Insulin Vial: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
The main function of insulin is to regulate blood sugar levels. It can inhibit the breakdown of glycogen in the liver, reduce glucose release, and promote the synthesis of fat, protein, and glycogen. The connection between the insulin vial allows for one handed operation, improving fault tolerance and injection efficiency.
How much do you know about insulin vials? Do you know its production process? What should you pay attention to during the storage and transportation of insulin vials? Next, let’s take a look at complete FAQ guide of Insulin vial together.
1.What is Insulin Vial?
Insulin Vial - Sourced: Diabetes Voice
Insulin is a protein hormone secreted by pancreatic beta cells in the pancreas, which plays a crucial role in the human body. It is secreted by pancreatic beta cells stimulated by endogenous or exogenous substances such as glucose, fructose, glucagon, arginine, etc. It is the only hypoglycemic hormone in the human body.
According to usage, insulin can be divided into insulin vials and insulin pens. Insulin via refers to insulin packaged in penicillin vial, which is a small bottle sealed with a rubber stopper and aluminum-plastic composite cap.
2.What Are the Functions of Insulin Vial?
Insulin vial is a hormone secreted by pancreatic beta cells, which has the following functions and effects.
Promotingcarbohydrate metabolism

Promoting Carbohydrate Metabolism - Sourced: Healing Gourmet
Insulin vial is a protein hormone secreted by the pancreas under stimulation, which can promote the metabolism of carbohydrates and facilitate normal growth of the body.
Fully utilizingglucose
Due to the role of insulin vial in promoting carbohydrate metabolism, the body can fully utilize glucose when using insulin, which can promote oxidative degradation of glucose and facilitate its entry into cells. Glucose can only exert its effects when it enters cells, which is beneficial for the health of the body.
Treatingdiabetes

Treating Diabetes - Sourced: ProtoKinetix
Insulin vial also has the function of lowering blood sugar, which can promote the synthesis of liver glycogen in the body or inhibit the breakdown of liver glycogen in the body, thereby reducing blood sugar. Therefore, insulin vial is commonly used in clinical treatment of various types of diabetes. Common insulin drugs include insulin injection, aspart insulin injection and other types.
3.What Types of Insulin Are Available In Vials?
Insulin can be divided into multiple types. Which types of insulin can be bottled in vials?
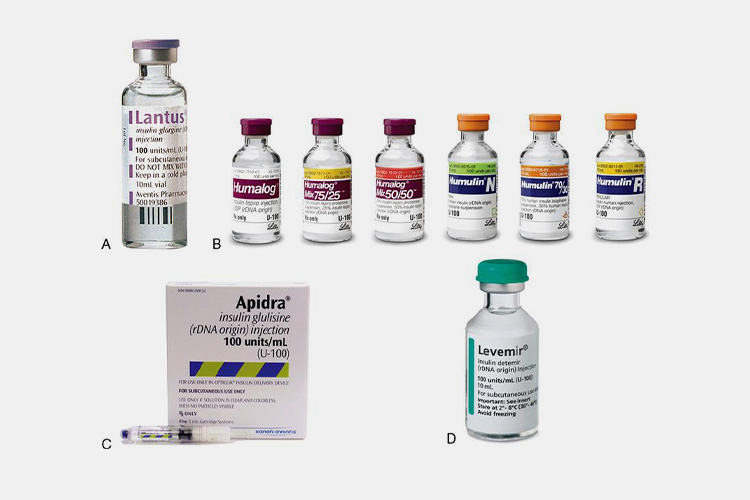
Types of Insulin - Sourced: Basicmedical Key
| Another name | Effective time | Time of duration | Usage time | |
| Rapid-acting insulin | Asparagus insulin, lispro insulin | 10-15 minutes | 3-5 hours | Usually injected immediately before meals, it can effectively simulate insulin secretion during meals and control postprandial blood sugar. |
| Short acting insulin | Soluble insulin | 30-60 minutes | 6-8 hours | Usually injected about 30 minutes before meals, mainly used to control postprandial blood sugar. |
| Intermediate-acting insulin | npH | 2-4 hours | 10-16 hours | Injecting 1-2 times a day can effectively control fasting blood sugar. |
| Long-acting insulin | Insulin glargine and insulin detemir | 2-4 hours | Up to 24 hours | Injecting once a day is sufficient, which can effectively control basal blood sugar throughout the day. |
| Premixed insulin | Biphasic insulin | 5-60 hours | 10-16 hours | Short acting ingredients can quickly lower postprandial blood glucose, while medium acting ingredients are slowly and continuously released, serving as a substitute for basal insulin. |
4.What Is the Production Process of Insulin Vial?
The insulin vial production is an important link in the production process of heparin preparations. The principle of insulin vial production is achieved through biological fermentation technology and chemical synthesis technology.
Step 1: Genetic engineering
The production of insulin usually uses microorganisms such as Escherichia coli or yeast as hosts. Firstly, it is necessary to introduce the human insulin gene into host cells, which requires genetic engineering technology to complete. Insert the human insulin gene into the chromosome of the host cell, making it a part of the host cell.
Step 2:Fermentation
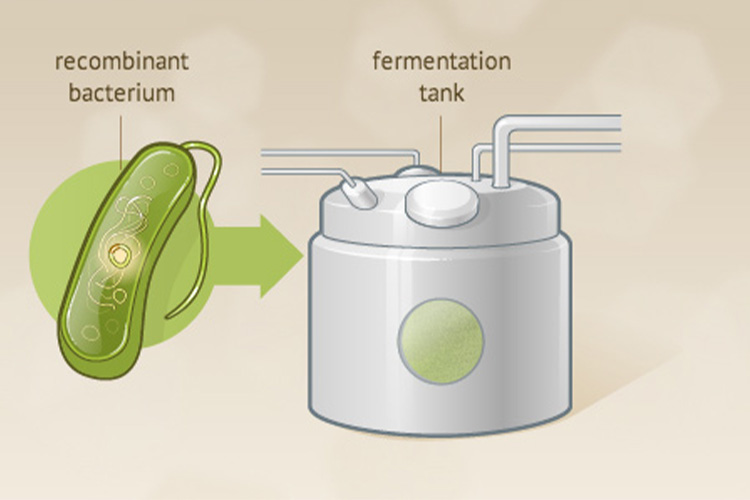
Fermentation - Sourced: www.nlm.nih.gov
The next step is the fermentation process, in which genetically engineered host cells are cultured in a fermentation tank to provide appropriate temperature, pH, and nutrients, promoting the expression of insulin genes and synthesis of insulin proteins in the host cells. The fermentation process usually takes several days to weeks until the insulin protein reaches a certain concentration.
Step 3: Cell harvesting and lysis
When cells reach a certain density, they need to be separated and extracted. This is usually done using an insulin pump, which extracts insulin from the culture medium through negative pressure.
Step 4: Protein purification
The extracted insulin usually contains other proteins and impurities. In order to obtain insulin products with high purity, purification and refining processes are required. This includes using techniques such as filtration, centrifugation, and chromatography to remove impurities and improve purity.
Step 5: Chemical modification
After the separation and purification of insulin precursors, they need to be modified by chemical or biological methods, such as cleaving intermediate peptides, forming disulfide bonds, etc., to form mature insulin molecules.
Step 6: Formulation
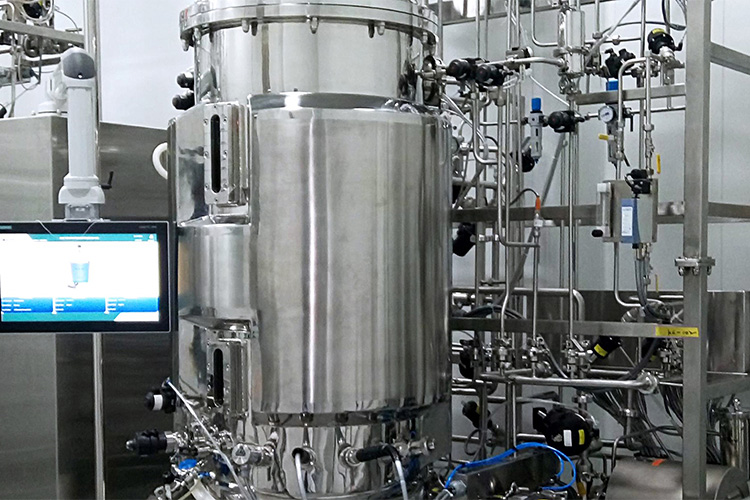

Insulin Preparation Production - Sourced: Innovation News Network
The enzymatically hydrolyzed insulin stock solution is subjected to a step of filtering impurities to remove suspended solids, particles, and other insoluble impurities from the insulin stock solution. This can purify the insulin stock solution, making the subsequent steps smoother. Mixing a certain proportion of stabilizers and preservatives into insulin to obtain insulin preparations.
Step 7: Filling
Preparing sterile vials by washing and drying, and filling insulin preparations into the vials under sterile conditions. Accurately filling drugs or other liquids into vials in a sterile environment. Filling equipment usually uses high-precision peristaltic pumps or piston pumps to ensure accurate filling volume in each vial. After filling, perform plugging and capping.
Step 8: Quality control
Strict quality control is required for insulin products throughout the entire production process. Including host cells and formulations are tested to ensure that the purity, activity, and safety of insulin products meet the requirements.
Step 9: Labelingand packaging
After filling, it is necessary to attach labels to the insulin vials. Labels usually contain information such as vials number, specifications, drug name, etc. for easy management and use. For the convenience of insulin transportation, insulin vials can be repackaged by cartoning.
Step 10: Distribution

Distribution - Sourced: Pharma Logistics
The insulin vials after secondary packaging should be transported to hospitals and pharmacies according to demand, and strict standards should be followed during transportation to avoid affecting the quality of insulin.
5.What Machines Can Be Used in the Insulin Vial Production?
Insulin is a powerful hormone that can be said to be the energy ambassador in the body. Penicillin bottles are one of the main packaging for insulin. Do you know the production equipment for insulin vials?
| Fermentation tank
Fermentation Tank - Sourced: Micet Group |
Fermentation tanks, as a type of bioreactor equipment, are mainly used for microbial fermentation processes under controlled conditions. Fermentation tanks can achieve high-density cultivation of microorganisms, improving the yield and quality of fermentation products. |
| Centrifuge
Centrifuge - Sourced: Amazon |
A centrifuge is a device that uses centrifugal force to separate mixtures. Its working principle is to use the centrifugal force generated by rotation to separate different substances in insulin cultured cells according to their density and mass differences, thereby achieving the purpose of separation. |
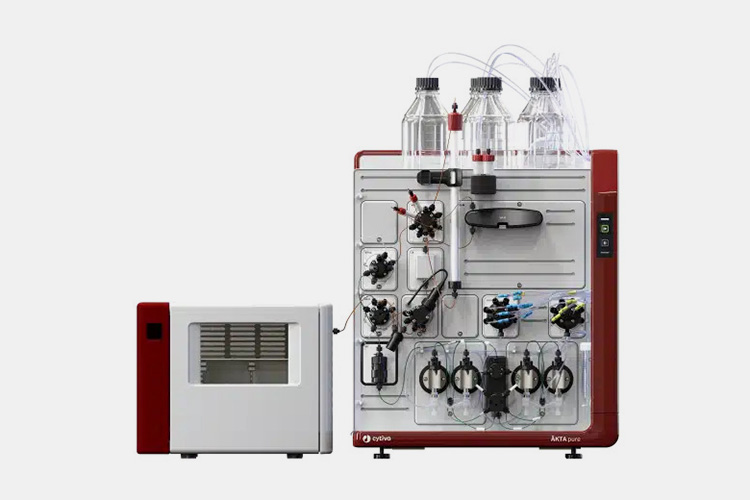
| Chromatography purification system
Chromatography Purification System - Sourced: GMI Inc |
Chromatography purification system is a commonly used analytical instrument for separating and purifying proteins, with the aim of isolating and purifying target proteins from biological samples for research. This system usually has automation functions, which can automatically complete the processes of sample injection, separation, detection, and data processing, reducing human errors and operation time. |
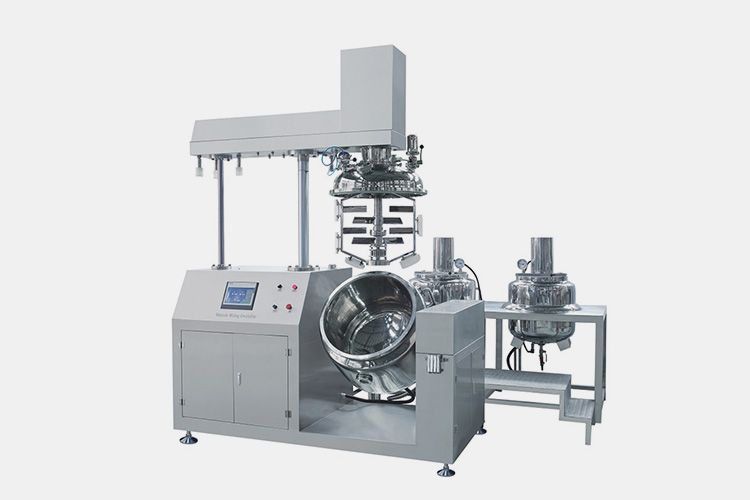
| Vacuum emulsifying mixer
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer |
The vacuum emulsifying mixer adopts a 3-layer stainless steel structure pot body, with a middle layer (heating layer, insulation layer) insulation layer, which has excellent anti scalding effect and meets GMP standard engineering. This machine uses a high-speed rotating shearing blade to fully emulsify materials in a short period of time, greatly improving production efficiency. |
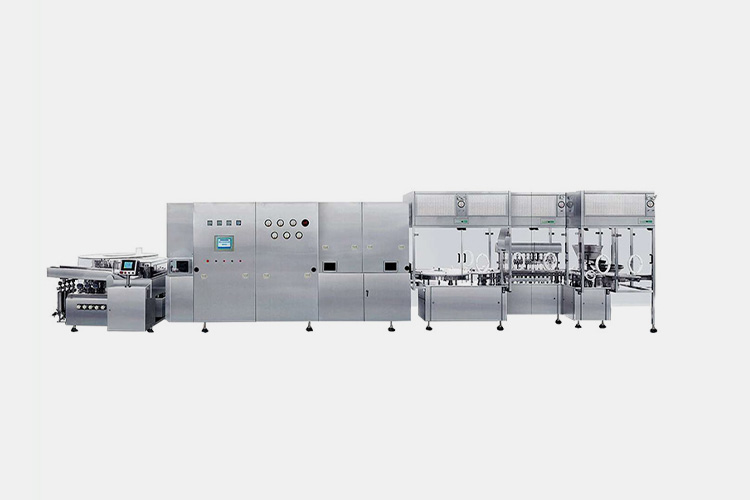
| Insulin vial filling line
Insulin Vial Filling Line |
The entire insulin vial filling line includes bottle washing machines, sterilization machines, and filling and capping machines. The working principle of this fully automatic penicillin bottle filling machine production line is mainly to use equipment such as mechanical arms and conveyor belts to grasp, position, fill, and seal penicillin bottles according to specific procedures. By adopting automation and intelligent technology, human errors and mistakes can be greatly reduced, and the quality and stability of products can be improved. |
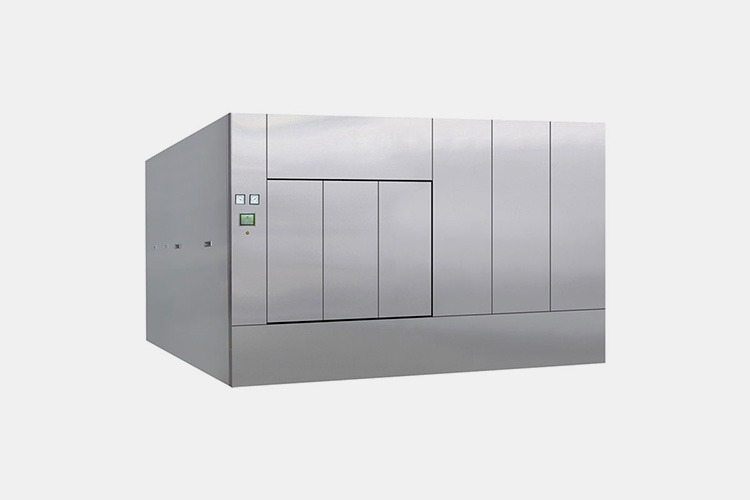
| Pharmaceutical autoclave
Pharmaceutical Autoclave |
The pharmaceutical autoclave uses a mixture of steam and air as the sterilization medium, which can sterilize insulin vials. The material of the interior, door panels, jacket, coil, and steam generator is S304, and 316L can be selected to avoid air and steam stratification and ensure uniform temperature in the interior. |
| Labeling machine
Labeling Machine |
The labeling machine has excellent performance characteristics, and its primary function is to accurately detect the amount of insulin and foreign objects inside the bottle. It can automatically identify and eliminate defective products such as glass shards and impurities, improving the accuracy of detection Adopting advanced sensors and mechanical control systems to ensure that each label can accurately adhere to the vials. |
| Cartoning machine
Cartoning Machine |
The cartoning machine can achieve automatic sealing and encapsulation of insulin vials boxes. This machine uses PLC control system and photoelectric monitoring technology to accurately control the actions of each component, ensuring the smooth progress of the production process. During operation, it can automatically identify and eliminate non-conforming products to ensure product quality. |
| Microbial limit detector
Microbial Limit Detector - Sourced: BIOBASE GROUP |
The microbial limit detector measures the microbial content in insulin to ensure the quality and safety of the final insulin vials, ensure the sterility of the drug, and comply with GMP requirements. |
6.What Are the Side Effects of Insulin Vial?
Reasonable use of insulin under the guidance of a doctor generally does not result in side effects. But if used improperly, side effects may occur, as detailed below
Hypoglycemia

Hypoglycemia - Sourced: Metropolis Healthcare
If insulin is used improperly, such as in excessive doses, due to its regulatory effect on blood sugar, it may lead to a rapid decrease in blood sugar, causing hypoglycemia, dizziness, palpitations, sweating and other symptoms.
Subcutaneous fat atrophy
After injecting insulin, the insulin crystals at the injection site form an immune response to subcutaneous fat, leading to fat atrophy and local skin depression.
Edema
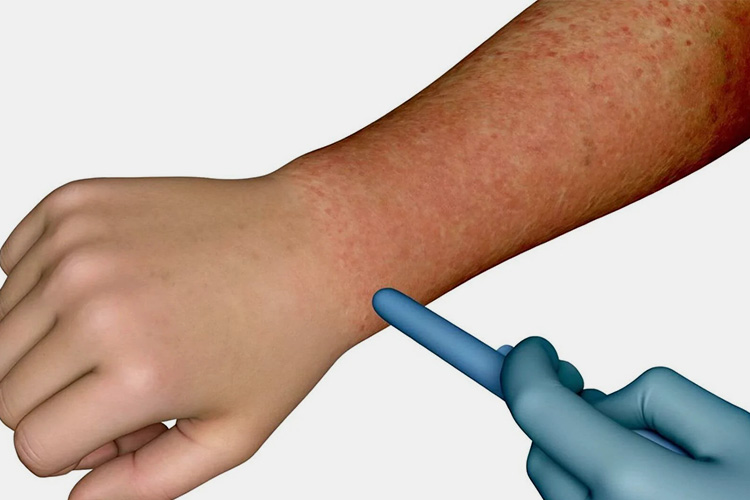
Edema - Sourced: Lawyers. Law
If a large amount of insulin is used, the increase of insulin may also promote the reabsorption of sodium in renal tubules, thus causing water and sodium retention, edema, and elevated blood pressure.
Insulin resistance
Long term unreasonable injection of insulin may also lead to a decrease in the body's sensitivity to insulin, forming insulin resistance, which may occur after medication without a significant decrease in blood sugar.
Allergic reactions
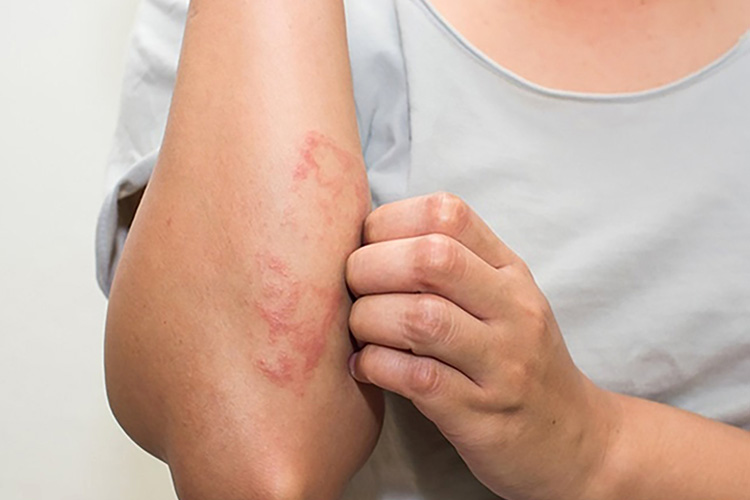
Allergic Reactions - Sourced: Allergy Affiliates
Some patients are allergic to insulin components. If relevant tests are not conducted before injection, allergic reactions such as rash, itching, discomfort, and difficulty breathing may occur after injection.
7.How Long Can a Insulin Vial Be Used After It Is Started?
The time limit for the use of regular insulin vial after activation has always been a concern for nursing and infection control personnel.
Time Limit For Insulin Vial - Sourced: Gluroo
The insulin product manual states that during use after opening, this product does not need to be stored in the refrigerator and can be stored at room temperature (up to 25 ℃) for up to four weeks, avoiding light and heat.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) recommends that if multiple doses of medication are opened or taken (such as needle aspiration), the medication should be labeled with the opening date and used within 28 days, unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer. And the maximum usage period after opening shall not exceed the expiration date. When the sterile state of multiple doses of drugs is disrupted or cannot be determined, the drugs should be discarded.
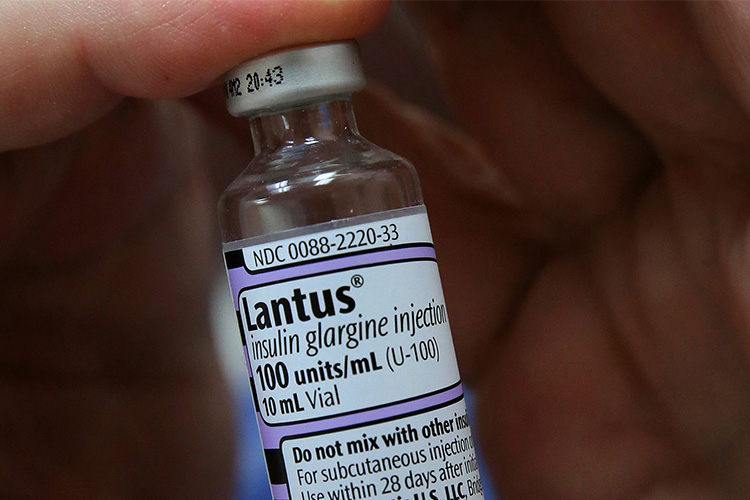
Insulin Used Within 28 Days - Sourced: CNN
If the instruction manual indicates the presence of preservatives, this insulin can be stored for 28 days after activation, but only in the drug preparation area and should not be brought into the treatment area. It should also be kept by a dedicated person as much as possible.
8.Where Are the Injection Sites of Insulin Vial?
Generally speaking, the commonly used injection sites for insulin include the abdomen, outer thigh, outer upper arm, and buttocks, and the recommended distance between injection points is at least 1 centimeter to avoid subcutaneous fat hyperplasia and tissue hardening.
Abdomen
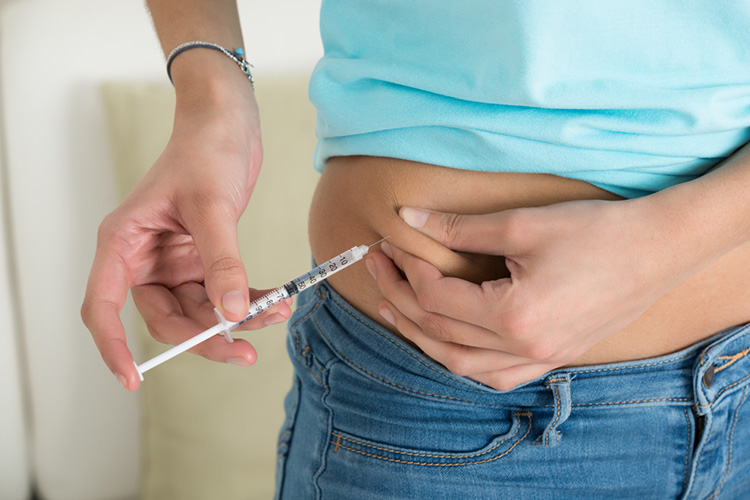

Abdomen - Sourced: Progressive Physical Therapy
The abdomen is the preferred site for insulin injection, as its subcutaneous fat is thicker, resulting in relatively less pain during injection and stable absorption.
Outer thigh
The outer thigh is also a commonly used injection site, especially for patients who require frequent injections. The abdomen and outer thigh can be used alternately to reduce skin damage.
Lateral arm

Lateral Arm - Sourced: Verywell Health
For thin patients, the outer upper arm is a suitable injection site, but the absorption rate may be slightly slower than in the abdomen and thighs.
Hip
Although the buttocks can also be used as injection sites, they are usually not the preferred choice due to their slow absorption rate.
9.What Is the Difference Between Insulin Vials And Insulin Pens?
Insulin vials and insulin pens each have their own advantages and disadvantages, suitable for different patient needs and lifestyles.
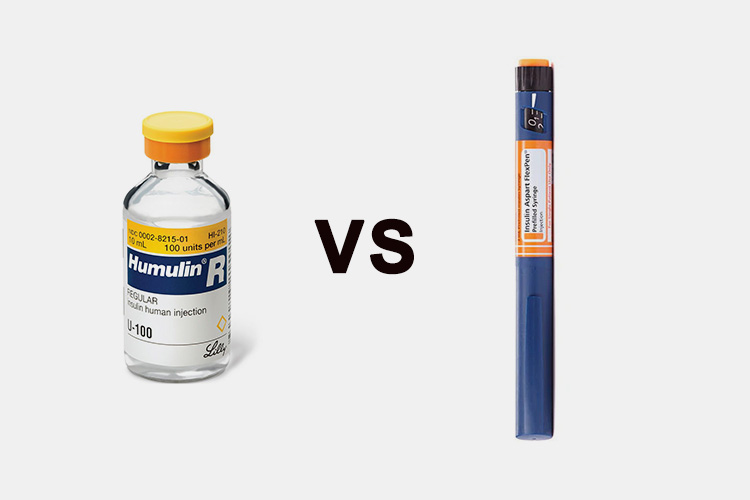

Difference Between Insulin Vials And Insulin Pens - Sourced: ADA Consumer Guide
| Insulin Vials | Insulin Pens | |
| Method of application | Insulin vials are prepared by professionals and then transported to hospitals or pharmacies for sale to patients in need. Doctors then guide patients to choose the appropriate injection dose for subcutaneous injection to control blood sugar levels. | Insulin pens are generally treated by subcutaneous injection of insulin into a household special insulin syringe after diabetes patients purchase insulin injection by themselves. |
| Applicable people | For patients with unstable conditions and prone to hypoglycemic reactions, insulin vials are more suitable for use. | For diabetes patients with stable condition, if they can master the correct insulin injection technology, they can use insulin pens for subcutaneous injection at home. |
| Mechanism of action | Insulin vials may deteriorate due to external environmental factors during delivery, so they can only be administered at regular intervals and cannot achieve personalized drug treatment. | Insulin vials may deteriorate due to external environmental factors during delivery, so they can only be administered at regular intervals and cannot achieve personalized drug treatment. |
| Convenience of use | It should be worn outside the body and the infusion tube and needle should be replaced regularly. Although the operation is relatively complex, it can reduce the inconvenience of multiple injections per day after getting used to it. | It is simple and easy to use, just follow the doctor's instructions for timed injections. Especially suitable for elderly people and patients who are unwilling or unable to accept complex equipment. |
10.How To Determine If An Insulin Vial Is Ineffective?
To determine whether insulin vial is ineffective, various measures can be taken, including examining the appearance, checking the expiration date, observing storage conditions, comparing usage effects, and inspecting drug packaging to avoid affecting the effectiveness of drug treatment.
Checkingappearance
Checking Appearance - Sourced: iStock
Color change: Normal insulin is usually a colorless and transparent liquid. If insulin changes color, such as yellow or brown, it is likely to have expired.
Turbidity or precipitation: Insulin should be clear and free of impurities. If turbidity, precipitation, or flocculent substances appear, it indicates that the stability of insulin has been disrupted and cannot be used again. For example, insulin is prone to this situation after expiration or improper storage, such as freezing.
Checkingthe validity period
The insulin vials are clearly marked with the expiration date, and must be used within the expiration date. Once the expiration date is exceeded, even if there is no significant change in appearance, the activity of insulin will be greatly reduced, or even completely ineffective.
Observingstorage conditions

Observing Storage Conditions - Sourced: ParcelPath
Temperature: Unopened insulin should be stored in a refrigerator compartment at 2-8 ℃ and should not be frozen. If insulin has been stored in the freezer compartment for a short period of time, it can damage its structure and properties, leading to failure.
Light exposure: Insulin should avoid direct sunlight and strong light exposure. Long term exposure to light may accelerate the deterioration process of insulin and reduce its effectiveness.
Comparison of usage effects

Comparison Of Usage Effects - Sourced: Gluroo
If insulin is used according to the normal dosage and injection method, but the blood sugar control effect is significantly worse than before, such as high blood sugar or large fluctuations, after excluding the influence of other factors such as diet and exercise, insulin should be considered whether it is ineffective.
Check the vials of insulin
If the vials of insulin has cracks, loose vial caps, etc., it may allow air to enter the bottle, affecting the stability of insulin and leading to its failure.
11.What Should Be Consider When Storing and Shipping Insulin Vial?
Insulin needs to be stored under appropriate conditions to ensure its efficacy and safety. The storage conditions for unopened insulin, opened insulin, and insulin carried outside are different.
Storage temperature
Insulin vials should be stored in a refrigerator compartment at 2 to 8℃when unopened. Excessive or insufficient temperature can lead to insulin failure. Opened insulin vials can be stored at room temperature (15 to 30℃), but generally not for more than 28 days.
Avoidingfreezing

Avoiding Freezing - Sourced: Gerresheimer AG
Insulin vial cannot be frozen because freezing will render it inactive. Even if the thawed insulin appears normal, it cannot be used again.
Light protection
Insulin vial should be stored away from light, especially direct sunlight. It is best to store it in a medicine box or bottle and place it in the middle of the refrigerator compartment. It should not be placed on the door because frequent opening and closing of the door can cause temperature changes.
Transportation precautions

Transportation Precautions - Sourced: ACS Time Critical
When leaving parental time, you can use a cooling bag or a dedicated insulin vials carrying case to maintain a suitable temperature. However, care should be taken not to directly contact ice cubes to prevent insulin from freezing.
12.What Preparations Need To Be Made Before Injecting Insulin Vial?
In order to maintain the efficacy of insulin and reduce adverse reactions, some issues need to be noted before injecting insulin.
Paying attention to the dining time

Paying Attention To The Dining Time - Sourced: The Parkhurst Dining Blog
Determining the meal time before injection insulin, and some insulin such as Novolin 30R should be injected 30 minutes before meals.
Preparing other tools
Prepare alcohol swabs, needles, insulin pens, and insulin, and note that the insulin pen and insulin must be products from the same manufacturer to avoid mismatches.
Premixed insulin before injection should be shaken well
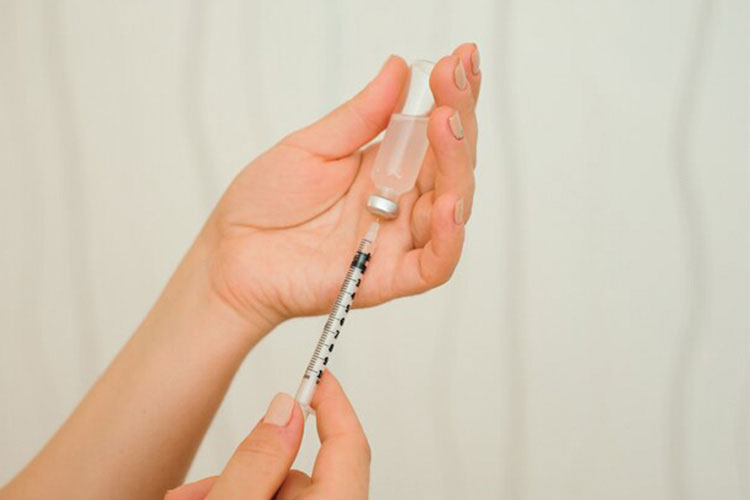
Premixed Insulin Before Injection Should Be Shaken Well - Sourced: Freepik
If premixed insulin is used, such as Novolin 30R, as it is a suspension, be sure to shake it well when using it. Shake it up and down more than ten times, shake it thoroughly before injection, otherwise the concentration inside may be uneven, affecting the concentration of insulin and thus affecting the quality of sugar reduction.
Keeping the skin clean
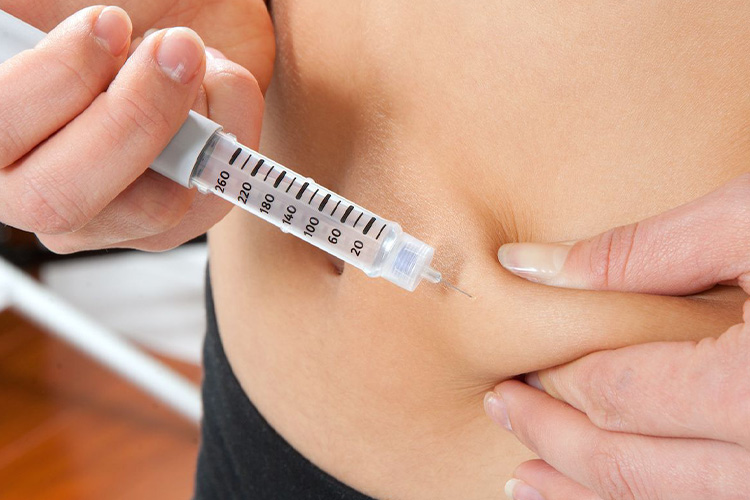
Keeping the Skin Clean - Sourced: Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center
During the use of insulin vial, the local skin should be kept clean and dry, and patients should choose to inject it into the appropriate body part. If there are lumps or ruptures in the areas where insulin is injected, be sure to avoid these areas when injecting. Some patients may find that after injection, they will put some insulin on the needle tip, which should be noted. Generally speaking, this situation occurs because the injection speed is too fast.
Conclusion
Insulin is the longest history, most clinically experienced, and most effective hypoglycemic drug among existing hypoglycemic drugs. It can lower any high concentration of blood glucose levels, and insulin does not reach the highest dose that is ineffective. And there are various types of insulin. After reading this article, have you gained a deeper understanding of insulin vials? If you would like to learn more about insulin vials, please feel free to contact AIPAK Engineering at any time.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours