Reverse Osmosis Pharmaceuticals: The Complete FAQ Guide In 2025
How does a tiny drop of water go from ordinary to extraordinary and ready to save lives? In the pharmaceutical and medical care arena, water isn’t just a need but also a core ingredient. You find the utility of water everywhere in pharmaceutical processing- from developing therapeutics to cleaning instruments. However, it is only possible with the sterility of water.
And this is where reverse osmosis comes into play. But how to explain this sterility technique? Why is it gaining a giant stride in the pharmaceutical industry? It is not simply a filtration method but a technological marvel that transforms regular tap water into pharmaceutical-grade water. Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals have a transformative power that ensures complete sterility of water by eliminating soluble salts, organic matter, microbes, dust particles, and other debris.
How is it possible? Why this technique is regarded as the backbone of the pharmaceutical sector? This article will answer these queries and more about reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals. It is a one-stop guide to unravel mysteries regarding the discipline of reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals. Let's get purified!
1.What is reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals?
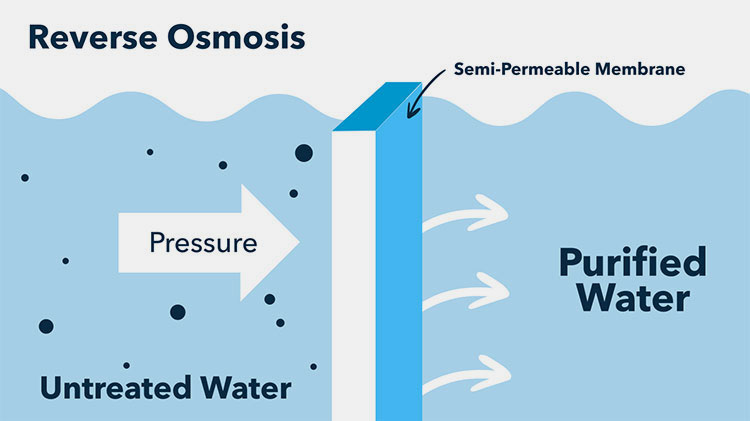
Reverse Osmosis Pharmaceuticals- Picture Courtesy: Goldwin Plumbing
It is a water purification technique, applied in the pharmaceutical sector to filter out impurities and other biological contaminants from water. This approach makes water pure for use in medication formulation and preparation. It is an industrial treatment process in which 97-99% of total dissolved solids (TDS) are removed from water.
Water is a core ingredient in the pharmaceutical process and sterility of every drug preparation relies on its purity. So, pharmaceutical manufacturers use a reverse osmosis process in which water is circulated through a semi-permeable membrane under intense forces.
It is called reverse osmosis because it is the opposite of the natural osmosis process and in this procedure, a pump is employed to induce a strong pressure by which water having a high concentration of dissolved solids penetrates the membrane for filtration.
The water also known as product water or permeate is filtered out, while dissolved salts are retained on the surface of the membrane and are consistently discharged and flushed as waste.
2.Why is reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals important in the pharmaceutical sector?
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals has unmatched potential to formulate pharmaceutical-grade pure water, so it is quite well-accepted and widely applied in aseptic processing industries. Let’s uncover the fundamental benefits of reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals to the pharmaceutical sector.
Adherence with Regulatory Protocols

Adherence with Regulatory Protocols- Picture Courtesy: BioSpectrum Asia
First and foremost, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a key technology to clear out impurities, making it refined for complying with strict purity practices stipulated in various pharmacopeias, for instance, USP, EP, and JP. It is readily utilized to produce Purified Water (PW) and Water for Injection (WFI) by fulfilling sterility guidelines.
Drug Safety and Potency

Drug Safety and Potency- Picture Courtesy: TSA Process Equipments
You cannot incorporate impure water to formulate pharmaceutical products. Because it will result in a loss of medication quality, stability, potency, and, safety. Consequently, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is highly popular among healthcare sectors due to its capacity to remove every type of impurity from water, preventing adverse reactions in patients or disruptions to the chemical composition of preparations.
High Sustainability

High Sustainability- Picture Courtesy: Proventa International
In addition to drug safety, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is an energy-efficient treatment approach in contrast with standards or traditional water purification methods, for example, distillation. It does not employ harsh and damaging chemicals, which makes it a more eco-friendly and safer method for working personnel.
Scalability

Scalability- Picture Courtesy: TSA Process Equipments
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a synergistic combination of high operational throughput and scalability. As a result, it is easily employed in home-based settings, small-scale laboratories, pharmaceutical manufacturing plants, and, diagnostic centers.
3.What kinds of contaminants are removed by reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals?
Can reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals remove all kinds of contaminants? This question is always a source of concern for pharmaceutical developers. They want their pharmaceutical-grade water to be completely free of contaminants. Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a standard technique to take out a wide array of impurities to meet purity criteria. A list of various contaminants eliminated by reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is discussed below:
Dissolved Salts and Metallic Impurities

Dissolved Salts and Metallic Impurities- Picture Courtesy: ALTANA AG
Several salts for instance, calcium, magnesium, and sodium salts primarily contribute to the hardness of water, making the latter unsafe for consumption. Furthermore, metallic components like those of lead (Pb), arsenic (As), mercury (Hg), and cadmium (Cd) are present in potable water and toxic even in minute amounts. Both these chemical impurities are readily cleared out by the reverse osmosis pharmaceutical process.
Microbial Entities
Microbial Entities- Picture Courtesy: ABC
The potable water is full of diverse types of microbes and their byproducts; thus, it is not safe to utilize for medication formulation. Harmful bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Pseudomonas are deadly and cause life-threatening infections. Their presence severely impacts the quality of drugs. Fresh water also has different viruses, for example, hepatitis A or norovirus. Also, untreated water has the growth of fungus, and mold spores may proliferate in water, increasing the chances of health problems upon consumption.
The reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a remarkable technique for entirely eradicating various microorganisms from water.
Endotoxins
Endotoxins- Picture Courtesy: BioPhorum
These are chemical molecules (lipopolysaccharides) that originate from the cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. They bind to immune cell receptors, instigating inflammatory reactions, resulting in fever or in extreme cases septic shock and organ failure. However, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals easily eliminate these endotoxins.
Chemical Compounds

Chemical Compounds- Picture Courtesy: Distinguished Programs
Water has numerous kinds of organic compounds- for example, pesticides and herbicides- from running off agricultural lands. Plentiful toxic industrial wastes and volatile organic compounds are also found in water. Furthermore, pharmaceutical residues or traces of drug ingredients and their byproducts are discharged in water from pharmaceutical industries. These organic materials and waste byproducts are filtered out by reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals.
Particulates and Sediments

Particulates and Sediments- Picture Courtesy: Colossal
With reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals, it is quite easy to remove suspended solids, total dissolved solids, and, colloidal matter. Suspended solids are usually slit, rust, sand, etc.
4.What types of pharmaceutical water do reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals generate?
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a dedicated approach regularly employed in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors to formulate various kinds of pharmaceutical waters. These water products have different levels of purity and use and fulfill specific regulatory standards. The subsequent description summaries the various types of pharmaceutical water and their specifications:
Purified Water

Purified Water- Picture Courtesy: Waterdrop
This water as the name indicates, is a water that has passed the semi-permeable membrane of reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals to acquire purity. It is devoid of different impurities and particulate matter, like chemicals (chlorine, phosphates), dissolved or suspended solids, and microorganisms. It is utilized in the preparation of non-sterile formulations- whether as excipient, diluent, or solvent. Purified water is primarily employed in research analytical laboratories and quality control testing. It is manufactured from drinking water.
Water for Injection (WFI)
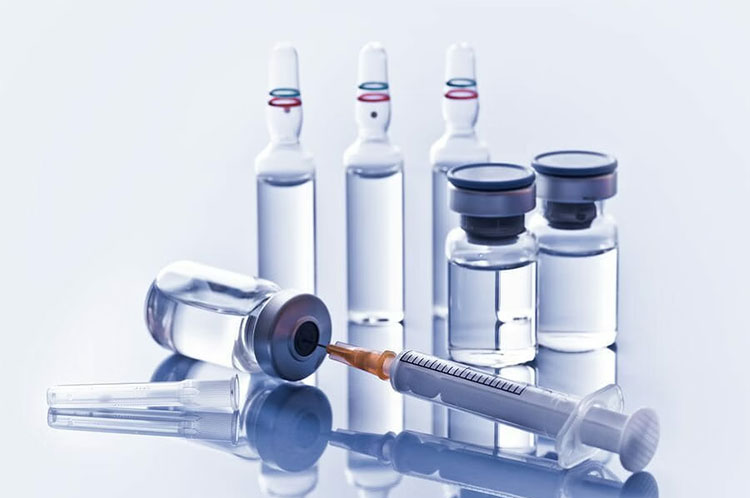
Water for Injection (WFI)- Picture Courtesy: Tecno Products
It is highly purified water that satisfies stringent regulatory criteria and there are no microbial contaminants or entities, such as endotoxins, spores, pyrogens, and chemical molecules. It is utilized as a core component in the development of parenteral or injectable remedies. Pharmaceutical chemists also use it as a solvent in preparation for dialysis and irrigation fluids.
Highly Purified Water
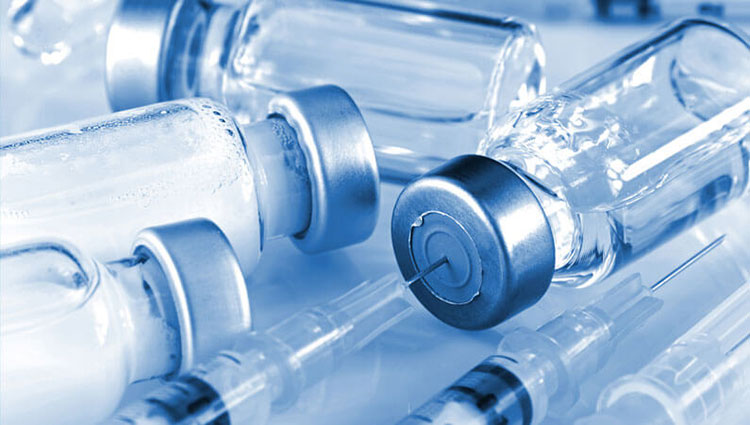
Highly Purified Water- Picture Courtesy: Airplan
This pharmaceutical water is purified by extensive purification techniques, for instance, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals to filter large organic or inorganic compounds, microbes, and other particulate sediments. However, it still has trace levels of ions, microbes, and total organic carbon content. Therefore, it does not conform to rigorous quality control standards.
Sterile Water for Injection
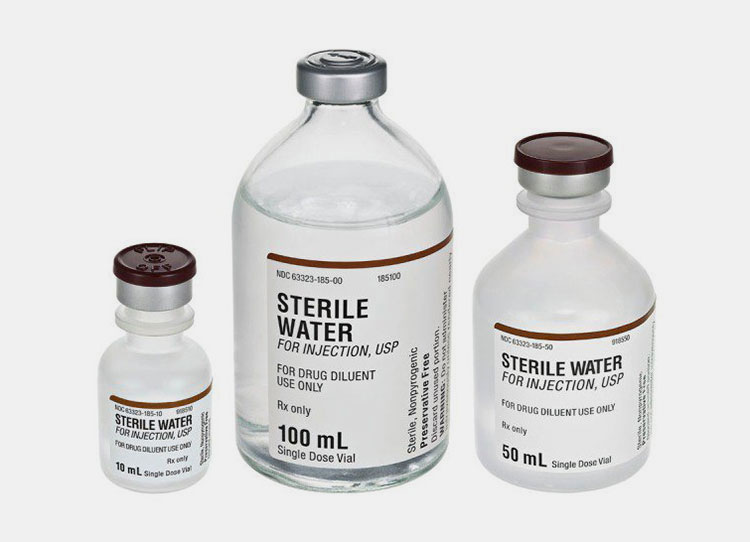
Sterile Water for Injection- Picture Courtesy: McKesson
It is a highly sterile water that is developed by complying with strict regulatory protocols. It does not have any microbial content and has minimal levels of endotoxins typically less than 0.25 EU/ml, so it is entirely safe for parenteral use. It is applied as a diluent in the formulation of injectable medication for administration through vascular, muscular, and, subcutaneous routes.
Sterile Water for Irrigation
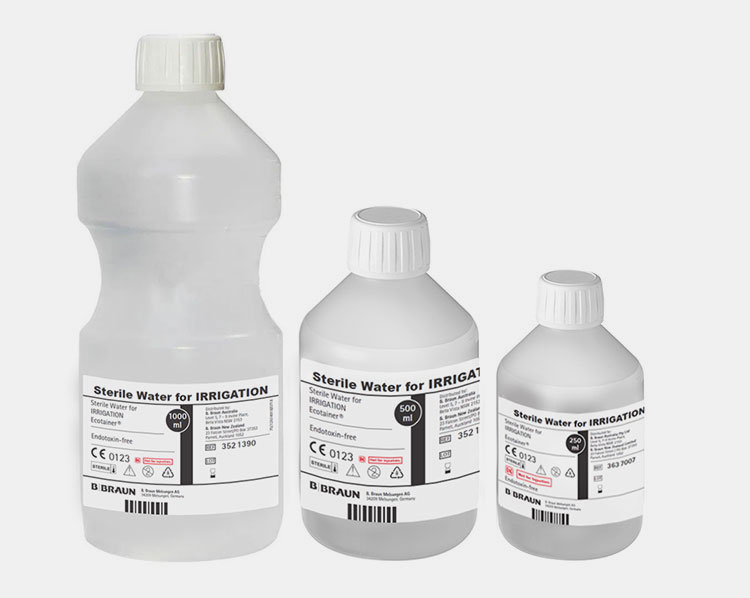

Sterile Water for Irrigation- Picture Courtesy: B. Braun
It is also a pure form of pharmaceutical-grade water and is specifically developed for external applications, for instance, cleaning of skin wounds, surgical areas, and surgical and medical instruments. It clears body tissues of blood and other debris and is employed in aseptic surgical and medical environments to prevent the entry of microbes. It is void of health-affecting pyrogenic molecules, like endotoxins.
Sterile Water For Inhalation
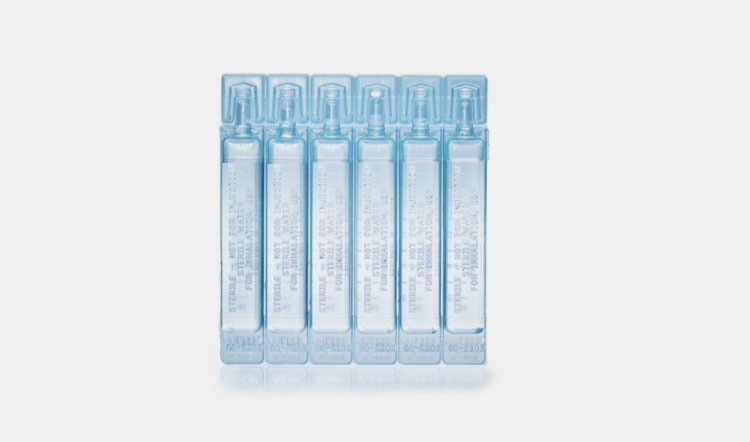
Sterile Water For Inhalation- Picture Courtesy: Vitality Medical
It is sterile water and is exclusively utilized in various kinds of respiratory treatments. It is generated through similar procedures as that of sterile water for injection, but it contains some additional additives depending upon its utility. Usually, its job is to serve as a vehicle for drug delivery in respiratory disorders. It is also employed in nebulizers and humidifiers.
Water for Hemodialysis
Water for Hemodialysis- Picture Courtesy: Charles River Laboratories
It is an excellent treatment option for patients undergoing dialysis. It is high-purity water and is employed as a base for creating dialysis fluids. Since it is intended for systematic use, hence, it fulfills sterility guidelines and does not have any type of bacterial, fungal, pyrogenic, chemical, or, physical impurities.
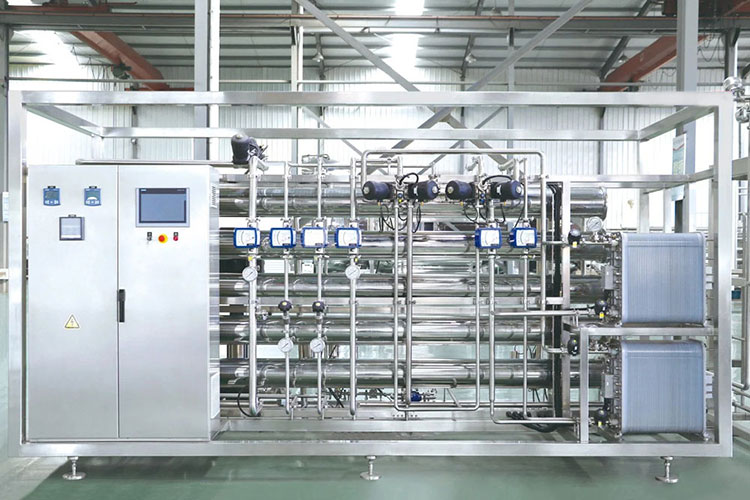
5.What equipment is used for reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals in industries?
You might wonder what kind of devices are used for reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals. This filtration approach requires specialized devices and other auxiliary components to prepare ultra-purified water. These equipments are specifically fabricated to ensure efficiency and reproducibility at every step. Let’s explore innovative devices behind reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals.
Reverse Osmosis Unit
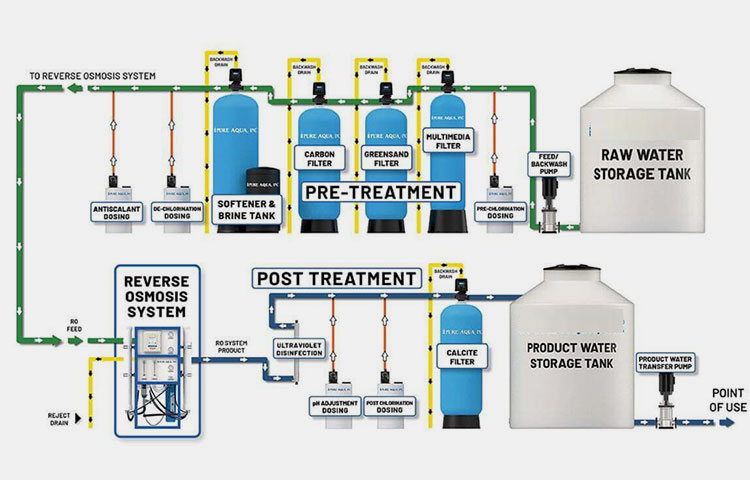
Reverse Osmosis Unit- Picture Courtesy: Pure Aqua, Inc.
It is the central device in the water treatment system and is designed with a delicate semi-permeable membrane through which water is flowed using high pressure. It consists of the following units:
Pre-Treatment Devices

Pre-Treatment Devices- Picture Courtesy: Pure Aqua, Inc.
These instruments are extremely integral in reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals to pre-treat water before actual reverse osmosis treatment.
| Multimedia Filter | It protects the delicate membrane of reverse osmosis instruments and improves their efficiency by screening out larger and heavier particles, for instance, sand, silt, gravel, debris, and clay. This averts the blockage of downstream sterility components. |
| Activated carbon filters | It filters out chlorine, chloramines, and organic molecules. These filters are pivotal in safeguarding reverse osmosis pharmaceutical devices. |
| Water Softener | It constitutes ion-exchange resins to eliminate hard dissolved salts, especially those of calcium and magnesium from processed water. It is essential in not only improving the quality of water but also averts the scaling of fragile reverse osmosis membranes. |
| Cartridge Filters | These filters act as a final barrier to take out particulates before the transfer of water to the reverse osmosis unit. It is comprised of media or pleated components to successfully eliminate solid particulates and other chemical and physical objects. |
High-Pressure Pump System
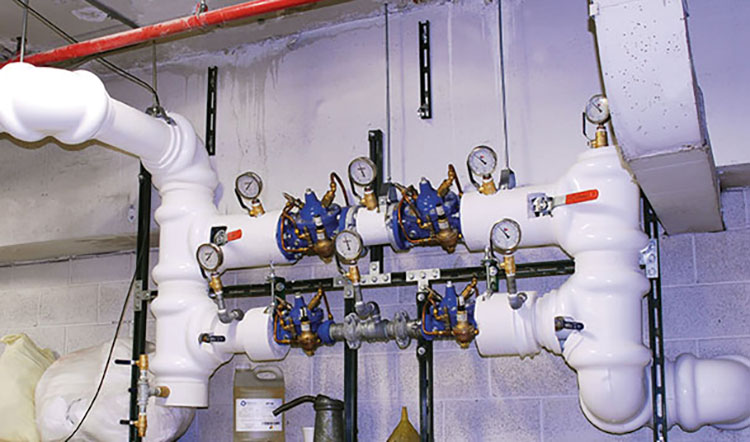

High-Pressure Pump System- Picture Courtesy: Metropolitan Industries
It is a vital part of the reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals and induces pressure forces on the processed water so that it will infiltrate the reverse osmosis membrane. These pumps- comprising of centrifugal pump, piston pump, or diaphragm pump- generally apply pressure of about 0 to 100 bar (725 to 1450 psi) or higher.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane
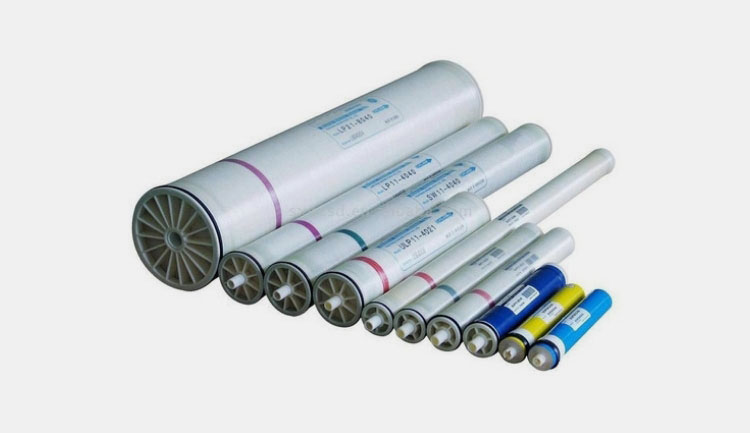

Reverse Osmosis Membrane- Picture Courtesy: Water Filters
It is the core component in the reverse osmosis unit. This membrane is selectively permeable, spiral-wound configuration, and has a minute-sized opening approximately size of 0.0001 microns- specifically designed to permit the influx of water molecules but small enough to retain contaminants, organic molecules, dissolved salts, bacteria, microbes, and other impurities. It is manufactured from cellulose acetate, polysulfonate, and, polyamide.
Post-Treatment Units
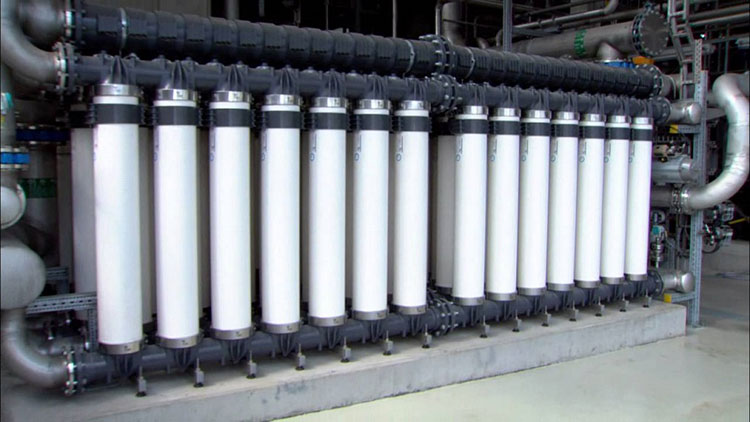

Post-Treatment Units- Picture Courtesy: Hydrotur
These units are incorporated after the reverse osmosis membrane to further refine the permeate water and make ready it for diverse pharmaceutical applications.
| Ultrafiltration Unit
|
It is composed of ultra-fine membrane that clears out extremely minute particles. It removes sub-micron contaminants that enter reverse osmosis membranes, typically bacteria, endotoxins, and, spores. |
| Ultraviolet Sterilization Unit | It stops bacterial and microbial growth and colonization using high-frequency ultra-violet light of about 254 nm. It destroys the DNA of microorganisms, making them inactive. It is used for regulating microbial load. |
| Ozonation Unit | As the name implies, this unit has ozone systems to oxidize organic molecules and microbial components. It offers ultra-high disinfection procedures to completely eradicate microbial entities in storage tanks and distribution pipes. |
| Heat Sterilization Unit | Steam or hot water is employed in heat sterilization systems to kill microorganisms. It is generally used to generate water for injection. |
| Electrodeionization System | It is made of ionic exchange resins to eliminate residual ions left behind after reverse osmosis treatment. It has a function of polishing permeate water. |
6.Can reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals be utilized for all types of pharmaceutical uses?
Yes, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is utilized as a standalone technique or in combination with other water treatment systems for all types of pharmaceutical uses. Here is a comprehensive detail of different pharmaceutical uses in which reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is applied:
Topical and Oral Use

Topical and Oral Use- Picture Courtesy: Naturecan AU
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals has an integral role in producing purified water, free of microbes and other solid content. This water is added to the preparation of both solid and liquid dosage forms, such as tablets, capsules, suppositories, and syrups. In addition, high-purity water is incorporated in topical formulations to make stable emulsions for creams, gels, and, ointments.
Critical Drug Manufacturing

Critical Drug Manufacturing- Picture Courtesy: JTA Health
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is employed en masse with other water treatment options to prepare ultra-sterile water for critical drug manufacturing. This water is used in the creation of parenteral injectable drugs, IV solutions, inhalation therapies, and, aseptic wound treatment solutions, etc. Moreover, it is employed in sterile environments, such as cleanrooms.
Preparation of Analytical Reagents

Preparation of Analytical Reagents- Picture Courtesy: Sciencing
High-purity water acts as a solvent for solubilizing chemicals and making different types of laboratory reagents, analytical solutions, and buffers. This water is supplied by reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals. This ultra-purified water does not interfere with chemical reactions and has a stable pH, which is vital for chemical, cell culture, biochemical, and, molecular biology research.
Cleaning Laboratory Equipment

Cleaning Laboratory Equipment- Picture Courtesy: Boekel Scientific
It is vital to uphold standards of cleanliness in the pharmaceutical laboratories and research areas. Thus, purified water generated by reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals has an integral part in cleaning laboratory devices, for instance, glassware, pipettes, autoclaves, hoods, etc. It also washes different surfaces, such as benches, sample preparation areas, workplaces, and more.
7.How do reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals differ from other water purification methods?
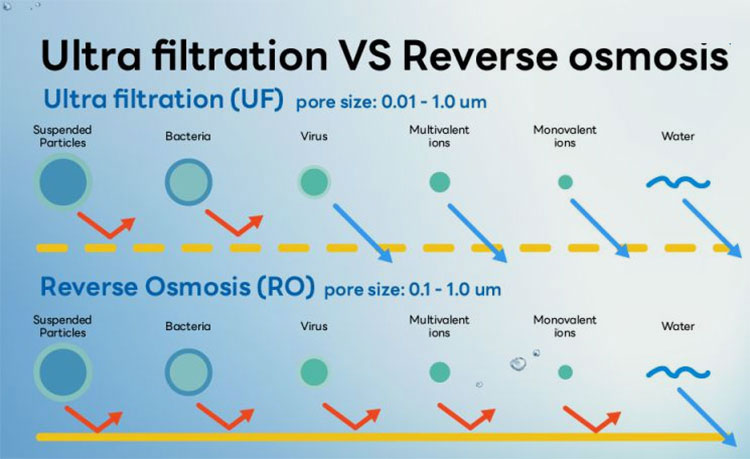
Reverse Osmosis vs Ultrafiltration- Picture Courtesy: Aqua Science
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals stand out as a reliable water treatment approach and is well-accepted in the pharmaceutical industry to eradicate a wide spectrum of impurities, Nevertheless, it is quite distinct from other water purification methods due to its principal mechanism, performance, and uses. Some of the differences between reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals and other standard purification techniques are mentioned below:
| Feature | Reverse Osmosis | Distillation | Ultrafiltration | Deionization |
| Principle | This technique has a semi-permeable membrane for filtering contaminants with the application of pressure to force water across the membrane. Afterward, the impurities are left on the surface of the membrane. | In this approach, water is boiled and then its vapors are condensed back to liquid to separate out dissolved contaminants. | It also utilizes a membrane with increased aperture size than reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals. | In this technique, ion-exchange resins are utilized for capturing and clearing cations and anions present in raw water. |
| Contaminants Removed | It removes dissolved salt, heavy metals, organic particulates, and, microorganisms. | It is effective in removing minerals, toxic metals, microbes, pyrogens, and, endotoxins. | Although ultrafiltration eliminates large particulate, microbes like bacteria, molds, pyrogens, and some viruses, it is not successful in clearing out dissolved salts or smaller molecules from processed water. | It is ideal for removing dissolved salts of calcium, magnesium, and, nitrates. |
| Efficiency | It eliminates 97-99% of impurities. | Distillation yields ultra-pure water, ideal for water for injection. | It is less meticulous than reverse osmosis. | It is least effective because it does not filter out non-ionic impurities. |
| Energy Needs | Moderate for driving pumps. | Extremely high due to boiling of water. | Low for low-pressure pumps. | Low but it requires constant regeneration of resins. |
8.What is the expected lifespan of a reverse osmosis pharmaceutical membrane in a pharmaceutical setting?
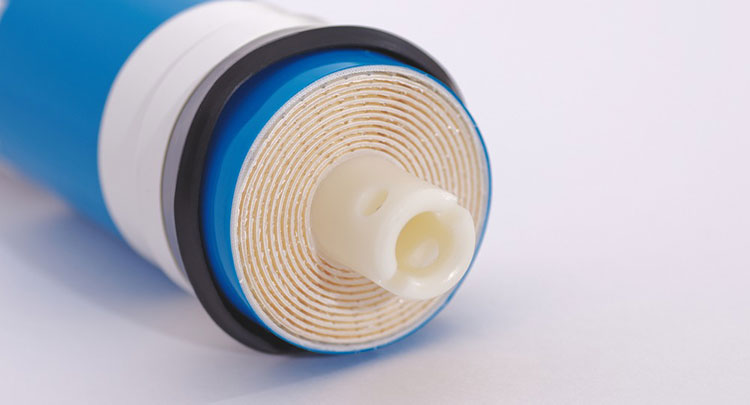

Reverse Osmosis Membrane- Picture Courtesy: IPI Singapore
The estimated lifespan of a reverse osmosis pharmaceutical membrane in the pharmaceutical sector is normally around 2 to 5 years. However, with routine cleaning and maintenance, you can extend the lifetime to about 7 years. Pretreatment of water prior to reverse osmosis is integral in minimizing the burden on the reverse osmosis membrane, which increases its lifespan. Failure to implement pretreatment procedures will lead to fouling, scaling, and membrane wear.
Furthermore, to increase its service life, you should operate the equipment on the recommended pressure, temperature, and flow rate. This averts physical strain on the membrane.
Also, experts advise daily cleaning of the membrane to eradicate material buildup or microbial growth. Periodic inspections, such as pressure drops assist in the early detection of problems in the membrane. These practices are necessary to uphold the functionality of the reverse osmosis membrane and improve its operating period.
9.Is the water treated after reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals for further sterilization?

Reverse Osmosis Pharmaceuticals- Picture Courtesy: Xylem
To answer your question, in short, yes. Permeate or clean water after reverse osmosis pharmaceutical treatments normally undergo additional treatment procedures to guarantee that high-purity water aligns with the regulatory sterility framework. It is particularly important for generating various types of sterile waters.
These procedures are compulsory because although reverse osmosis membrane is exceptional in rejecting microbes, it does not guarantee absolute sterility, as biofilms or endotoxins may grow in storage tanks after reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals.
In addition, drug regulatory bodies have mandated different sterility thresholds and endotoxin limits for water for injection and other sterile-grade water solvents, so other purification treatment methods must be applied because these requirements are not attainable by conducting reverse osmosis alone.
10.What are the frequent problems associated with reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals in the pharmaceutical industry?
Even though reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a powerful water purification technique, however, it’s not without its drawbacks. These problems detrimentally impact treatment sterility and reduce its efficiency. Below mentioned are some frequent problems associated with reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals and their possible solutions.
Membrane Fouling
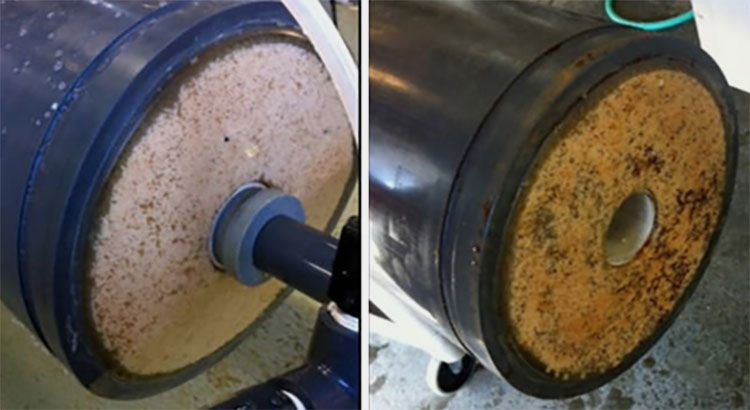

Membrane Fouling- Picture Courtesy: Hazen and Sawyer
Did you notice particle fouling on your reverse osmosis membrane? It is a common problem, happening due to the accumulation of colloids, suspended solids, biological contaminants, organic compounds, and other mineral depositions on membranes. It drastically lowers the water influx and efflux and filtration quality. Furthermore, you have to increase the pressure value to move water across the membrane, thus needing more energy.
Solutions
You will need to pretreat water with sediment, activated carbon, and other types of filters to lower its contamination levels. You should also employ routine cleaning and maintenance protocols to avoid membrane fouling. It is best to use antiscalants to avoid membrane scaling.
Membrane Damage
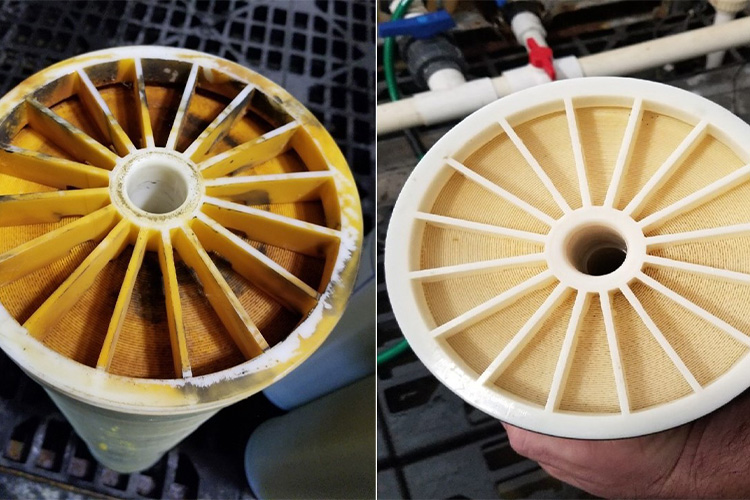
Membrane Damage
After some reverse osmosis cycle, you’ll observe wear of the membrane. It is due to exposure to increased pressure surges and constant encounters with chemicals, such as chlorine or strong oxidizing agents. It not only decreases the serviceable life of the membrane but also affects its performance.
Solutions
You can rectify this problem by incorporating dechlorination systems, like activated carbons or sodium bisulfite dosing devices to eliminate chlorine and other oxidizing agents from processed water. Secondly, you should adjust the operation pressure so that it will not exceed the value mentioned in the manufacturer's manual.
High Energy Consumption

High Energy Consumption- Picture Courtesy: Square Yards
Is your reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals consuming more energy? Well, it could be due to ineffective membrane performance and utility of high-pressure pumps to mechanize reverse osmosis process. This increased energy utility will ultimately increase your operational expenditures.
Solutions
There is no reason to be concerned; this problem is easily resolved by utilizing energy recovery systems to increase energy optimization. Implementing a regular and meticulous maintenance schedule will improve system functioning.
Varying Water Quality

Varying Water Quality- Picture Courtesy: Atlas Lab
Sometimes, you must have observed that permeated water has inconsistent levels of sterility. This is owing to differences in the composition of raw water and membrane wear with time.
Solutions
To resolve this problem, it is advisable to examine the quality of raw water and tweak your pre-purification procedures accordingly. Moreover, you should maintain a membrane replacement timetable based on its operational metrics.
Brine Disposal

Brine Disposal
Brine is a concentrated saline solution, retained on the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane. It is typically generated due to a high concentration of salts in water. Its disposal is a major concern due to its environmental impact and adherence to wastewater disposal bodies.
Solutions
It is recommended to address this challenge by surveying bribe treatment or reuse systems, for instance, zero-liquid discharge (ZLD), and installing them in your pharmaceutical plants. Also, you should customize the reverse osmosis unit design according to the composition of feed water to lower brine yield.
Conclusion
Reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is a vital pillar in the pharmaceutical industry. It is utilized to produce ultra-pure water that not only has an integral part in the preparation of topical and oral medications but also ensures the cleanliness of pharmaceutical devices and work areas. In addition, reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals is utilized with other technologies to produce super-clean water for aseptic uses and microbial-free environments. With its benefits- regulatory compliance, cost-effectivity, and, sustainability- the pharmaceutical industry can attain a competitive edge in the global arena. Elevate your water treatment performance with reverse osmosis pharmaceuticals by exploring your options with AIPAK ENGINEERING.
Don't forget to share this post!
CONTACT US
Tell us your raw material and project budget to get quotations within 24 hours.
WhatsApp Us: +86 181 7101 8586
 Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours
Tell us your material or budget, we'll reply you ASAP within 24 hours