Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
Vaccines are the most important line of defense against poultry and livestock, and for serious viral diseases such as influenza, vaccination is the most effective means of prevention and control. Among them, oil adjuvanted vaccine have the advantages of safety, stability, and long antibody protection time. The antibodies produced can last for 2-3 months, so they are frequently used by farmers.
How much do you know about oil adjuvanted vaccine? How much do you know about the production process of oil adjuvanted vaccine? Next, let’s take a look at the complete FAQ guide of oil adjuvanted vaccine together.
1.What Is Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine - Sourced: BOC Sciences
Oil-adjuvanted vaccine is a vaccine made by culturing bacteria and extracting live cells from the bacterial cells. Oil-adjuvanted vaccines are commonly used to protect animals such as ducks, pigs, rabbits, and cows from diseases. However, this vaccine have different side effects and applicability to different types of animals.
Oil-adjuvanted vaccines retain the characteristic of pathogenic bacteria stimulating the immune system of objects. When moving objects come into contact with this harmless pathogen, the immune system will produce certain protective substances, such as immune hormones, active physiological substances, special antibodies, etc.
2.What Are the Functions of Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
Why using oil-adjuvanted vaccine? What benefits can oil-adjuvanted vaccine bring to your animals?
Preventinginfectious diseases

Preventing Infectious Diseases - Sourced: UC Davis Health
Animals, like humans, can also suffer from various infectious diseases. And oil-adjuvanted vaccine is one of the most effective ways for us to prevent these diseases. Veterinarians tell us that vaccines can stimulate animals’ immune systems to produce antibodies, thereby helping animals resist pathogens.
Controllingthe spread of the epidemic
In animal populations, once one animal is infected with a certain infectious disease, it is easy to spread to other animals. This not only endangers the health of animals, but also poses significant risks to the animal community in the community. By vaccinating pets, we can effectively control the spread of the epidemic and protect the health of the entire pet population.
Preventing the spread of viruses to humans
Preventing the Spread Of Viruses To Humans - Sourced: American Society for Microbiology
Oil-adjuvanted vaccine not only protects animals from infection, but also prevents the spread of viruses to humans. The World Health Organization proposes that an animal immunization rate of over 70% can cut off the transmission of rabies from dogs to humans。
3.What Is the Manufacturing Process of Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
The production of oil-adjuvanted vaccine should be maintained in a sterile environment, and the production quality should be strictly controlled. The specific production process is as follows.
(1)Core manufacturing system
Water treatment
In the entire production process of oil-adjuvanted vaccine, purified water is used to prepare and clean packaging bottles, so relevant equipment is needed to purify the raw water.
In addition, the quality of its produced water also needs to meet the national laboratory water standards and meet the specific requirements for TOC, bacteria, heat sources, micro particles and other indicators in the experiment.
Preparation of bacterial strains
Preparation of Bacterial Strains - Sourced: Technology Networks
Extracting or preparing antigen proteins, polysaccharides, or viral capsid proteins from corresponding pathogenic microorganisms according to the needs of vaccines. This process needs to be carried out in a sterile environment to ensure the purity and growth quality of the bacterial strain.
Cultivation of bacterial strains
The selected pathogen must be the main pathogenic strain that causes the disease. In addition, pathogens should have strong immunogenicity and be able to elicit effective immune responses from the immune system.
Inactivation
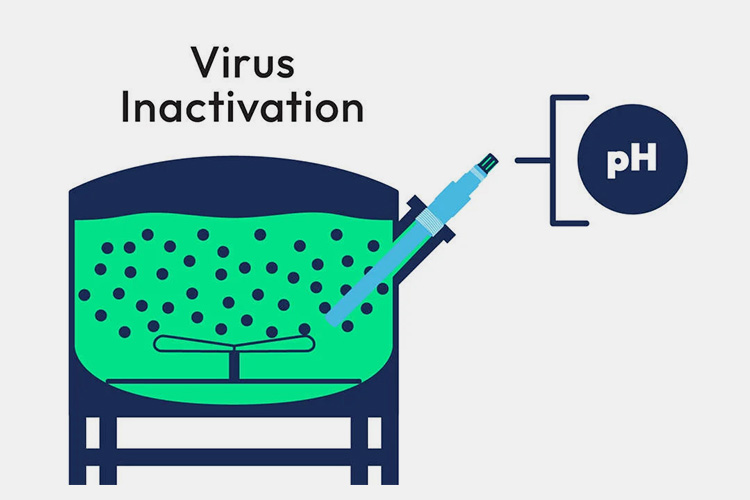
Inactivation - Sourced: Hamilton Company
For vaccines containing active pathogens, inactivation or attenuation may be necessary to ensure safety during use. The methods of inactivation usually include chemical inactivation and physical inactivation.
For chemical inactivation, some chemicals such as formaldehyde can be used to disrupt the biological activity of pathogens by interfering with their nucleic acid or protein structure. Physical inactivation often uses ozone. Methods such as ultraviolet radiation or heat treatment are used to achieve the same goal.
Mixing and emulsifying
The inactivated virus needs further processing to prepare a vaccine. This includes mixing the virus with appropriate adjuvants, which can enhance the immune system's response.
At the same time, a series of purification steps are required to remove potential impurities and harmful substances, ensuring the purity and safety of the vaccine.
Sterilization

Sterilization - Sourced: The Armoloy Corporation
For prepared oil-adjuvanted vaccines, sterilization are necessary to remove possible microbial contamination and ensure the sterility of the product. The workshop also needs to carry out cleaning and disinfection work, which is a key link to ensure the quality and safety of oil-adjuvanted vaccines.
Filling and packaging
Fill the vaccine into an appropriate container, such as a glass bottle or syringe. oil-adjuvanted vaccine injection is made by filling, plugging, capping, light inspection, packaging and other processes.
(2)Quality system
Raw material testing
Bacterial purity testing: Ensure that the strain is not contaminated by other microorganisms, thereby ensuring the accuracy of experimental results.
Bacterial activity testing: Evaluate the biological activity of bacterial strains to ensure their normal growth and reproduction under expected experimental conditions.
Monitoring manufacturing process
Strict monitoring is also required during the production process, it is necessary to test the inactivation effect, antigen concentration, and emulsification stability.
Product testing
Product Testing - Sourced: Riverside University Health System
Strict quality testing for oil-adjuvanted vaccine will be conducted, including checking the efficacy, safety, and purity of the vaccine. Only vaccines that meet all quality standards will be approved for vaccination.
4.What Machines Should be Used in Manufacturing of Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
The production of oil-adjuvanted vaccine requires the use of machines that have undergone strict GMP standards to ensure product quality and effectiveness. The specific products are as follows.
Core manufacturing system
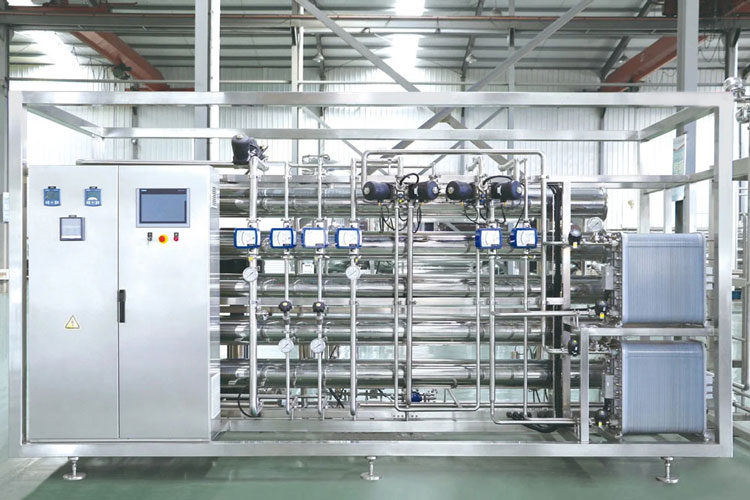
| Purified water equipment
Purified Water Equipment |
In order to provide purified water for cleaning and preparation, purified water equipment is required. The process design and installation of such equipment must comply with relevant GMP certification standards.
This device is mainly used in the process field and integrates reverse osmosis technology and EDI high-purity water technology. Its significant advantage is a desalination rate of up to 99.9%. |
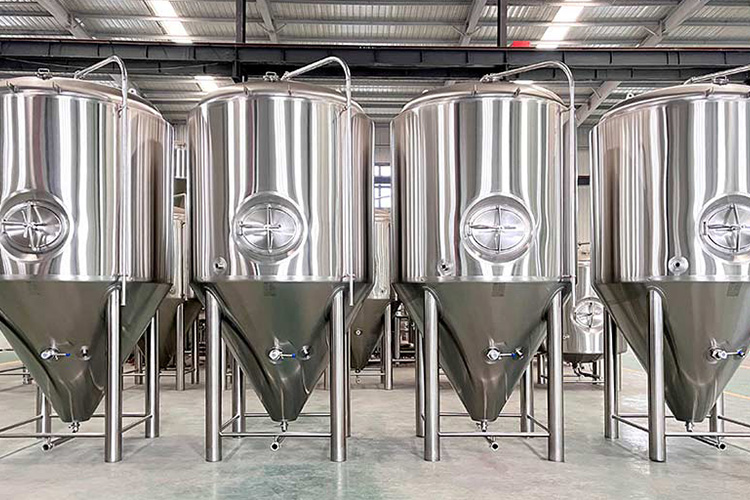
| Fermentation tank
Fermentation Tank - Sourced: Micet Group |
The fermentation tank is equipped with various safety devices, such as pressure relief valves, temperature alarm systems, and emergency stop buttons, to ensure timely measures can be taken in case of abnormal situations and ensure production safety. |
| Centrifuge
Centrifuge - Sourced: 1 Microbiology Resourced Hub |
Centrifuge is an indispensable tool in research processes such as cell culture, virus purification, and protein separation. The centrifuge body, drum, and parts in contact with the material are all made of stainless steel, with a beautiful appearance, simple cleaning, and compliance with GMP requirements. |
| Inactivation system
Inactivation System - Sourced: Sartorius Croatia
|
The inactivation system suitable for the field of biological vaccines adopts a high-temperature resistant rock wool insulation layer and is equipped with a sanitary pressure gauge, tailored to the production characteristics of oil-adjuvanted vaccines.
All pipe openings are treated with stretching and drawing to form smooth transitions, avoiding cleaning dead corners caused by direct insertion welding. They have temperature display function, which can accurately control the deactivation temperature. |
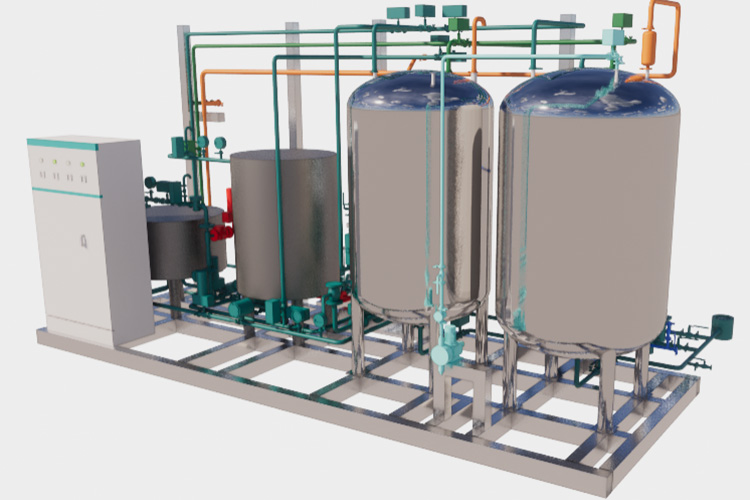
| Waste liquid inactivation treatment system
Waste Liquid Inactivation Treatment System - Sourced: TIANS Engineering Technology Group |
This system will be used to collect and treat waste liquid from the production process in the workshop. After deep treatment, the wastewater still contains some suspended solids and biological pollutants, which need to be precipitated through secondary precipitation to remove these substances. |
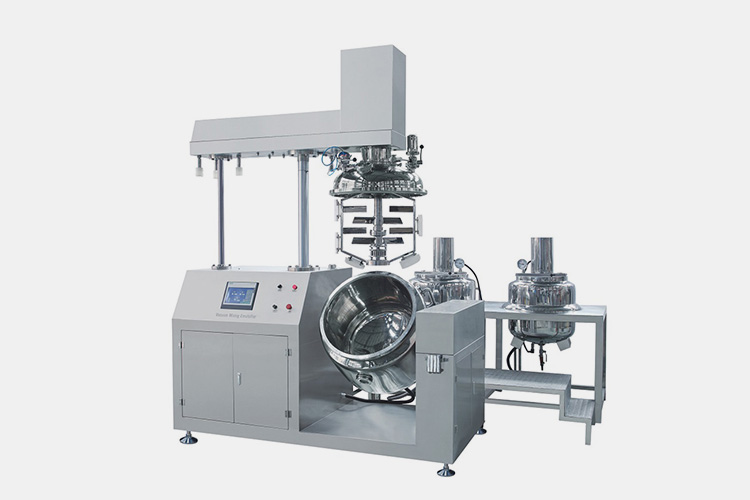
| Vacuum emulsifying mixer
Vacuum Emulsifying Mixer |
As a device used for mixing and dispersing processes, the vacuum emulsifying mixer has continuous operating characteristics and is therefore also known as a continuous high-speed mixing and dispersing machine. It can well meet the requirements of large-scale continuous production operations. |
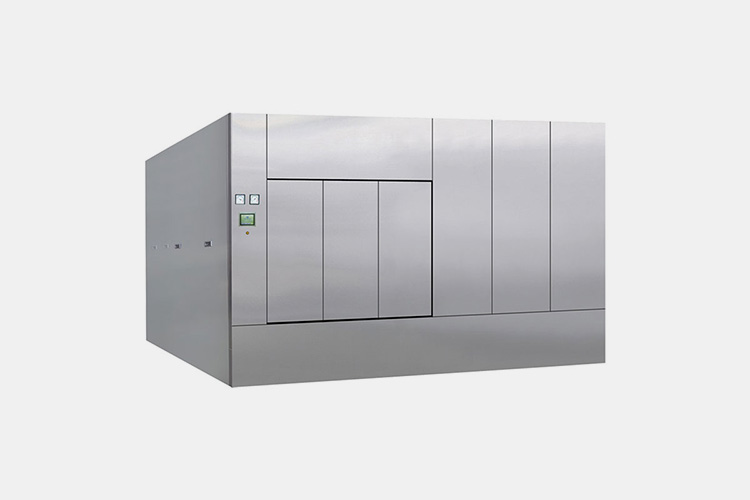
| Pharmaceutical autoclave
Pharmaceutical Autoclave
|
A pharmaceutical autoclave performs high temperature and high pressure sterilization treatment by placing oil adjusted vaccines in a closed container. This sterilization method can completely eliminate microorganisms on the surface and inside of the instrument, ensuring the sterile state of the instrument.
Specifically, the water inside the pharmaceutical autoclave is heated to a high temperature while increasing pressure, creating a high-temperature and high-pressure environment. In this environment, microorganisms cannot survive, and pathogens such as bacteria and viruses will be completely killed. |
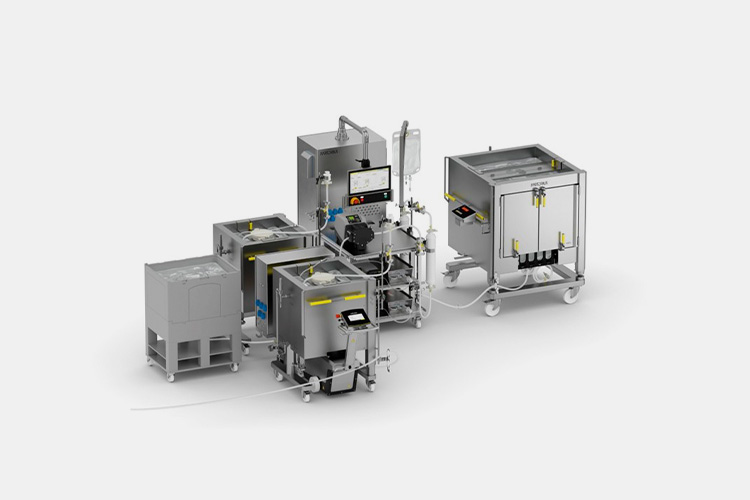
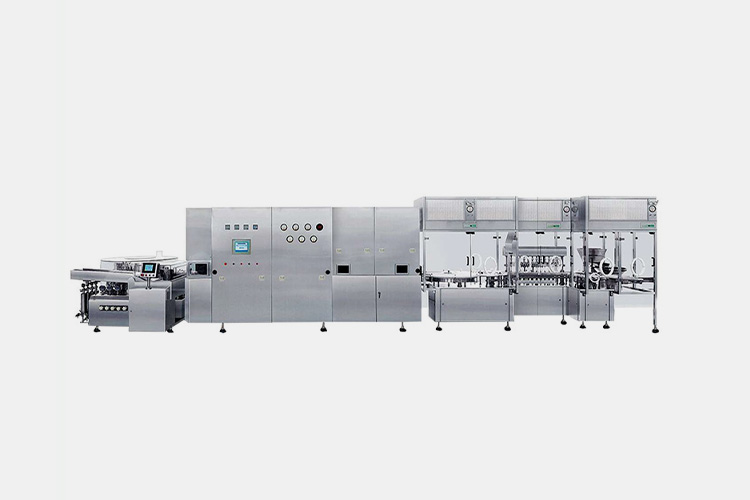
| Oil-adjuvanted vaccine filling line
Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine Filling Line
|
The oil-adjuvanted vaccine filling line includes a fully automatic bottle sorting machine, filling machine, and high-speed capping machine, designed specifically for vaccine production. It has a wide range of adaptability and can be used for the production of vaccines with a capacity of 1ml-100ml (according to user requirements).
The body is made of 304 stainless steel, and all liquid materials that come into contact with the filling vaccine liquid are made of 316 stainless steel or materials that meet FDA requirements to ensure that the equipment meets the cleanliness level requirements and complies with pharmaceutical product GMP management requirements. |
Quality control system
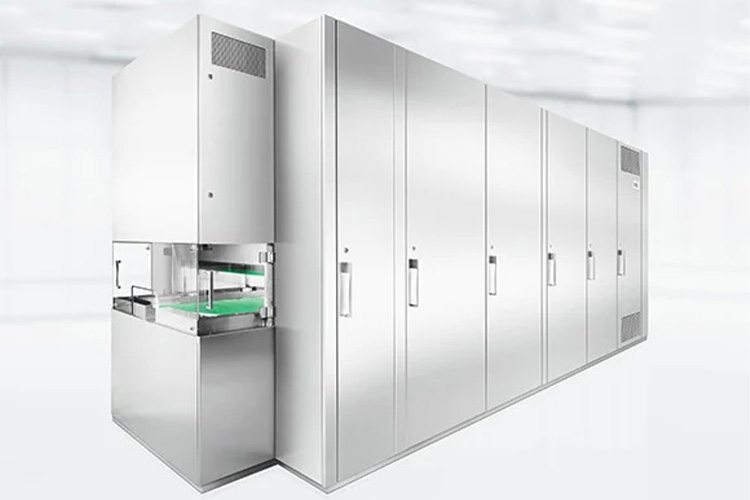
| Dry heat sterilization tunnel (vial sterilization)
Dry Heat Sterilization Tunnel - Sourced: Syntegon |
The workflow of the tunnel tunnel is relatively simple and efficient. Firstly, place the vial of oil-adjuvanted vaccine in the tunnel, and then set the desired temperature and time. The heating elements inside the tunnel will heat the air and evenly blow it to every corner of the oven through an efficient circulation system. Under continuous high temperature, microorganisms are completely killed. Finally, after the cooling stage, the item can be safely removed. |
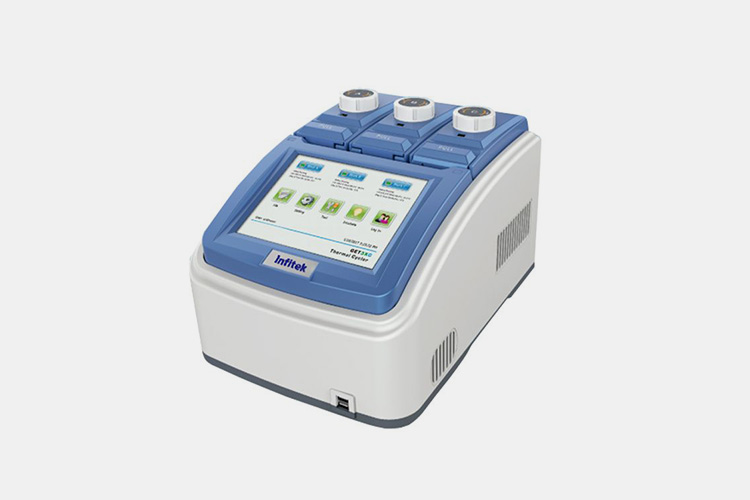
| PCR instrument
PCR Instrument - Sourced: Infitek |
By amplifying and analyzing DNA or RNA sequences in vaccines, the safety of vaccines can be improved by detecting viruses and bacteria in oil adjuvant vaccine samples. |
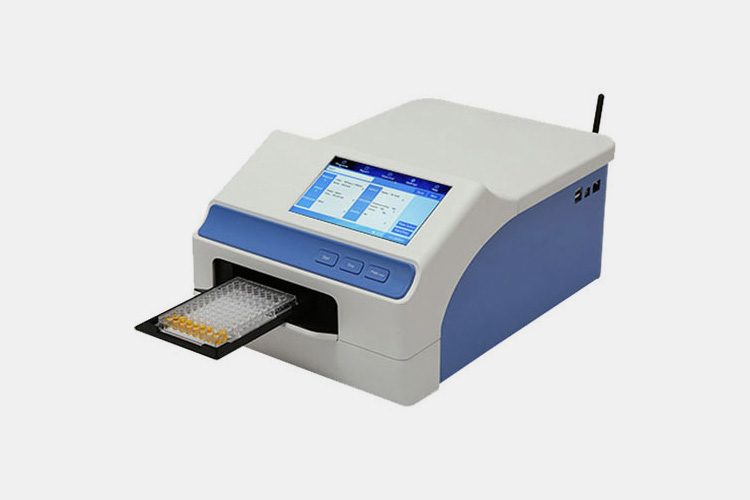
| ELISA detection system
ELISA Detection System |
This device is used to detect antigen and antibody levels in vaccines to evaluate their immunogenicity. The ELISA detection system is mainly used to detect specific antibodies and antigens in animals, and is widely used in immunological research and disease monitoring. Common detectable antibodies include IgM, and IgA, which are produced in animals after infection with pathogens or vaccination, reflecting their immune response status. |
5.What Are the Conditions Required For the Storage And Distribution of Oil-Adjuvant Vaccines?
The oil-adjuvant vaccines currently used in clinical practice are mostly prepared by microorganisms themselves or their derivatives, and their characteristics are easily affected by uncomfortable temperatures. Therefore, vaccines must be transported and stored in appropriate environments to maintain their stability and ensure corresponding immune effects.
Cold-chain transportation

Cold-chain Transportation - Sourced: Fleetx
Oil-adjuvant vaccines should be transported via cold chain and ensure that the cold chain system is functioning properly. Vaccines can be directly stored in refrigerated trucks with stable refrigeration from cold storage or warm storage, or transported in insulated boxes with ice cubes.
During transportation, they should be kept away from light, sunlight, and high temperatures. Upon arrival at the destination, they should be immediately stored in refrigerated or freezer according to storage requirements and labeled.
Refrigerated storage

Refrigerated Storage - Sourced: Financial Times
Due to different types of vaccines, the temperature requirements for transportation and storage are also different. Oil-adjuvant vaccines are generally stored at 2-8℃. This kind of vaccines should be protected from strong light, direct sunlight, and high temperatures during transportation and storage to prevent damage to vaccine activity.
6.What Are the Pre Warming Method for Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
The temperature difference between oil-adjuvanted vaccines and animal is quite large, and direct injection into animals can cause serious cold stimulation, leading to side reactions in pigs. If pre warming the oil-adjuvanted vaccines, it will reduce stimulation and minimize side effects.
Pre warming in room temperature

Pre Warming In Room Temperature - Sourced: The HVAC Service
When the room temperature is within the range of 25-30 ℃, remove the oil-adjuvanted vaccines from the 2-8 ℃ refrigerator 2-3 hours in advance and place them indoors. After sufficient time, use heat transfer to raise the temperature of the oil-adjuvanted vaccines to room temperature.
The preheating effect is not sufficient when the room temperature is below 25 ℃, and it is necessary to use indoor preheating or equipment assisted preheating.
Using auxiliary tools

Using Auxiliary Tools - Sourced: Smartclima
Use easily accessible containers such as water basins, buckets, and vaccine incubators to add 35-40 ℃ warm water. Place the oil-adjuvanted vaccines in the warm water until the liquid level reaches the vaccine bottle.
Pay attention to changes in water temperature during the period, replenish warm water in a timely manner after the temperature drops, maintain the water temperature at 35-40 ℃, and shake the vaccine 2-3 times to ensure even temperature distribution. The preheating time should not be less than 1 hour, and vaccine preheating should not be a formality to ensure the preheating effect.
7.What Should Be Paid Attention When Inject Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
In order to improve the efficiency of oil-adjuvanted vaccine, strict attention should be paid when administering vaccines to animals to avoid side effects or vaccination failure.
The vaccine dosage should be accurate

The Vaccine Dosage Should Be Accurate - Sourced: 960th Cyberspace Wing
The optimal injection dose for each product is determined through multiple clinical trials and repeated validation. At this dosage, it not only saves the cost of oil-adjuvanted vaccine and avoids waste, but also provides the best protection for animals.
The vaccination time should be shaken evenly
Due to the effect of gravity during long-term storage, even the best adjuvant can cause some antigens to settle down. If not shaken thoroughly before injection, it can lead to uneven injection and varying amounts of injection.
Immune procedures need to be meticulous

Immune Procedures Need To Be Meticulous - Sourced: Plant Based News
High quality vaccines must be accompanied by high-quality immunization techniques to ensure that the overall antibody level reaches the desired protective value. A legitimate immunization service team must undergo unified training and training, be proficient in injection skills, and have a sense of responsibility.
Change needles frequently
The significance of frequently changing needles for infection prevention is self-evident. Do not be reluctant to part with those two or three needles, and do not lose big for small reasons. If a large group of cross infections are caused by needles, the loss will not be due to the needles.
Regular calibration of injection dosage
It is irresponsible for most immunization operators to not correct the vaccine dose for a day or even several consecutive days after correcting the syringe once before use. When using a syringe, the screws may loosen due to external forces, resulting in inaccurate injection measurement.
Therefore, when injecting oil-adjuvanted vaccines, it is necessary to constantly calibrate the scale of the syringe. In addition, it is also necessary to shake the oil-adjuvanted vaccines while injecting to facilitate even mixing of antigens.
8.What Are the Difference Between Lyophilized Vaccine and Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine?
Vaccine
Any biological agent that can produce active immunity and prevent diseases after vaccination with animals is called a vaccine. According to the activity classification of antigens, they are divided into Lyophilized (freeze-dried) vaccines and inactivated vaccines.
| Types | Description |
| Status of pathogenic microorganisms | Lyophilized vaccines are low virulence live pathogenic microorganisms, while oil-adjuvanted vaccines are non virulent dead pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Antibody speed | Lyophilized vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies quickly and maintain a short duration. Oil-adjuvanted vaccines stimulate the body to produce antibodies slowly and last for a long time. |
| Storage method | Lyophilized vaccines usually require cryopreservation, while oil adjuvant vaccines are generally stored under refrigeration. |
| Injection method | Lyophilized vaccines can be administered through various methods such as eye drops, nasal drops, oral administration, drinking water, injection, etc. Oil adjuvant inactivated vaccines can generally only be immunized through injection. |
9.What Validation and Requirements Does Oil-Adjuvanted Vaccine Manufacturing Need to Meet?
Oil-adjuvanted vaccines are related to animal safety, and vaccine production must strictly follow production standards in order to maximize the effectiveness of vaccines.
Technological requirements
Every step in the oil-adjuvanted vaccines production process, such as virus cultivation, inactivation, extraction, purification, etc., must be strictly carried out in accordance with GMP regulations, and each step must undergo quality inspection and recording, including process validation, equipment calibration, and tracking of batch production records.
Staff

Staff - Sourced: CIDRAP - University of Minnesota
Production personnel must undergo strict occupational training and health checks, and wear protective equipment such as sterile clothing, masks, gloves, etc. during work to reduce contamination of vaccines.
Equipment verification
Before the production equipment is put into use, it must be verified to ensure its stable performance and reliable operation. This includes steps such as equipment installation verification (IQ), operational verification (OQ), and performance verification (PQ).
Conclusion
Animals also need to be vaccinated, and oil-adjuvanted vaccines are specially designed for animals to prevent infection and improve survival rates. After reading this article, have you gained a deeper understanding of the production process and basic overview of oil seedlings? If you have any further questions, please feel free to contact AIPAK Engineering at any time.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours