin vaccine ever produced was Diphtheria antitoxin therapy. Emil Von Behring won the first noble prize for his work in the invention of antitoxin vaccine, diphtheria antitoxin therapy.
3.What are the advantages of antitoxin vaccines?

Vaccines saving lives- Picture courtesy: Weill Cornell medicine
Immediate protection:
As they are ready to use and already have the antibodies for specific toxin, they produce immediate action and quickly neutralize the toxin, which is important in life threatening infections like tetanus or diphtheria.
Essential in emergencies:
They are ideal to be used in prophylaxis condition, when the body has been already exposed to the toxin and there is no time for the body to produce immunity.
Used in immune compromised patients:
As the antitoxin vaccines have neutralized toxins, so they are well suited for people who have compromised immune system, and for elderly and children who cannot receive a live vaccine and have a strong immune response on their own.
Save lives in critical conditions:
When the toxin has already entered the body, antitoxin vaccines can still counter the effects of toxin and prevent severe infections.
No need for immune system activation:
When in urgent or emergency conditions, patient has no time for the activation of immune response; these antitoxin vaccines produce immediate response by passing the need of immune system activation.
4.What is the composition of the antitoxin vaccine?
Here is a general composition of the antitoxin vaccine, given below:
| Ingredients | Functions | picture |
| Antitoxins | They are main active ingredient of the vaccine, which neutralizes the specific toxins, e.g., equine-derived or recombinant antibodies. | 
Antitoxin reacts with toxins-picture courtesy:science photo library |
| Stabilizers | They are essential for maintaining vaccine stability, e.g., sterile sucrose. | 
Sterile sucrose-picture courtesy: bio world |
| Preservatives | They prevent any kind of contamination, e.g., phenol | 
Picture courtesy: natural pigments |
| Buffering Agents | Their function is to maintain pH, e.g., phosphate or citrate buffers. | 
Picture courtesy: stat lab |
| Solvents | It could be any liquid medium according to the suitability of formulation, e.g., sterile water for injection. | 
Picture courtesy: Dreamstime |
| Adjuvants | They are added for improved efficacy, e.g., aluminum hydroxide. | 
Picture courtesy: G biosciences |
5.How antitoxin vaccines are formulated?
Antitoxin vaccine vial
Extraction of toxins:
It is a crucial step in formulation of vaccines, the specific pathogenic bacteria is cultured in lab which produce toxins under special conditions. These toxins are than harvested from the culture. This isolation of toxins from the culture requires techniques like precipitation, ultra centrifugation or gel filtration.
Inactivation of toxins:
The toxins are inactivated by the use of high temperature or by chemicals, like formaldehyde and converted into harmless toxoids, which are not potent or and dead version of the toxin but can still trigger an immune response in the body.
Stabilizers:
After the inactivation of the toxin, the stabilizers or adjuvants are added to enhance the immunity.
Formulation:
The purified antigen obtained after the purification procedure than undergoes the process of formulation, in which other ingredients which are adjuvants, preservatives and stabilizers are added to enhance the immune response, prevent bacterial contamination and maintain vaccine potency respectively, leading to the final vaccine product.
Then it is prepared into dosage forms for injections, which can be liquid or freeze dried.
Lyophilization:
This is the process of freeze drying the liquid vaccines to increase their shelf life and preserve their potency by preventing degradation due to temperature fluctuations. This process includes the removal of water from the product under vacuum and the liquid vaccine is converted into powder form. The freeze drying process takes place is low temperature vacuum dryers.
Packaging and distribution:
The final product obtained is packed in vial or syringes as per the requirements or type of vaccine made after that it is distributed under strict cold chain conditions.
These toxoids production form the basis of modern antitoxin vaccines, common example include:
- Diphtheria toxoid vaccine.
- Tetanus toxoid vaccine.
6.What are the requirements and machines used for the production of antitoxin vaccine?
Tetanus antitoxin vaccine
The production requirements for the preparation of antitoxins are explained below:
Pharmaceutical clean room system:

AIPAK engineering clean room
It is to make sure that the production must take place in sterile area to ensure safety and purity. They control the air quality, temperature and humidity. They are classifies in zones, from A to D, depending upon the stages of filling, sealing or packaging. The lab conditions along with the safety of the lab workers are ensured, following the GMP standards.
Bioreactors for culturing of bacteria:

Large scale bioreactors-Picture courtesy: frigs
The specific toxin producing bacteria is grown under controlled temperature, providing optimal conditions of pH and oxygen conditions. This is carried out in special apparatus, bioreactors, which are also called fermenters, which are specialized vessels for the cultivation of bacteria. They are specially engineered for the maintenance of optimal conditions for proper growth of the bacteria.
Toxin inactivation system:
The chemical agent, usually formaldehyde is used for the inactivation of the toxins. This inactivation comprises of toxic – nontoxic relation, which is neutralizing the toxin while maintaining the ability of the toxin to trigger the immune system. This inactivation can also be done through heat, providing high temperature.
The equipment used for inactivation process is referred to as inactivation reactor or a batch reactor depending upon the method used.
Inactivation reactor:

Inactivation reactors
They are specialized vessels made of stainless steel, or sometimes glass lined material to avoid corrosion. The toxin containing solution is added to the vessel and exposed to the inactivating agent, which can be a chemical agent or by the use of heat. Unlike batch reactors, they are continuous operators. They maintain a steady flow of the inactivating agent through the reactor, thus continuous exposure of the toxin to the inactivating agent is achieved.
This operation include the maintenance of optimal temperature, chemical concentration, radiation intensity if being used and the flow rate to achieve the required inactivation without disrupting the antitoxin activity. They have sampling ports from which samples are taken after regular intervals of time to check the level of inactivation.
Batch reactor:

Batch reactor-picture courtesy: chemEnggHelp
It is a closed system where the inactivation agents are added in a timed and monitored way. The reactants are added in the closed vessel, allowing them to react with each other for a set period of time. There is no continuous flow of material in or out, means there is no addition or removal of any product during the reaction. The products are removed at the end after a desired aversion is achieved.
There are sensors for the monitoring of temperature, pressure and pH during the process. Agitation is the process going on to ensure uniform mixing and reaction conditions in the vessels. It is provided with sampling valves to check for the progress of reaction.
Purification system:

HPLC-picture courtesy: CET- scientific services
There are different methods to remove the impurities and to isolate the toxoid. The purification and separation method includes:
Plasma separator:
They are used in case of animal source, horse based production. As the name suggest they are used to separate the plasma from the blood.
Chromatography systems:
They are used for purification of antitoxins using the protein A/G column. Protein A and G are bacterial protein that bind to the specific regions of the antibodies produced. These proteins are stationed on the column matrix and the mixture containing antibodies is allowed to pass through it, the required antitoxins bind to the protein A/G on the column. Impurities flow through the column. Lastly, these purified antitoxins are eluted by changing the pH or by using a special buffer solution.
Formulation unit:

AIPAK engineering liquid preparation system
They are large stainless steel tanks which mixes the purified antitoxins with stabilizers, adjuvants and buffer making them a solution to be filled in vials or syringes. It operates through controlled system of mixing tanks, maintaining sterile conditions. It is an important step regarding the potency and uniformity of the vaccine.
Sterile liquid filling machines:

AIPAK aseptic liquid vial filling line
The prepared final product is filled into vials through automatic sterile vial filling machines. The filling takes place in cleanroom under laminar air flow system. It is provided with HEPA filters (High Efficiency Particulate Air filters) to maintain ultra-clean air in sterile zones. Peristaltic Pumps for the precise and sterile flow of liquid, without the contact of fluid to any mechanical parts. A robotic arm for minimal human contact to avoid any kind of contamination.
In this machine, stoppering and capping of the vials also take place. Some highly advance machines also offer the ultrasonic cleaning, drying, preheating and sterilization of the vials before filling of the product. The filled unit is checked automatically or visually as well to ensure the volume, clarity and integrity of the vial.
Lyophilizer:

AIPAK vacuum low temperature automatic continuous belt dryer
They are used to remove water from the vaccine and convert them into dry powder form. This process is called freeze drying. It is done to protect the sensitive formulation from temperature fluctuation and provide long term stability. The liquid is first converted to ice at low temperature than the liquid molecules are directly converted into vapors under vacuum.
Sterile filling machines for lyophilized powder:

AIPAK aseptic vial powder injection filling line
These machines are designed to accurately fill the dry powder into vials or ampoules, maintaining an entirely aseptic environment. The main features of HEPA filters and laminar air flow in this sterile powder filling machine is same as of sterile liquid filling machine. Sterile powder is stored is stored in hopper above.
The vials are filled with accurate doses using this vacuum feeder from the hopper or the auger feeder. Auger feeder is a rotating screw inside a tube that push the powder in a controlled measured amount. The vacuum feeder use vacuum suction to pull a controlled amount of powder into the dosing chamber, which is then filled into the vial. After filling the powder vials are either partially stoppered if further lyophilization is required or can be stoppered fully if already dried completely, to maintain the sterility.
Labeling machine:

AIPAK high speed round bottle automatic labeling machine
After the filling and inspection of vials, they are moved to the labeling machine. The vials or syringes are loaded in the machine using the conveyor belt. The dispenser holds the roll of preprinted label, with batch no., expiry etc. Each of the labels from roller is peeled off by the machine and prepares it for placement on the vial. The machine has roller, tamp pad or air jet which applies the label on to the vial.
The faulty unit either misalignment or missing data is rejected by the automatic inspection of the machine through a vision system.
Cartoning machine:
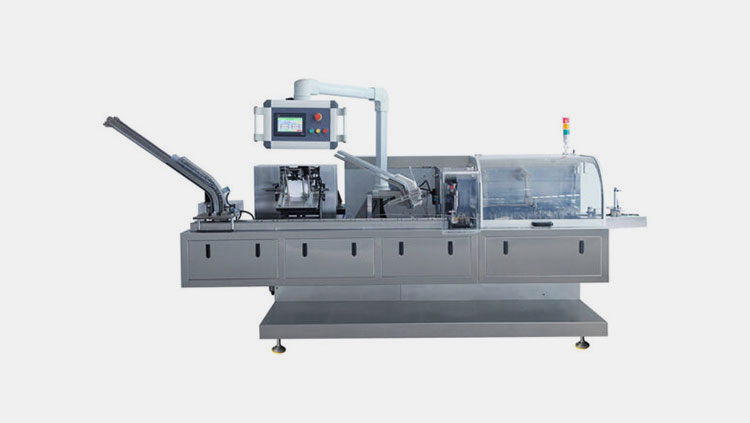

AIPAK high speed automatic cartoning machine
The final packaging of vials into their carton after filling labeling is done through high speed automatic cartooning machines which can pack vials and injections in carton with high speed and accuracy. The automatic machines make sure the proper insertion of leaflet, vial, proper sealing, traceability through batch coding and safe handling of the vial. This step is essential for the protection of vial and prepares the vaccine vials for distribution and further storage.
There are sensors which check the accuracy of cartons packed.
Pharmaceutical autoclave:
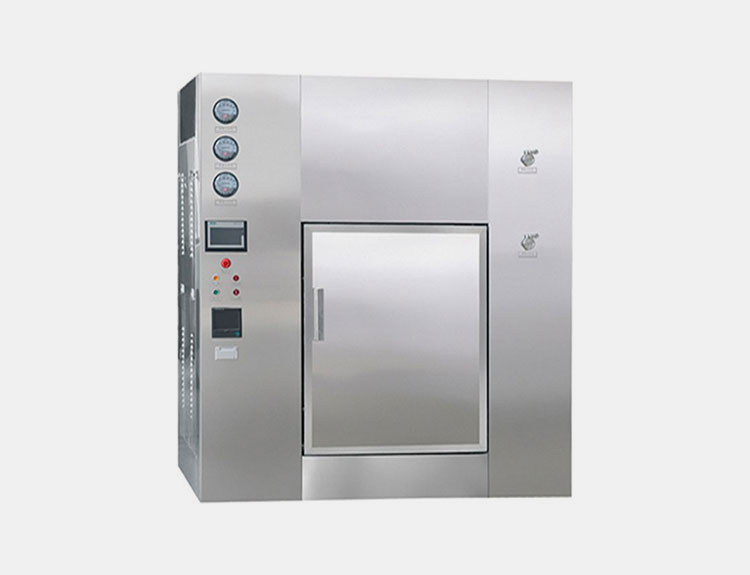

AIPAK dry heat autoclave
A pharmaceutical autoclave is used to sterilize any kind of equipment used during the sterile procedures. The products to be sterilized are placed in autoclave chamber. The saturated steam, which has a temperature of 121̊ C to 134̊ C, is injected into the chamber. The temperature and pressure of the chamber is maintained for 15-30 minutes for effective killing of the microbes. After that the steam and pressure is released slowly to get to a atmospheric level. The sterilized items are removed in a sterile environment to maintain aseptic filling of products.
7.What are the packaging and storage conditions of antitoxin vaccines?
Antitoxin vaccines cold chain system– picture courtesy: Research Gate
Temperature control:
Most of the antitoxin vaccines are to be stored at 2̊ C- 8̊C, which is standard refrigeration. It must be noted to avoid freezing of the vaccines as it can reduce the efficacy and destroy toxoid.
Cold chain maintenance:
The continuous temperature control and refrigeration is essential even during the transport of the vaccine to preserve its potency and avoid any kind of damage to the vaccine formulation.
WHO and UNICEF guidelines require strict monitoring of temperature throughout the supply chain of vaccines.
Following are the storage requirements of the antitoxin vaccines:
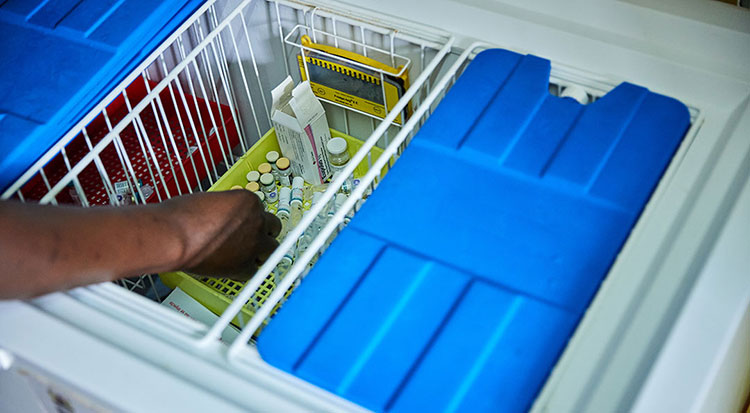

Cold storage for antitoxin vaccines –picture courtesy: Gavi
| Condition | Requirement |
| Temperature | 2°C to 8°C (Refrigerated) |
| Avoid Freezing | Because freezing can destroy the toxoid proteins. |
| Light Sensitivity | Direct light especially sunlight can affect the potency and efficacy. |
| Humidity | Should be controlled, especially for the lyophilized forms. |
| Cold Chain | It is integral part in storage and transportation and must be maintained from production to point of use. |
| Shelf Life | If properly stored, it is usually 2-3 years. |
8.What are the various delivery systems for the antitoxin vaccines?

Innovation in vaccines is the future of protection-Picture courtesy: technology networks
It must be great to imagine the vaccination procedure without the needles especially for children. So here the good news, vaccines are being produced other than the traditional shots, into smart and more adaptable forms, thanks to cutting edge technology and innovation.
These various news forms of the vaccines delivery systems also enables them to remain stable without high refrigeration and still training your body to fight against the toxin better than ever before.
Here are a few examples of the vaccines delivery systems:
Micro needle patches:
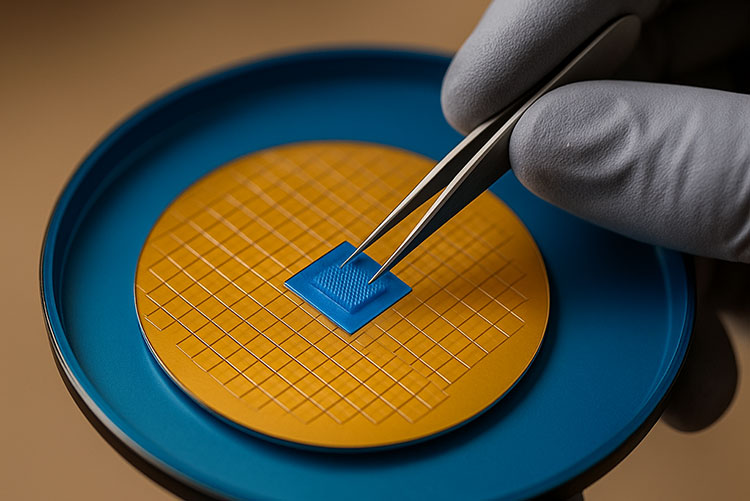
Micro needle patch
Micro needle patches or micro array patches are compact micro sealed devices, which are used to administer vaccines, drugs and other therapeutic agents into the human body without the use of conventional needle use.
They are micron sized needles constituted with the appropriate amount and formulation of the drug, and they are penetrated directly into the skin in a direction perpendicular to the plane of skin, and target an abundant amount of immune cells in the skin.
They are a best choice in especially remote areas due to their thermo stable characteristic and ease of self-administration, also making them cost effective.
Mucosal delivery:
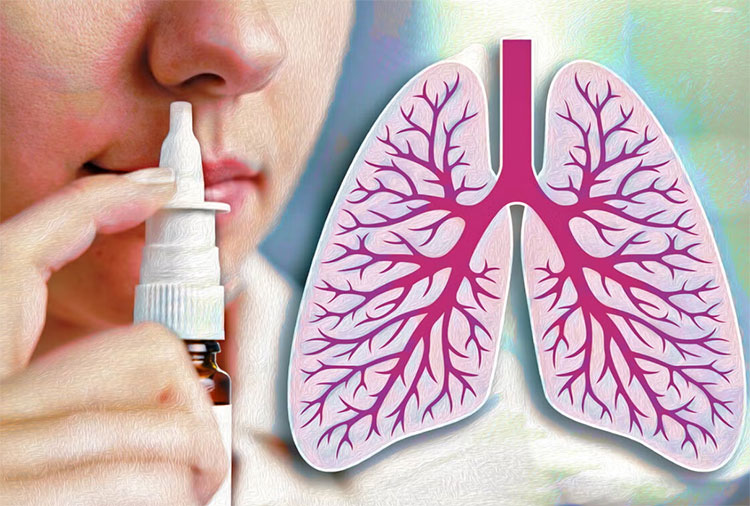
Drug delivery through nasal pathway-picture courtesy: Yale news
The mucosal delivery of vaccine means the delivery of vaccine through one of the mucosal routes, which are usually nasal or oral. This drug delivery system has a significant effect on the drug absorption, as this route can avoid hepatic first past metabolism, slow absorption and drug metabolism in the GIT.
The nasal route is very effective in respiratory infections, studies shows that nasal vaccines can trigger a strong immune response in the respiratory tract, without even the help of immune booster ingredients, adjuvants, in the vaccine.
A study at Yale school of medicine suggests:
“Viral proteins in nasal spray may be used as a safe way to promote antiviral immunity at the site of viral entry.”
Biodegradable implants or hydrogel:

Conductive hydrogel structure –Picture courtesy: scapa health care
Injectable polymeric nanoparticle hydrogel are used to provide a simple and effective way for delivery of the vaccines into the system. They provide a long term effect, by slow release mechanism and they also decrease the need of multiple doses.
The covalently cross linked hydrogels are not suitable for vaccines, as they cannot be easily administered, rather polymeric nanoparticles hydrogel (PNP) are supramolecular hydrogel, that are more suitable and provide greater drug loading capacity, gentle encapsulation and sustained drug delivery. The slow release system provides a long term exposure to the antigen.
9.Who should receive antitoxin vaccine?
Picture courtesy : AAAS
Antitoxin vaccines are equally important for children and as well as adults who need boosters, for pregnant women, travellers and high risk workers.
Protection against dangerous toxin producing bacteria is provided through these vaccines.
The target population for antitoxin vaccines includes:
Children:
Tdap vaccine –picture courtesy: alamy
The antitoxin vaccination is an integral part of childhood immunization. E.g. the Tdap vaccine for Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis is given to children of 10-12 years of age as a booster, while the vaccine DTaP (Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis) is given to infants before 2 years of age, in a series of well-defined doses.
Adults:

Picture courtesy: medical express
It is recommended in adults to have booster dose of Tdap or Td vaccine after every 10 years, for protection against tetanus and diphtheria. Td vaccine is given after wounds and injuries if one is not certain about tetanus protection. It is also given to the patients who can’t take Tdap vaccine, due to pertussis component.
Pregnant women:
Picture courtesy: Australian medical association
It’s a common perspective to have concerns about getting vaccines during pregnancy, but one dose of Tdap is recommended in the 3rd trimester of each pregnancy. Ideally, it is given in between 27 to 36th week of gestation as it maximizes the maternal antibody transfer to the baby and provides best protection.
Travelers to endemic areas:

Antitoxin vaccines are recommended for people who are about to travel in areas with poor vaccination coverage or who have toxins outbreaks, especially, the annual seasonal antitoxin vaccines should be essential part of your travel plan.
High risk lab workers:

Close interaction of the lab worker with specimen
It is important for the lab workers to receive antitoxin vaccines for any specific disease toxins they are being exposed to, e.g. clostridium tetani.
Prophylactic use of antitoxin vaccine:

Kid exposed to tetanus toxin due to fall on the road –Picture courtesy: shutterstock
Antitoxin vaccines have a very important role to be used for prophylaxis, in which it is administered to prevent the disease before even the symptom occurs, especially when the person has been exposed to the potential risk of toxin.
The very common cases of prophylaxis use of antitoxin are:
Tetanus prophylaxis, given after injury of a wound or burn which is likely to expose the body to clostridium tetani.
Another important use is Botulism prophylaxis, although this is not a routine vaccination, but antitoxin vaccines for it is given to people working in high risk environment, bio terrorism or foodborne incidents.
10.Are antitoxins vaccines same as regular vaccines?
Vaccine against toxins-Picture courtesy: Thalassemia international
Before explaining the difference of the antitoxin vaccine from a regular vaccine lets imagine our body as a high profile secure premises.
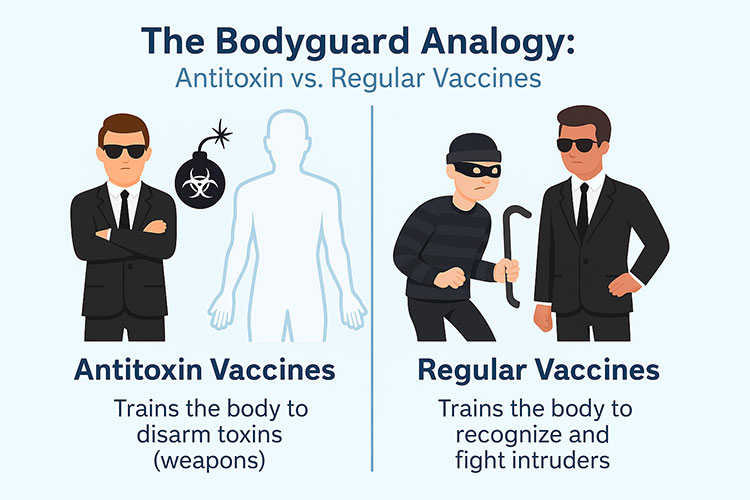
Antitoxin vaccine VS regular vaccines
Regular vaccines:
Normally the regular vaccines are bacterial or viral substances, sometimes they are live, modified and attenuated in least strength unable to cause any disease, or sometimes they are dead. They are produces by selecting those strains of bacteria and virus which can trigger an immune response but themselves cannot cause any disease. These vaccines train your body to recognize and fight the attacking pathogen, also making the body remember these intruders for a very long time.
Live vaccine:
When the vaccine is produced from a live pathogen, they are called live vaccines, in this case the body immune system react very well to these pathogens, and memory cells remember these intruders for a very long time, which causes no need of boosters or additional doses. E.g. in case of measles, mumps and chicken pox vaccine.
Inactivated vaccine:
The regular vaccines which have the inactivated pathogen strain are called inactivated vaccines. They can still produce the immune response without causing the disease. In this case, multiple doses can be needed for complete immunization and boosters are also required. E.g. polio and influenza vaccines.
Antitoxin vaccine:
Antitoxin vaccines use neutralized toxins to target the toxins produced by bacteria, rather than targeting the bacteria. The goal is to provide a way to neutralize the toxins with antibodies through the vaccination. They offer a short term passive immunity, as explained earlier.
The antitoxin vaccine is pre formed anti bodies and they directly attack the toxin, providing an immediate response. But this response is short term and can require the booster dose, usually after a period of 10 years.
In simple words we can say antitoxin fight for the body, rather than making the body fight, and provide immediate response.
11.What type of immunity is produced by antitoxin vaccines?

Picture courtesy: Yale medicine
The antitoxin vaccines produced passive immunity.
Passive immunity:
Passive immunity refers to receiving the antibodies from an outside source rather than body itself creating the antibodies. Passive immunity could be natural, that is passed down from the mother to the baby and artificial passive immunity is the one which is produced through these antitoxin vaccines.
The immunity produced through antitoxin is short termed but immediate that’s why it is used in situations where immediate protection is needed.
12.What are the innovations in antitoxin vaccine formulation?
A beautiful illustration of antitoxin defense in action –Picture courtesy: Pfizer
In today’s world, where there is a rise of drug-resistant infections and surge in the potent toxins, the traditional vaccines alone cannot fight against them. Therefore, as the germs evolve so does our defense mechanism. There is a significant advancement in the innovation of antitoxin vaccine formulary and delivery.
This innovation has led to the ease of administration, increased efficacy, safety and stability. Brief information about the key innovations is given below:
Recombinant antitoxin vaccine by recombinant DNA technology:

DNA
The traditional way or producing antitoxin vaccines is using neutralized or dead toxins but the recombinant DNA technology helps to create nontoxic variants of the specific targeted toxin, which still have the ability to trigger the immune response. This help creating a vaccine with more purity and less side effects.
The most common example of the recombinant DNA antitoxin vaccine is recombinant diphtheria and tetanus toxoid.
Nano particle based formulations:
Drug delivery through nano particles –Picture courtesy society for brain mapping
Nano particles based formulations which are usually liposomes, metallic nano particles or polymeric nano particles, they work by encapsulating the toxoid, the weaken version of toxin.
This formulation increase the stability of the product, also providing a more controlled release of the vaccine and the uptake of the toxoid by the specific antigen presenting cell is enhanced.
Adjuvant enhancements:
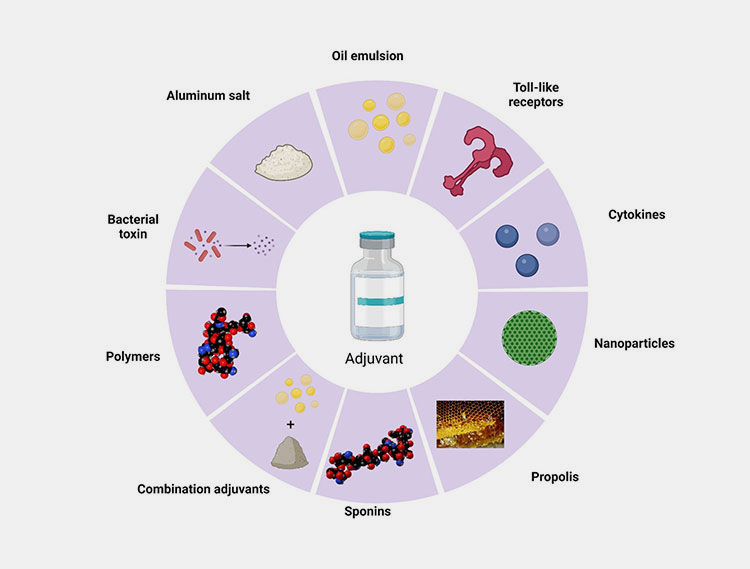
Different types of adjuvants –Picture courtesy: frontiers
Adjuvant is the substance which is added to the vaccine to enhance its immune response and it makes the vaccine more effective. They work by triggering the body immune to identify the vaccine antigen more effectively which leads to a stronger and effective immune response.
The adjuvants have been in use in the vaccines for decades. Aluminum salts are the most traditional adjuvants. The innovative adjuvants like ASO4, MF59 or saponin based adjuvants boost the immune response more effectively.
Multiple epitope vaccine:
Image showing different type antigen attaching to antibody –Picture courtesy: Bio World
Epitope is the part of antigen molecule or you can say the foreign particle, which attaches to the antibody and stimulate the immune response.
The multiple epitope vaccine is an advance form of antitoxin vaccine, in which epitopes of different toxins or pathogens are combines together in a single vaccine.
For example, tetanus-diphtheria-pertussis (TDaP) vaccines include pertussis along with tetanus, diphtheria toxoids.
13.What are the quality control standards and regulatory approvals required for antitoxin vaccines production?

Lab workers in the sterile area – picture courtesy: the Irish times
Source Validation
To verify the purity and complete removal of any kind of contaminants, the source of the pathogen, especially if it is from an animal source is screened for purity validation.
Toxin Neutralization Testing
In order to verify, whether the antitoxin is effective enough to neutralize the toxin, in vitro and in vivo assays are done before making it available for the commercial use.
Sterility Testing
The vaccine should not have any kind of microbial contamination; therefore sterility testing is done according to given SOP.
Endotoxin Limits
The different type of vaccines has different endotoxin levels. FDA has provided guidelines about the combination of the vaccines. Therefore, the final product must be in accordance to the endotoxin level criteria, especially if derived from bacterial cultures.
Stability Testing
The stability of an antitoxin vaccine is defined by it shelf life. The evaluation of shelf life is done to ensure that the vaccine remains effective under recommended storage conditions.
Following are the regulatory approvals required for the production of antitoxin vaccines:

The GMP guidelines should be followed by the manufactures to ensure controlled and hygienic environment.
Whenever a new recombinant antitoxin vaccine is produced, preclinical and clinical trials are made before starting the manufacturing for commercial use.
There are licensing authorities like FDA, WHO or as per according to the country, every country has its own licensing authority, whose approval is needed for production of antitoxin vaccines.
Every batch of the antitoxin vaccine being produced has to undergo official batch release testing, and the documentation is verified and approved by the national control labs.
To ensure and monitor long term safety and any kind of adverse effects, it is mandatory to have post marketing surveillance.
Conclusion:
Now we have understood enough to know about the importance of antitoxin vaccines. They are a vital tool in the modern medicine and they offer rapid and targeted protection against the bacterial toxins. Unlike the traditional vaccines, antitoxin vaccines offer immediate effects, especially in emergency conditions or when the body has already been exposed to the toxins. The production of these vaccines is although a complex procedure and there are also strict regulatory standards to ensure their efficacy and safety. The ongoing innovations in formulations and the delivery system as well as the machinery used in the preparation of antitoxin vaccines, the future of antitoxin vaccines seems to be at a safe place. For more information about the production of these antitoxin vaccines contact our AIPAK ENGINEERING team now.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours