Injectable Anesthetics: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Anesthesia is widely used in clinical practice, but many people are unaware of the relevant knowledge of clinical anesthesia and still have a fear of it, which affects the patient’s cooperation between anesthesia and surgery.
Injectable anesthetics is a common method of surgery, which can alleviate patients’ pain and keep the body in a suitable state for surgery. How much do you know about injectable anesthetics? Do you understand its production process and equipment? Are you interested in this injectable anesthetics?
Next, let’s learn about the complete FAQ guide of injectable anesthetics together.
1.What Are Injectable Anesthetics?
Injectable Anesthetics - Sourced: Anesthesia Services
Anesthetic refer to drugs that have an anesthetic effect on the central nervous system, and can be used continuously, abused, or improperly, leading to physical and mental dependence and addictive tendencies. In general, commonly used anesthetics include lidocaine hydrochloride injection, procaine hydrochloride injection, lidocaine hydrochloride injection, bupivacaine hydrochloride injection, ropivacaine hydrochloride injection, etc.
Injectable anesthetics are mainly injected intravenously or intramuscularly. Intravenous injection is the process of injecting anesthetics into the bloodstream, which act on the central nervous system through circulation, exerting an anesthetic effect and causing the patient to lose consciousness, systemic pain sensation, forgetfulness, reflex inhibition, and skeletal muscle relaxation.
2.What Are the Types of Injectable Anesthetics?
Anesthetic drugs can be classified into various types based on their site of action and effectiveness. Local anesthesia and general anesthesia are common anesthesia methods, with differences in anesthesia scope, applicable surgery, risk level, recovery time, cost, and other aspects.
Types Of Injectable Anesthetics - Sourced: The Pain Source
| Item | Local anesthetics | General anesthetics |
| Anesthesia scope | Local anesthesia mainly causes local areas of the body to lose consciousness, and patients may remain awake during the surgical process. | General anesthesia is the process of causing the patient to completely lose consciousness and enter a state of sleep. |
| Applicable surgery | Local anesthesia is suitable for some local surgeries, such as hernia repair, limb surgery, etc. | General anesthesia is suitable for larger surgeries such as open chest and abdominal surgeries. |
| Risk level | The risk of local anesthesia is relatively low. The impact on the body is relatively small. | The risk of general anesthesia is relatively high and may have certain effects on the respiratory and circulatory systems. |
| Recovery time | The recovery time is usually short. | The recovery time of patients after general anesthesia is relatively long. |
| Cost | The cost of is generally lower than that of general anesthesia. | In contrast, the cost of general anesthesia is higher. |
3.What Are the Functions of Injectable Anesthetics?
The mechanisms of action of anesthetic drugs are diverse, but overall, they all achieve the goal of temporarily paralyzing the body or a specific part of the body by affecting the function of the nervous system.
Nerve block
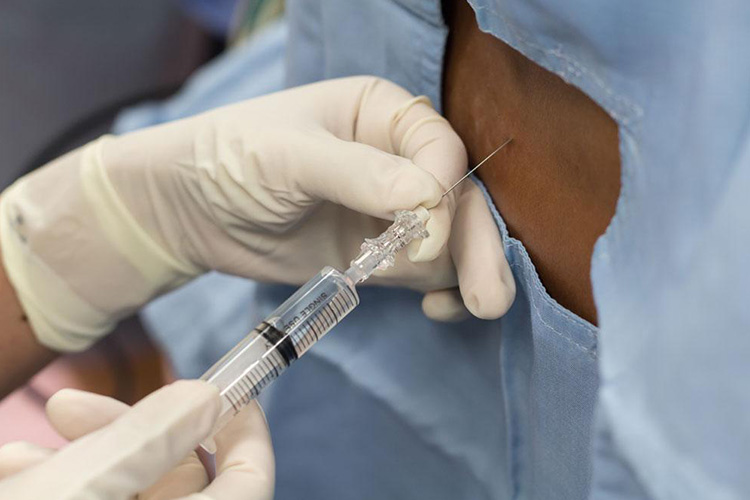
Nerve block - Sourced: West Texas Pain Institute
Local anesthetics achieve the effect of local anesthesia by interfering with the permeability of nerve fibers, preventing the generation and transmission of nerve impulses. After injecting local anesthetics, the patient’s pain in the surgical area will disappear, but consciousness will still remain clear.
Inhibition of the central nervous system
General anesthetics produce anesthetic effects by affecting different parts of the central nervous system, such as the cerebral cortex, brainstem, spinal cord, etc. Drugs have inhibitory effects on the central nervous system, leading to the suppression of brain and spinal cord function. This inhibition manifests as loss of consciousness and disappearance of pain sensation, making patients feel no pain or discomfort during the surgical process.
Calming and forgetting
Calming and Forgetting - Sourced: Harvard Gazette
General anesthetics also have sedative and forgetting effects. They can affect the process of memory formation in the brain, causing patients to have no memory of their experiences during surgery. This forgetting effect helps alleviate patients' psychological trauma and anxiety.
Muscle relaxation
Muscle Relaxation - Sourced: Healthline
In addition to inhibiting the central nervous system, general anesthetics may also produce muscle relaxation effects by affecting the function of the neuromuscular junction. The neuromuscular junction is the connection point between neurons and muscle cells, responsible for converting nerve impulses into muscle contractions. General anesthetics may inhibit muscle contraction and achieve muscle relaxation by interfering with ion channels or neurotransmitter transmission during this process.
Inhibit neuronal excitability
General anesthetics reduce the excitability of neurons by binding to specific receptors on the membrane of nerve cells. This weakens the response of neurons to external stimuli, thereby reducing sensitivity to pain and other sensations.
Regulating neurotransmitter release
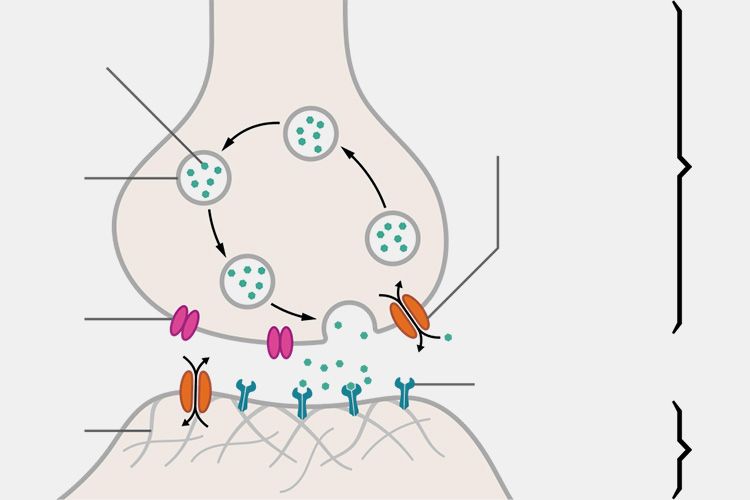
Regulating Neurotransmitter Release - Sourced: Wikipedia
These neurotransmitters play an important role in transmitting information in the nervous system, and anesthetics can regulate their release and intensity of action, further inhibiting the activity of the nervous system.
4.What Are the Manufacturing Process of Injectable Anesthetics?
Due to the various types of anesthetics, this article selects Benzocaine, a local anesthetic, for introduction. Except for the different formulas in the early stage, the production process of other injectable anesthetics is basically the same.
Raw material preparation
Starting from p-nitrobenzoic acid and anhydrous ethanol, concentrated sulfuric acid is added as a catalyst to generate ethyl p-nitrobenzoate through esterification reaction.
Mixing and reaction
Heating the mixture to 80-85 ℃ and reflux for 2-3 hours to complete esterification and generate ethyl p-nitrobenzoate. After the reaction is complete, the solid is cooled in an ice water bath, filtered, and residual acid is neutralized with sodium carbonate solution.
Purifying
The obtained medicine still needs further purification processes. The general method is to purify the drug through crystallization, solvent crystallization, or counter current distillation to ensure its purity and quality.
Filling

Filling - Sourced: Marchesini Group
The purified anesthetic needs to be filled, and the commonly used packaging methods are glass or plastic bottles, which have good sealing and stability. After filling, the container will be immediately sealed to prevent external contamination of the medication.
Sterilization
During the hot press sterilization process, the sealed injection anesthetic is filled with saturated water vapor at a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure. This high-temperature and high-pressure environment can effectively kill bacterial colonies and spores in the medicine, ensuring the sterility of the drug. Meanwhile, by precisely controlling the sterilization time and temperature, the damage to the active ingredients of the drug can be minimized, ensuring the stability and efficacy of the drug.
Quality checking

Quality Checking - Sourced: Technology Networks
At the same time, quality inspection is also required to test the appearance, solubility, purity, content and other indicators of the anesthetic to ensure that the quality of the anesthetic meets the standards.
Labeling
In order to display relevant information about anesthetics, such as drug name, dosage, and ingredients, it is necessary to label the anesthesia ampoule. Labels should be made of waterproof and chemically resistant materials, and strict SOPs related to labeling and packaging should be strictly followed.
Packaging
In order to further facilitate the storage and transportation of injectable anesthetics, secondary packaging will be carried out by bottling the injectable anesthetics into boxes to reduce damage to the drugs.
5.What Machines Should Be Used in the Manufacturing of Injectable Anesthetics?
The equipment used for producing anesthetics must meet pharmaceutical grade standards, such as GMP. Do you know the production machines involved in injectiable anesthetics?
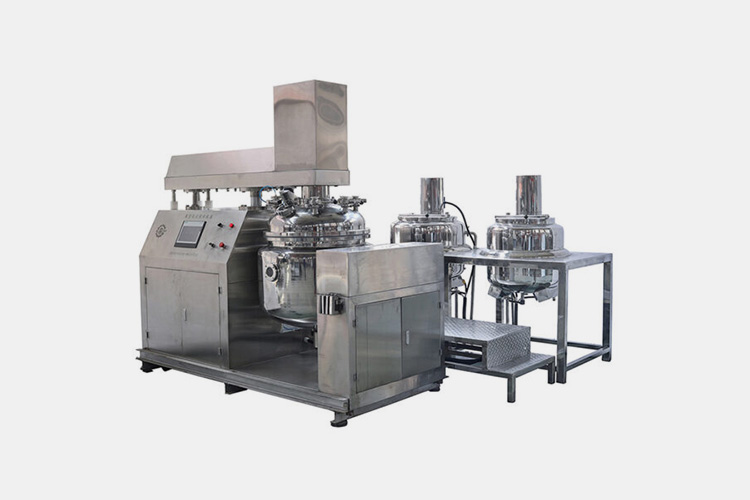
| Vacuum emulsifying mixer
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer |
The vacuum emulsifying mixer is suitable for solid-liquid dispersion, dissolution, and emulsification, as well as liquid-liquid homogenization and emulsification. The speed of its high shear homogenizer and stirring blade are both controlled by frequency conversion, which can adjust the motor to the necessary speed according to the process requirements, achieving energy-saving and environmental protection effects. |
| Purification equipment
Purification Equipment - Sourced: Axonia Medical |
Purification equipment can efficiently separate target drugs and impurities based on differences in molecular weight, charge properties, etc., such as removing salt, small molecule organic matter, pigments, etc. No need to add chemical reagents, no secondary pollution, more environmentally friendly. |
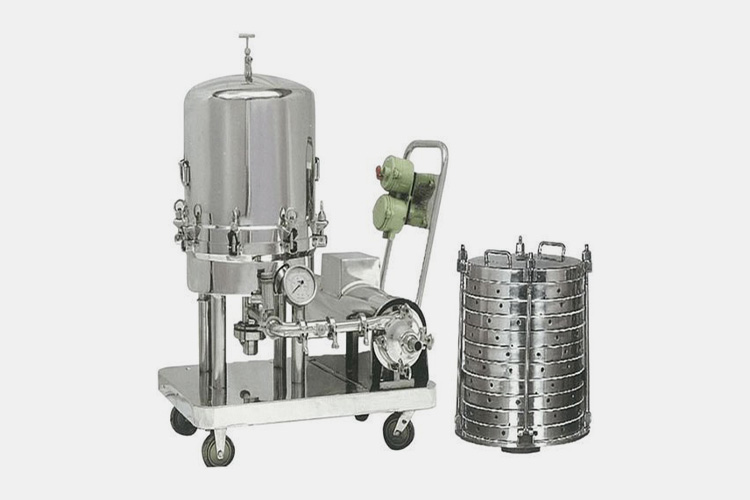
| Filter
Filter - Sourced: Pharma Engineering |
The filter forms a dense barrier through microporous filter materials such as polyether sulfone, polypropylene, etc., and uses the pore size sieving effect to intercept microorganisms in anesthetics. According to FDA standards, sterilization grade filters must ensure a pore size of ≤ 0.22 μm and be able to effectively intercept bacterial challenges (such as Pseudomonas) of ≥ 107 cfu/cm², achieving sterile assurance. |
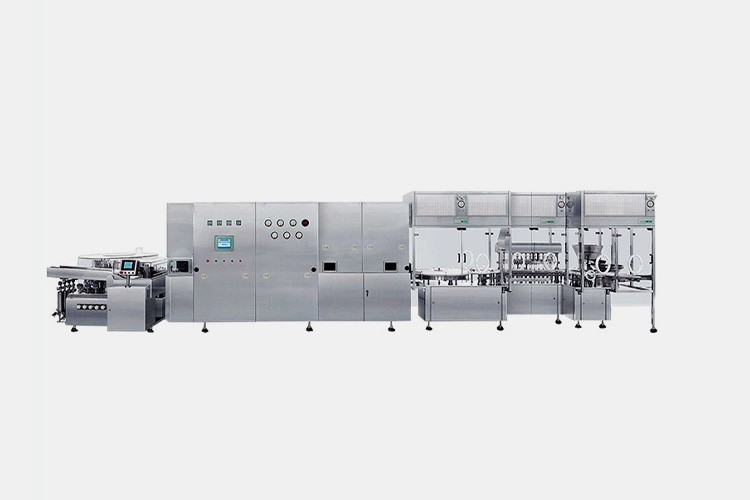
| Injectable anesthetics filling line
Injectable Anesthetics Filling Line |
The injectable aesthetics filling line includes a vial washing machine for cleaning, a sterilization tunnel for drying, sterilization, and solidification of the silicone layer, and a filling machine. This system can achieve soft bottle separation at the feeding point of the production line, and a special conveying unit can fix the vial through a customized buckle system during the processes of plugging, filling, and sealing. |
| Autoclave
Autoclave
|
Autoclave uses high-temperature deionized water as the sterilization medium, which circulates internally and sprays evenly on the sterilized items for a period of time to achieve the purpose of sterilization. It has a wide temperature control range, good temperature uniformity, and avoids secondary pollution during the working process. At the same time, it combines vacuum and color water leak detection methods to ensure a 100% waste detection rate. |
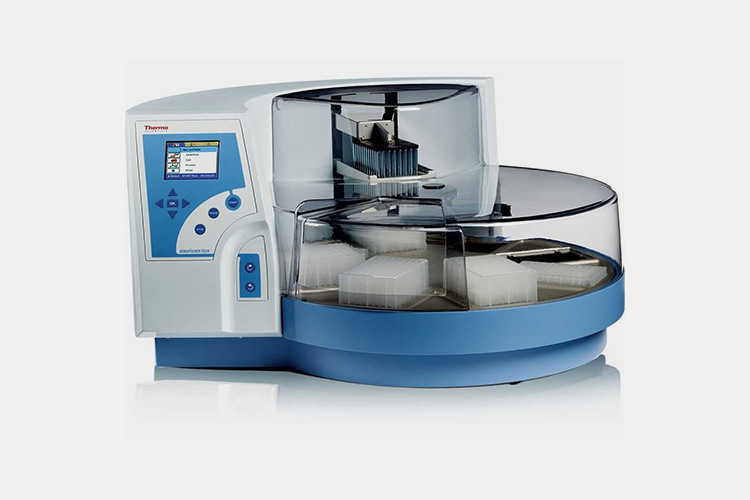
| HPLC equipment
HPLC Equipment - Sourced: KWIPPED |
To control the quality of anesthetics, HPLC can be used. High performance liquid chromatography detectors commonly use HPLC technology for drug component detection, which can detect drug components at the level of μ g/mL or even ng/mL and effectively separate structurally similar compounds. |
| Labeling machine
Labeling Machine |
Adopting high-precision detection sensors, the automatic labeling machine can detect the position and direction of the label, ensuring that the label is pasted in the correct position. Using patented technology, there is no intermediate buffer, the conveyor belt does not flatten the bottles, does not require special supervision, and does not break the bottles. The insertion site adopts a structure of clamping the tray with a clamp, which ensures the accuracy of the tray position during insertion. |
| Cartoning machine
Cartoning Machine |
The cartoning machine is used to automatically place injection anesthesia ampoules and instructions into a folding paper box and complete the sealing action. It can change the packaging specifications according to different user requirements. It is easy to adjust and debug, suitable for large-scale production of single varieties, and can also meet the production needs of users for small batches and multiple varieties. |
6.What Are Other Common Anesthetics Besides Injectable Anesthetics?
In addition to injecting anesthetics, there are also inhaled anesthetics, which are administered to the human body through respiration.

Inhalation Anesthesia - Sourced: Global Banking
Inhalation anesthesia is administered to patients through the respiratory tract, and patients inhale anesthetic gases or vapors through the respiratory tract.
Inhalation anesthesia involves the absorption of drugs in the lungs, which are then transported through the bloodstream to the brain and other tissues, producing an anesthetic effect.
Advantage
| High safety | With have a wide history of use, inhaled anesthetics are mature and reliable, and are widely recognized as safe anesthesia methods. |
| Long lasting effect | Inhaled anesthetics are quickly transported to the brain and other tissues through alveoli and pulmonary blood exchange after being absorbed in the lungs, thus usually providing a long-lasting anesthetic effect. |
| Analgesic effect | Some inhaled anesthetics have a certain analgesic effect and can play an auxiliary role in surgery and pain management. |
| Strong adjustability | Inhalation anesthesia can flexibly adjust the concentration and flow rate of drugs, as well as accompanying oxygen parameters, according to the patient’s response and needs. |
Disadvantage
| Respiratory depression | Inhalation of anesthetic drugs may cause respiratory depression, requiring close monitoring of the patient’s respiratory condition. |
| Sensational stimulation | Some inhaled anesthetics have a stimulating odor, which may cause discomfort such as coughing and throat spasms in patients. |
7.What Are the Side Effects of Injectable Anesthetics?
Anesthesia side effects are a common phenomenon after surgery, most of which are temporary and usually disappear on their own within 24 hours or less.
Allergic reaction
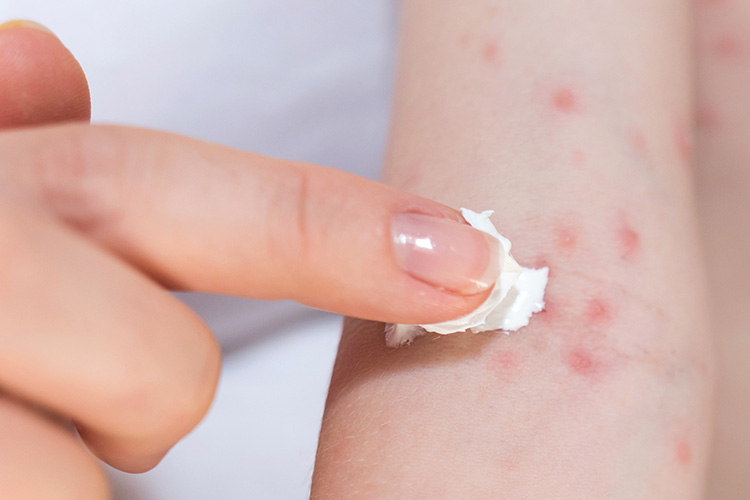
Allergic Reaction - Sourced: GoodRx
Although not common, it can occur, manifested as rash, itching, erythema at the injection site or throughout the body, and in severe cases, laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, and even anaphylactic shock.
CNS toxicity
When drugs accidentally enter blood vessels or are used in excessive amounts, they may cause dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, and numbness around the mouth, which can further develop into convulsions and seizures.
Cardiovascular system toxicity
Affects myocardial contractility, leading to a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, and affects the stability of the cardiovascular system.
8.How Long Do Injectable Anesthetics Last?
The duration of anesthesia generally varies due to various factors, including the type of anesthesia, administration method, dosage, patient’s physical condition, and type of surgery.
How Long Do Injectable Anesthetics Last - Sourced: NHS Inform
Local anesthesia:
Long acting local anesthetics: The duration of action is usually longer, lasting 4-6 hours or even longer. Drugs are often used in surgical or therapeutic settings that require a longer period of anesthesia.
Short acting local anesthetics: have a relatively short duration of action, ranging from a few minutes to several tens of minutes, and are suitable for some simple surgical or therapeutic procedures.
General anesthesia:
Intravenous anesthetics, such as propofol, have a relatively short duration of action. The efficacy time of propofol is about 30-60 minutes, while remifentanil is shorter, possibly only a few minutes, and is commonly used in painless gastroscopy, painless colonoscopy, painless abortion and other surgeries.
Inhalation anesthetics: Administered by inhalation, their duration of action is also relatively short, but the specific duration depends on the type of drug and the amount inhaled by the patient.
Other influencing factors:
| Patient’s physical condition | Factors such as age, weight, and metabolic rate can affect the metabolism and duration of anesthesia. For example, obese patients may experience prolonged anesthesia duration due to slower metabolism. |
| Surgical type | Different surgical types have different requirements and durations for anesthesia, and complex surgeries may require longer anesthesia effects. |
| Dosage | The dosage of anesthesia drugs is also an important factor affecting their duration, with larger doses typically resulting in longer lasting effects. |
In practical applications, doctors will choose the appropriate type of anesthesia, administration method, and dosage based on the patient's specific situation and surgical needs to ensure the smooth progress of surgery or treatment and the safety of patients.
9.How to Store and Transport the Injectable Anesthetics?
In order to ensure the quality of the final anesthetic product and deliver it intact to hospitals or customers, strict storage and transportation rules need to be followed.
Special personnel for storage

Special Personnel For Storage - Sourced: K2 Scientific
Special personnel are responsible for storing anesthetic drugs. Establish a dedicated account book for the entry and exit of narcotic drugs in the designated warehouse (cabinet), and record each entry and exit transaction. Inpatients using anesthesia drugs need to have nurses collect them from the pharmacy with an anesthesia prescription.
After receiving the prescription, the personnel in charge of dispensing in the pharmacy carefully check the prescription information, and the prescription must clearly state the purpose of the anesthetic drugs taken.
Storage environment

Storage Environment - Sourced: Twin Oaks Anesthesia Courses
The storage location for injectable anesthetics should be chosen in a safe and stable place, moisture-proof, fireproof, anti-theft, rodent proof, and snake proof. The storage environment should be kept clean, ventilated, and dry, with stable temperature, humidity, and other conditions. Drugs with biological requirements should be stored in the refrigerator. The temperature of the refrigerator should be maintained at 4-8 ℃, and the humidity should be kept at 45% -75%.
Individual transportation
Injectable anesthetic drugs must be transported separately and not mixed with other drugs. At the same time, protective measures must be taken to prevent drug leakage and to prevent drugs from being subjected to external vibrations and impacts. During transportation, a dedicated person should be assigned to supervise and ensure the safety of the drugs.
10.Who Can Administer Injectable Anesthetics?

Who Can Administer Injectable Anesthetics - Sourced: The Anesthesia Consultant
Anesthetics are injected by doctors or anesthesiologists in the operating room. However, in some cases, nurses may also receive training and qualify to administer anesthesia to patients.
This depends on local regulations and hospital policies. Whoever gives anesthesia drugs needs to undergo sufficient training and qualification certification, and follow safety procedures to ensure the safety and health of patients.
11.What Are the Contraindications For Using Injectable Anesthetics?
Specific contraindications may vary depending on the individual patient’s condition and type of anesthesia. Before receiving anesthesia, patients should follow the doctor’s advice and guidance.
Fasting and water restriction
Before anesthesia, patients usually need to fast and avoid water for a period of time to avoid vomiting and aspiration during the anesthesia process. The specific fasting and water deprivation time will depend on the type of anesthesia and the patient's condition. Generally, adults need to fast for 6-8 hours and water deprivation for 2-4 hours.
History of drug allergies

History of Drug Allergies - Sourced: Knowles Apothecary
Patients need to inform their doctors if they have a history of drug allergies, including allergic reactions to anesthetic drugs. Doctors will choose appropriate injectable anesthesia drugs or take preventive measures according to the situation.
Cardiovascular disease
Patients with severe cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, etc., may require detailed evaluation and treatment before anesthesia to ensure the safety of injectable anesthesia.
Disease of respiratory system
Disease of Respiratory System - Sourced: Dr. Meghana Pande
Patients with severe respiratory diseases such as emphysema, asthma, etc. may need to undergo respiratory function assessment and treatment before anesthesia to avoid respiratory problems during the anesthesia process.
Nervous system disease
Patients with neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, etc. may require detailed assessment and treatment before anesthesia to ensure the safety of anesthesia.
Pregnancy

Pregnancy - Sourced: CDC
Pregnant women need to pay special attention before injecting anesthesia. Doctors will evaluate the risks and benefits of anesthesia based on the specific situation of the pregnant woman and choose the appropriate anesthesia method.
12.What Are the Preparation Measures For Patients Before Injection Anesthetics?
Anesthetics are related to human health, and in order to ensure their effectiveness, preparation measures need to be taken before injecting anesthetics.
Be mentally prepared
Be Mentally Prepared - Sourced: MIBlueDaily
During anesthesia, most patients may experience tension due to the unknown nature of the surgery and concerns about the disease. At this point, patients need to strengthen communication with doctors, inform them of their doubts and anxieties, establish a good trust mechanism, and provide a solid foundation for the success of the surgery.
Strictly follow instructions of doctors

Strictly Follow Instructions of Doctors - Sourced: The Perecman Firm
Before the patient undergoes surgery, the anesthesiologist usually visits the ward to visit the patient. The patient needs to inform the doctor of relevant information such as the medication they have recently taken, whether they are in their menstrual period, whether they have fever symptoms, and whether they are allergic to things. It cannot be concealed, so that the hospital can prepare for the surgery and anesthesia methods based on the patient’s actual situation, in order to reduce the risks during the surgery.
Be prepared in terms of diet

Be prepared in Terms of Diet - Sourced: Everyday Health
Patients undergoing injectable anesthesia should undergo enema before receiving anesthesia, fast for 6 to 8 hours in advance, and abstain from water for 4 hours to avoid reflux during surgery, which may lead to aspiration and pose a threat to the patient’s life safety.
At the same time, it is necessary to adjust the patient’s diet, water intake time, etc. one day in advance based on the patient's surgical condition. Before entering the operating room, it is necessary to remove one's dentures, hand over valuable items to relatives for safekeeping, and wear clothes, hats, etc. from the operating room.
Conclusion
Anesthetics act on the nervous system, causing reversible and temporary loss of pain and perception in the local or entire body, mainly used in various surgeries. Injectable anesthetics are generally packaged in vial and injected into injectable form during use. After reading this article, you must have gained some understanding of injectable anesthetics. If you have any further information you would like to know, please feel free to contact AIPAK Engineering at any time
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours