Animal Vaccine Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Have you ever heard about animal vaccines? You must have. Due to infections, many animals get sick every year, resulting in thousands of animal deaths on farms, ranches, and in the wild. Like humans, vaccines are also made for animals to immunize them against pathogens.
Are you wondering about the ingredients of animal vaccines? How are they made? Well, we’ve got the answer to your questions and more in this guide “Animal Vaccine Manufacturing: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025”.
If you’re a pharma manufacturer, student, or animal vaccine user interested in discovering every secret behind animal vaccine manufacturing, this blog post will serve as your backstage pass to various steps, equipment, ingredients, and, more in this process. Ready? Let’s get our reading goggles on!
1.What is animal vaccine manufacturing?
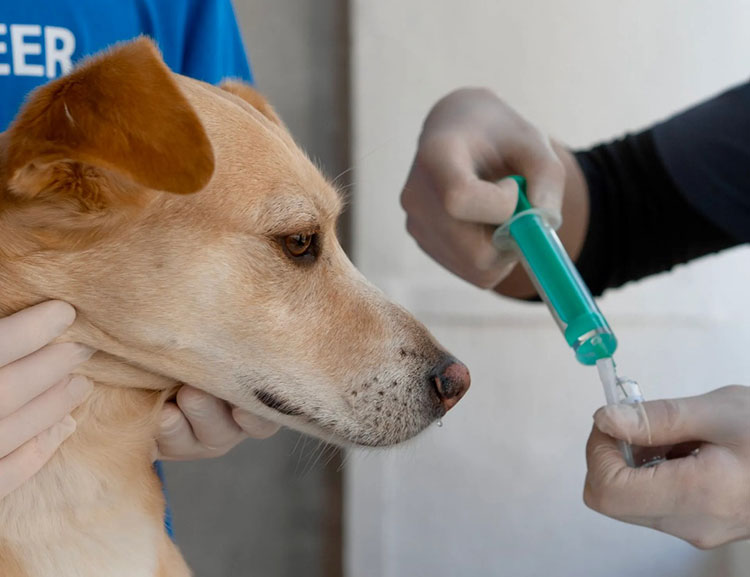
Animal Vaccine Manufacturing- Picture courtesy: LPS BioScience
Simply, you can define animal vaccine manufacturing as a complete operational procedure, carried out for the making of animal vaccines. These vaccines are regularly used every year in order to protect animals against deadly outbreaks of viruses, bacteria, and parasites.
Hence, animal vaccines are integral in stopping the spread of infections and saving the health of animals. You can imagine animal vaccine manufacturing as complex industrial-scale operations occurring in factories to prepare an immune-boosting vaccine for pets as well as farm animals.
2.In what ways does animal vaccine manufacturing benefit society?
In order to appreciate the true value of animal vaccine manufacturing, you must consider its benefit to society. So, in the following section, we’re penning some of its significant contributions to society, which will aid in the growth and health of communities.
Less Suffering for Animals

Less suffering for animal
Yes, obviously, it is one of the main and most direct advantages of animal vaccine manufacturing. As you know animal vaccines are developed to protect animals from a variety of infections. This aids in lowering the suffering and death of animals as well as sparing them from extreme pain, discomfort, and, body stress.
Controlling the Spread of Diseases
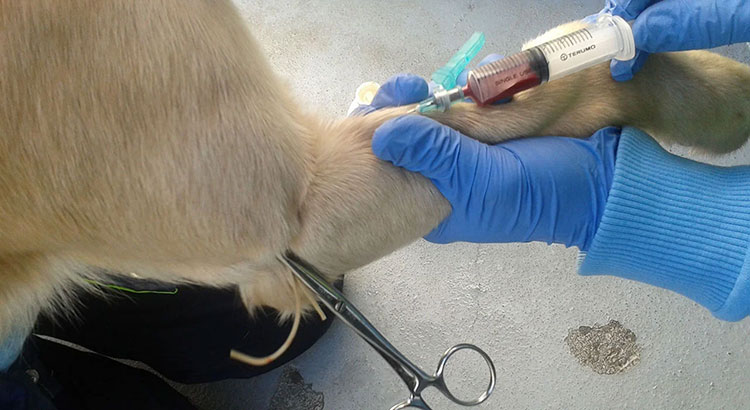
Controlling the Spread of Diseases- Picture courtesy: Techtitute
You may have watched the news of the transmission of avian flu from birds to humans. This holds true for other illnesses, like rabies, salmonella, and, brucellosis. In fact, many animal infections jump species and transfer to humans. These infections have a specific name called zoonotic diseases. So, vaccinating animals means protecting humans as well. Because animal vaccines are essential in breaking the spreading cycle.
Animal Free from Pathogen

Animal Free from Pathogen
If you’re a nonvegan individual, surely your major food source will be animal-based products. Due to animal vaccine manufacturing, vaccines are prepared, which keep livestock safe and disease-free. This prevents the pathogen contamination in milk, meat, and, eggs and improves food quality.
More Animal Growth and Output
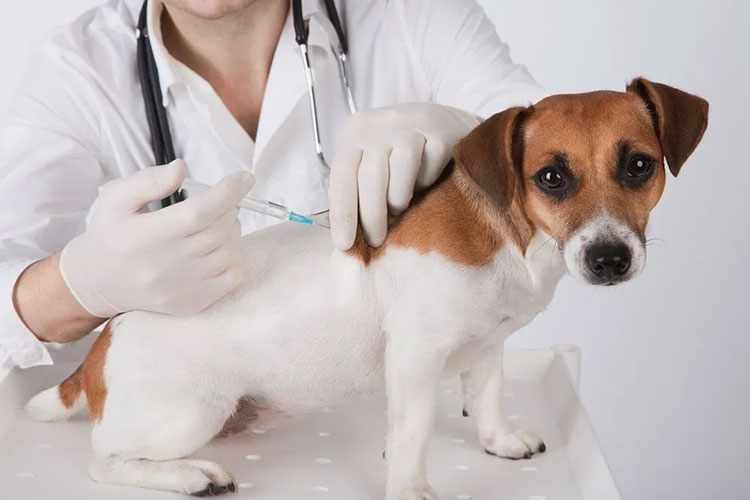
More Animal Growth and Output
Countries are always in the pursuit of strengthening their economies. In many countries, a strong agricultural system positively contributes to the growth of the economy. You can enhance the yield of agriculture by keeping your animals healthy by vaccinating them. It is seen that vaccinated animals tend to grow and reproduce better as well as produce more milk and eggs. This in turn brings more profits for you as a farmer and food producer.
Less Death in Animals

Long Life of Animals- Picture Courtesy: Perth Vet Pet
With the outbreak of diseases in animals, you’ll notice the decimation of large herds and flocks. Many farmers or ranch owners face severe financial damages because of their animal deaths and decreased animal product formation. Also, you and your fellow farmers will have to spend a large amount of money to treat diseases. However, by immunizing your animals, you can minimize these losses.
3.Can you describe the sequence of steps in animal vaccine manufacturing?

Steps of animal vaccine manufacturing- Picture courtesy: Cannington vet
Just like other pharmaceutical manufacturing, animal vaccine manufacturing is an extremely complicated operation with a number of distinct stages. And every step, without exception, needs great care and should be performed according to global standards. So, here is the complete detail of each stage in animal vaccine manufacturing for your knowledge:
Discovery Phase
No matter what type of animal vaccine is being prepared, usually first step is always the selection of the right kind of antigen from the host-pathogen (virus, bacteria, and parasite).
Preparation of Desired Antigens
| Cultivation | This step serves as the beginning of actual vaccine creation. In this step, manufacturers take either working seeds or cultures from a working cell bank with a host pathogen and place them in large bioreactors. Specialized nutrient media is included in these tanks to grow the pathogens. |
| Growth and Reproduction | Once you’ve introduced the pathogen, these grow and reproduce by feeding on media and producing your desired viral proteins. |
| Harvesting | As soon as you notice that your required concentration of pathogen or viral protein is attained, you’ll harvest your cultures from bioreactors. In this step, you just separate cells, viruses, or antigens from liquid media. |
Downstream Processing
| Clarification | Normally, before purification, you’ll use different techniques, like centrifugation or filtration to clear out suspended particulates or cell materials from harvested components. |
| Purification | The above step doesn’t fully remove impurities from the main antigen solution. So, methods, like chromatography, membrane filtration, or, crystallization are employed to entirely eliminate smaller impurities, for instance, small protein molecules, host genetic materials, and others to obtain pure antigens. |
| Inactivation | This is the stage only in the killed animal vaccine manufacturing. You’ll either heat or chemicals, such as formalin to inactivate purified pathogen. Careful handling is necessary to only make it non-infectious while upholding its immunogenicity. |
| Concentration | Sometimes, you’ll get a small quantity of pathogens or antigens after purification. To fix this, you must concentrate a pure solution containing antigen and evaporate the solvent to have a concentrated form of antigen. |
Mixing
It is an actual formulation step. Where you’ll correctly mix your active components with solvents, adjuvants, stabilizers, preservatives, and, other excipients to have a liquid animal vaccine.
Filling
The filling stage is where your animal vaccine packaging starts. You will fill your vaccine products in sterile vials sterile under aseptic conditions. Hence, sterile cleanrooms fulfilling ISO class 5 standards are a must for this step.
Stoppering and Capping
In case you need your final product in liquid form, vials are completely sealed in this step with rubber stoppers and crimps seals. On the contrary, for dry powder animal vaccine, after filling, vials are only sealed with rubber stoppers and are transferred to a lyophilizer.
Freeze-Drying
You must have seen white powdery animal vaccines in vials on pharmacy shelves. Ever wondered how they get in this form? For this step, you’ve to vaporize water from products frozen under subzero temperatures (-40°C or -60°C) and vacuum conditions. After that, you’re left with dry powder.
Labeling
Vials don’t have just animal vaccines but are also labeled with clear product facts. That’s why, after sealing, vials are moved to a vial labeler that applies pre-glued stickers on vials. Also, you’ll see that hot melt or cold glue is also used for sticking labels in this step.
Cartoning
Finally, the boxing of labeled vials occurs. Simply, cardboard or paperboard materials are erected and folded so that vials are placed in them. Afterward, they’re sealed with tape, stapler pins, or glue. You can also use premade boxes for storing and transporting your vials.
4.What are the major machines that you’ll use in animal vaccine manufacturing?
Obviously, it’s not the job of one machine. But you see a wide array of machines operating together in animal vaccine manufacturing to make products. Always remember to ensure sterile conditions to prepare effective animal vaccines. Now, let’s together have read about various devices seen in this production:
Preparation of Desired Antigen
| Bioreactor
Bioreactor- Picture Courtesy: Chemistry World |
Are central when preparing antigen batches. You can imagine them as huge tanks of various sizes for both small- and large-scale manufacturing. In these tanks, you can load hundreds or thousands of liters of media to cultivate various types of cells. Nowadays, you can get single-use fermenters that are disposed of after one use. |
| Centrifuges
Centrifuge- Picture Courtesy: New Scientist |
As you know by now harvested materials are full of impurities so you must separate large particulates from the cellular substances with the use of a centrifuge. High rotation speeds in this machine generate centrifugal forces that drive the separation of substances based on density. |
| Homogenizers
Homogenizer- Picture Courtesy: Ollital Technology |
In this system, cellular components are loaded and broken apart. In this way, intracellular proteins (antigens) are released in the media. |
Downstream Operating Systems
| Filtration Units
Filtration Devices- Picture Courtesy: Water Technology |
These units are all-in-one systems with which you can carry out various steps, such as clarification, concentration, as well as purification of antigens in one machine. |
| Chromatography Systems
Chromatography Columns- Picture Courtesy; Buchi |
One of the most vital systems for purification. Generally, has numerous sets of columns filled with resins. It assists in the purification of required antigen on the basis of its molecular weight, net charge, non-polar nature, or, binding affinity. |
Auxiliary Devices
Water Treatment System
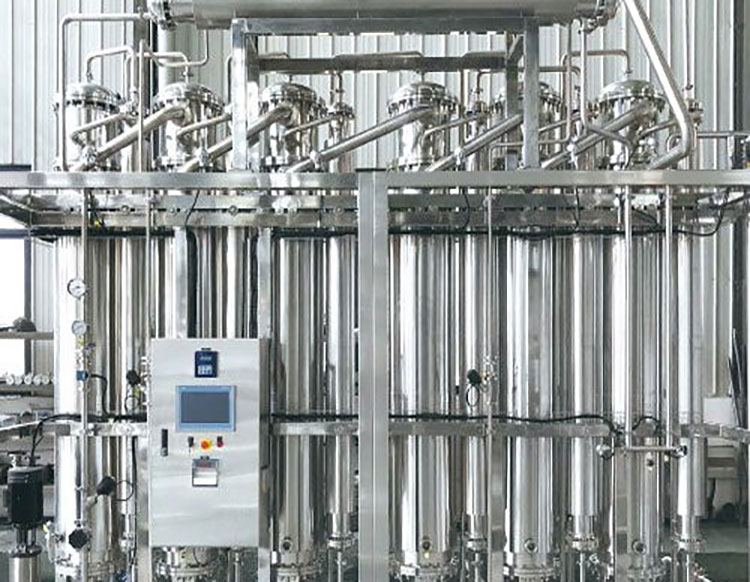

AIPAK ENGINEERING Water Treatment Plant
Without ultrapure water, you can’t have pure animal vaccine. So, you must use a water treatment plant to remove impurities and contaminants from your water source. With the setting up of these units, you can obtain 99.9% pure water. This water is then used for formulating sterile water for injection.
Mostly, this system is comprised of distillation units, reverse osmosis devices, steam generators, and, others.
CIP/SIP System
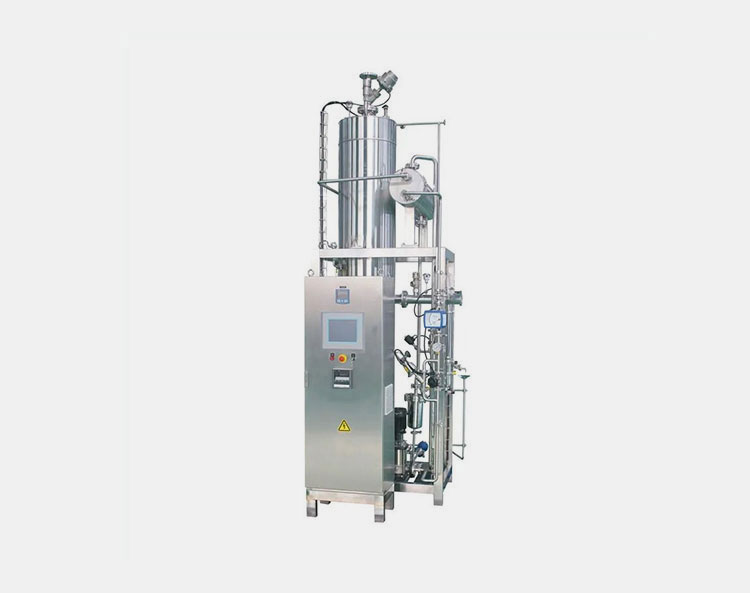

AIPAK ENGINEERING Clean Steam Generator
Proper cleaning of machines is an absolute must in animal vaccine manufacturing. So, with the installation of clean-in-place or sterilize-in-place systems, you can effortlessly and entirely clean your other machine components. Many of these units have integrated steam generators. The latter uses deionized water and converts it into steam to disinfect various machines.
Lyophilizer (Freeze-Dryer)
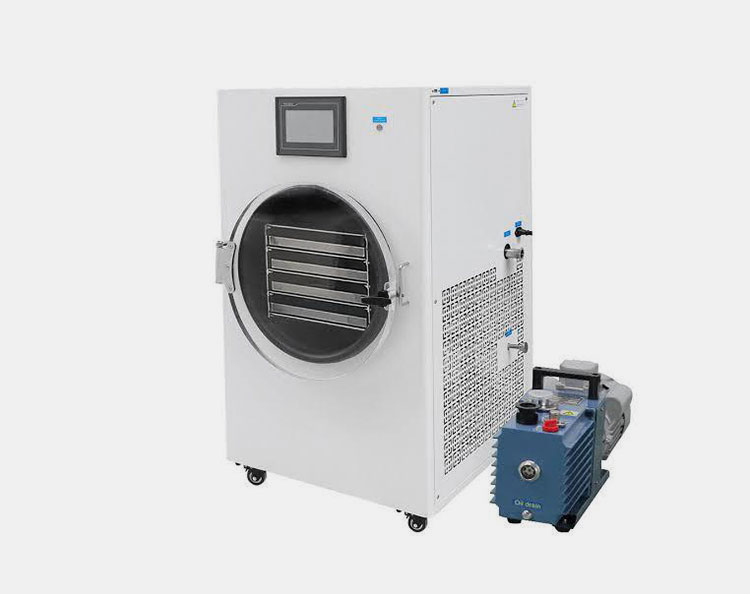

Freeze-Dryer
For freeze drying of animal vaccines, you must install a lyophilizer in your plants. The evaporation of solvents occurs in three stages- freezing product, primary drying, and secondary drying. To put it in simple words, you’ll freeze your vaccine by placing it in a machine under vacuum conditions. After complete freezing, temperatures are raised to transform frozen water into gaseous vapors. In this way, you’ll get white powder of animal vaccines.
Vial Filling Line

AIPAK ENGINEERING Vial Filling Line
Surely, you can consider a vial filling line as the heart of animal vaccine manufacturing. Why? Because you can’t pack your vials without it. Many people mistakenly believe that it is a single unit. On the contrary, it is a complex unit with several machines detailed in the table below:
| Vial Unscrambling Unit | At the starting point of the vial filling line, you’ll spot a vial unscrambling unit. Imagine it as an organizer because in its hopper, vials are randomly placed and this machine organizes them in the correct configuration and positions them in an upright manner with a constant distance between vials on the conveyor. |
| Ultrasonic Washing Machine | With the use of high-spray water jets and high-frequency sonic waves, this unit is deployed to wash and clean every vial. |
| Depyrogenation Tunnel | A large tunnel-like assembly present after an ultrasonic washing machine is known as a depyrogenation tunnel. Your vials are sterilized using hot air in this unit. It disinfects every microbial cell and its product so that no microbial growth is found in vials. |
| Filling and Stoppering Device | Lastly, there is a filling and stoppering machine. You’ve guessed it correctly; its job is to load animal vaccines in vials. After filling, stoppering components affix rubber stopper on vials to secure them. |
Pharmaceutical Autoclave
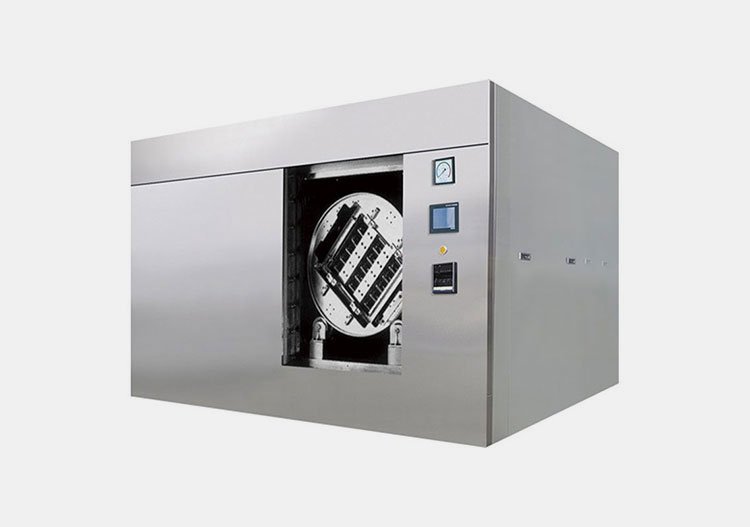

AIPAK Engineering Pharmaceutical Autoclave
To ensure sterility of the animal vaccine manufacturing, after filling and sealing, the final product has to be passed through a pharmaceutical autoclave machine. It works by inducing high steam and pressure which is helpful in the rupturing of the microbial cell membrane and makes them inactivate and ultimately die. It is capable of raising temperature usually 80 to 121 degrees centigrade which is suitable for microbial cell death hence ensuring a sterile product.
Vial Labeler
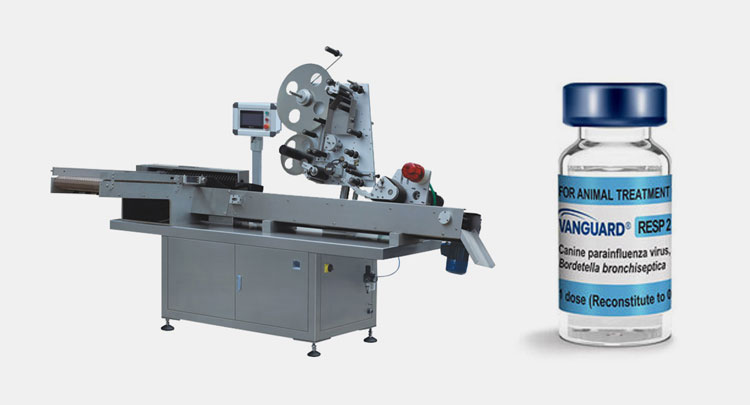

AIPAK Vial Labeler
For labeling required information on vials, you’ve got a vial labeler in your production. Its job is to affix labeling film at the center of the vial, generally in a wrap-around pattern.
Cartoner

AIPAK Cartoner
At last, your animal vaccine vials are loaded and sealed in durable boxes using a cartoner. Sometimes, it uses already-made cartons, or usually, it forms the carton itself by folding and erecting cardboard or paperboard materials.
5.What are the core ingredients required in animal vaccine manufacturing?
No animal vaccine doesn’t only have antigens. Instead, you’ll learn in the following section that there are a multitude of ingredients in its preparation, mixed together to obtain a highly effective immunogenic agent. A complete list of ingredients is written below:
| Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient | This ingredient is one that induces an immune response in the body when the vaccine is given to animals. So, you can think of it as an active component of animal vaccines. Often, antigens are of two main types- complete pathogen and subunit antigen. |
| Adjuvants | Generally, antigens by themselves aren’t enough to generate desired immune responses. That’s why, you’ve adjuvants in the animal vaccines. For example, aluminum salts, oily emulsions, saponins, and pathogen molecules act as adjuvants.
They with the help of antigens stimulate a stronger, extended, and, broad-spectrum immunity, so you may inject smaller or fewer doses into animals. |
| Stabilizers | To protect active components during handling, shipment, storage, or, retailing, you’ll add stabilizers in animal vaccine formulation. Especially, they’re used in cases when the end product has to face temperature changes. Gelatin, glycine amino acid, and sucrose are common stabilizers. |
| Preservatives | Included regularly in the multi-dose animal vaccine vials. The reason is that these vials are more suspectable to the growth of bacteria or molds, as they may enter into the vaccine due to puncturing of the vial stopper multiple times. But you’ll not find preservatives in single-use vials, since the latter are meant for single-use and then are disposed off. |
| Diluents | Yes, you may also know them by the name of solvents. Diluents are liquid agents that are added to animal vaccines to dissolve antigens and other vital ingredients. One of the most common solvents is sterile water for injection. Also, buffers are found in this preparation to prevent pH fluctuation. |
6.Are there any different forms of animal vaccines that you can produce from animal vaccine manufacturing?
Yes, absolutely! Animal vaccines are not available in one form. With innovation in microbiology, researchers have discovered a variety of animal vaccine types. Below are some major types that you may produce from animal vaccine manufacturing:

Different Forms Of Animal Vaccines- Picture courtesy: Broome Veterinary Hospital
| Live attenuated Vaccine | Although it is made with completely live organisms either bacteria, viruses, or pests, the host organism is weakened by various means. Consequently, you may call it an attenuated vaccine, as pathogens can divide in animals but don’t cause disease in them. |
| Inactivated Vaccine | As the name suggests, this type of vaccine is made by killing or inactivating host pathogens with the use of harsh chemicals or heat. Thus, they can’t reproduce and grow. They still have their antigens that elicit immune response. |
| Toxoid Vaccine | Produced from inactivated toxins expressed by some bacterial strains. The inactivation of toxins is done by treating them with heat or chemicals. By this, its virulence is removed but this toxin is still able to stimulate immune defense in an animal body. |
| Subunit Vaccine | In this vaccine, you’ll use specific fragments of pathogens instead of an entire pathogen. These pieces (proteins) are specific to a particular pathogen against which the vaccine is designed. Hence, the subunit vaccine is quite safe with little side effects. |
| Recombinant Vaccine | Just like subunit vaccines, it also uses particular pathogen parts. Your chosen antigens are created through genetic modification of other organism cells, for instance, yeast, bacteria, mammals, or insects. Pathogen genes are inserted in these cells to express the desired antigen. |
| mRNA Vaccines | The latest development in the field of an animal vaccine. And are made with mRNA molecules that encode antigens. When this vaccine is given to animals, their cells will produce antigen protein themselves by using mRNA. This triggers the immunity. |
7.How to store animal vaccine manufacturing formulation?
If you’re a farmer or a pet owner, this question will certainly come to your mind. For those of you treating animals on a routine basis, you would be familiar with the fact that proper storage of animal vaccines after their manufacturing is a failsafe way to ensure their long life. Here are major storing tips for you to protect the lifespan of your animal vaccines:
Storage-Picture Courtesy: Ringwood Veterinary Clinic
Keep Them Chilled Always
The golden rule is to always store your vaccines in chilly conditions with temperatures of 2°C to 8°C. For transportation, keep them in reliable fridges or portable coolers. Also, remember to equip these cooling devices with digital thermometers to monitor storage temperature. And never ever freeze your vaccine. You can only do so, it is specifically stated on the information panel to freeze it.
Abide by Expiry Date
Vaccines aren’t like honey that doesn’t age. Once their expiry date has passed, it’s time to throw them out. So, make sure to check the label expiry date before giving it to animals.
No Sunlight and Heat
Don’t expose animal vaccines to high heat or sunlight because they deteriorate vaccine antigens. It is best to place them in a dark and cold place. Remember to keep them out of hot cars, open sheds, and machines.
8.Is there any difference between monovalent and multivalent animal vaccine manufacturing?
Monovalent And Multivalent Animal Vaccine Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: MSD Animal Health
Since both these kinds of animal vaccines are vastly diverse from each other, so, you’ll find that monovalent and multivalent animal vaccine manufacturing is quite different from one another. You can learn some of these differences below:
| Aspect | Monovalent Animal Vaccine Manufacturing | Multivalent Animal Vaccine Manufacturing |
| Antigen Preparation | Only concerned with one type of antigen. You can easily purify your selected antigen. | This animal vaccine manufacturing type prepares two or more antigens, normally from different strains of the same pathogens or from various pathogens altogether. Difficult to purify these said antigens. |
| Formulation | Relatively easier to make a product, as there are fewer interactions between ingredients. | You’ve to conduct compatibility studies to make sure antigens and adjuvants don’t affect each other in any way. |
| Complexity | Manufacturing is less complex. Has straightforward quality control and analysis procedures. | Very complicated, as it involves hectic mixing techniques, stability testing, as well as possible cross-reactivity between ingredients. |
| Testing | Quick testing because of fewer components. | You’ve to test each antigen separately as well as in combination to ensure the effectiveness of vaccines. |
| Time and Expense | Lower cost and shorter operational time. | More costly and has lengthy lead cycles. |
9.How can you explain GMP for animal vaccine manufacturing?
GMP For Animal Vaccine Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: Head Up to Tail
Do you know that GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices? Simply, you can define it as a set of strict quality protocols and safety standards that every manufacturer has to follow in order to make animal vaccines. And with GMP, you can ensure your customers that every dose is safe, pure, and effective.
To fulfill GMP standards, you must implement sterile rooms with HEPA filters in your production. This prevents dust, microbial, and particulate contamination. Validate each operational stage, such as mixing, harvesting, filling, etc. by testing, recording, and, approving it.
Also, start regular training programs to equip your staff with the necessary skills to operate machines and supervise their operations. And yes, document everything from batch records to cleaning shifts. In addition to this, test the quality of every ingredient before using it.
10.What are the principal challenges that you face while animal vaccine manufacturing?
Principal Challenges- Picture Courtesy: Veterinary Product
Well, you should know that animal vaccine manufacturing is not like a walk in the park instead you might’ve to face many problems while creating vaccines on a mass scale. Rest assured these problems have clever solutions with which you can resolve former in no time. Some of the principal challenges and their remedies are detailed in the following section for your ease:
Microbial Growth
| Problem | Fix |
| There may be a chance of microbial growth while preparing antigens or filling vials. Which will not only ruin the whole vaccine batch but also result in monetary loss. And pose a severe health risk to animals. | To remedy this issue, you must carry out the following steps:
First of all, perform manufacturing in an ISO-certified cleanroom. Also, these rooms must have installation of HEPA filters and clean sterile machines. Regularly test your working environment to ensure it has particulate levels are within the specified limit. Lastly, make sure to train your staff on safety protocols. |
Variable Antigen Output
| Problem | Fix |
| This a major problem, because you don’t always get the same amount of antigen when culturing or fermentation. Consequently, you will have trouble meeting your planned product order or ensuring its potency. | What you can do in this case? Don’t worry, here are a few handy ideas for you to solve this:
You can get consistent antigen quantity by optimizing the nutrient media in the bioreactor and controlling its inside environmental conditions. Another thing you may do is to use seed strains that don’t mutate frequently. Furthermore, it is best to employ monitoring and automation approaches for culturing and harvesting. |
Antigen Change Frequently
| Problem | Fix |
| Did you notice the degradation of antigens during their processing? Indeed, they may get weak, lose their strength, or become less effective when they’re being handled, stored, or shipped. | Try these suggestions to resolve this issue, for instance, you should add stabilizers like trehalose or gelatin. Besides this, you may include buffers to stabilize pH. Always store your packed vials in cold chain settings with a temperature of 2–8°C or colder. Moreover, if your product degrades quickly, freeze-drying may be suitable for it. |
Labeling Errors
| Problem | Fix |
| Are you spotting the wrong label placement on vials? Like they’re upside down, creased, or, peeing off. Or do your vials have missing batch info? All these problems cause regulatory nightmares, financial penalties, loss of standing in the markets, as well as, batch recalls after delivery. | You can address these challenges by automating your labeling equipment with vision-assessing sensors. Furthermore, with the installation of barcode scanning devices and batch tracking units, you can prevent labeling mix-ups. Always use label films that are compatible with your packaging container. |
Conclusion
Now that we reach the end of this article, one thing must be crystal clear to you animal vaccine manufacturing is not as simple as you may’ve thought. In fact, it involves various carefully regulated steps. For this, each step- from strain selection to boxing of final vials, requires automated machines and other quality-checking systems. And you can acquire these high-quality machines from AIPAK ENGINEERING. We offer a complete selection of machines for animal vaccine manufacturing, designed to fulfill your varying processing requirements.
Don't forget to share this post!
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours